SAP PMGM Online Classes
SAP PMGM
SAP PMGM makes managing goals and performance permissions straightforward and scalable, providing complete control over new roles or modifications to existing ones.
SAP PMGM makes it time-efficient and straightforward to implement permission strategies for large teams quickly.
By employing its “Copy” feature, settings can be easily replicated across groups, saving time and maintaining consistency across settings.
SAP PMGM Goal and Performance Management
As we’ve advanced from goal management with SAP PMGM and created implementation guides, it is time to tackle performance management using this powerful system.
SAP PMGM provides us with access to existing templates, which we can then modify as desired. When designing these templates, consider rating scales, permission levels, and even button options such as ‘add’ or ‘delete’ goals when building them.
SAP PMGM also helps us successfully launch forms. Once employees receive the form, they begin self-rating it. Every section and field is carefully configured using role-based permissions (RBP).
What an employee sees versus what a manager sees is all controlled through template settings.
SAP PMGM Business Tools
The SAP PMGM workflow guide and implementation documents, along with screenshots of the business tool.
Thought these would eventually be shared, but hadn’t happened. Remain optimistic, though, as these files provide real-life scenarios essential for success in SAP PMGM implementations.
Wanted access to SAP PMGM releases. These updates are crucial for staying current and relevant.
Although an implementation guide was previously shared, newer PDF documents or workflow enhancements would also be of use.
Mastering SAP PMGM Rules and Parameters
Creating conditional statements in SAP PMGM is all about understanding its logic and the tools available to you.
Practice setting conditions by practising actions such as creating, deleting, and executing. Within dropdown menus lie logic operators, such as “equal to” and “not equal to,” that can make all the difference when crafting rules.
SAP PMGM is a method for combining multiple objects. For instance, say you need job and compensation details together in one condition.
SAP PMGM allows you to set one object as the base and then layer another object using parameters, making the combination flexible yet powerful once you understand how it works.
Setting Up Permission Roles in SAP PMGM
Once we finalise our group, the next step should be creating a Permission Role.
Ensure the role name is descriptive when adding permissions necessary for modules such as Goal Management, Calibration, and Performance.
SAP PMGM grants full access rights for each module created as a role. Once configured, it’s essential to review each setting carefully and verify its correctness before saving.
Role-Based Permissions in SAP PMGM
Before diving into templates in SAP PMGM, we must become familiar with Role-Based Permissions (RBP) in SAP.
RBP determines what data can be viewed or altered within the system by each user and has become one of the most versatile tools across various modules, including Enterprise Content Management (ECM), Resource Central Management (RCM), Learning Management System (LMS), and SAP itself.
RBP within SAP PMGM comprises two primary elements: Permission Group Management and Role Administration.
We define user roles and determine which user groups have access to specific data, including employee data, organisational charts, and administrative functions.
Mastering Permission Roles in SAP PMGM
Permission Roles in SAP PMGM encompass employee data, organisational data and administrative rights for each role mapped.
With such well-defined roles in place, SAP PMGM enables us to establish robust data governance.
What have observed is that when trainees understand SAP PMGM’s permission hierarchy Permission Groups, Roles, and Target Groups they gain confidence not only in administrative work but also when answering challenging interview questions.
Managed Permission Groups in SAP PMGM
Begin by accessing SAP PMGM’s Managed Permission Group section and creating new groups to control role-based access.
To create a group, select “Create New Group,” provide an appropriate name, and assign employees accordingly.
Add members using criteria such as name or department, whichever is applicable in SAP PMGM, to simplify the task.
Hierarchy in SAP PMGM Role Assignments
Understanding SAP PMGM’s management hierarchy is paramount.
Access levels such as direct manager, one level up, or all levels in the chain, providing precise granular control that only those intended to have access have, thus empowering HR technology.
Using SAP PMGM for Smart Permission Control
One of the smartest moves you can make when setting up SAP PMGM to handle permissions based on real-world criteria, such as locations, departments, or job codes, is to configure it in a way that reflects organisational realities digitally.
This is something that cannot be overemphasised when preparing for deployment scenarios or interview situations.
Permissions in SAP PMGM can be tailored dynamically by an HR Business Partner (HRBP); as long as roles are configured correctly, they should only grant access to the appropriate individuals and teams.
When prepping for interviews, you should expect questions related to such scenarios in SAP PMGM.
Setting the Stage for SAP PMGM Templates
SAP PMGM templates provide us with robust control of form processes. Everything from adding buttons and sections is managed through these templates.
At SAP PMGM, when we launched these templates, we employed four strategies to explore form routing processes.
 As soon as a form is launched, it is seamlessly transferred between employees and managers based on the employee information in Employee Central (EC). When this data is accurate and clean, SAP PMGM routing works like magic.
As soon as a form is launched, it is seamlessly transferred between employees and managers based on the employee information in Employee Central (EC). When this data is accurate and clean, SAP PMGM routing works like magic.
SAP PMGM Templates
SAP PMGM does more than provide predefined workflows; it encourages customisation. We spent an afternoon exploring templates, then created our own.
Rating scales can be applied in four distinct ways, and understanding which option best matches our situation is key to the successful management of project portfolios.
As previously discussed, SAP PMGM provides button-level customisation capabilities.
If employees need to add goals after launching the performance form, enable the ‘Add’ button. To limit delete operations directly in a template document, all options are possible via its multiple configuration layers.
Routing Dynamics Inside SAP PMGM
The designed workflows in SAP PMGM direct employee forms directly to managers; however, if any manager listed is inactive or incorrect in Employee Central (EC), these forms stall.
To maximise SAP PMGM’s effectiveness, ensure that every supervisor and manager is correctly connected to their reporting structure within Enterprise Central (EC).
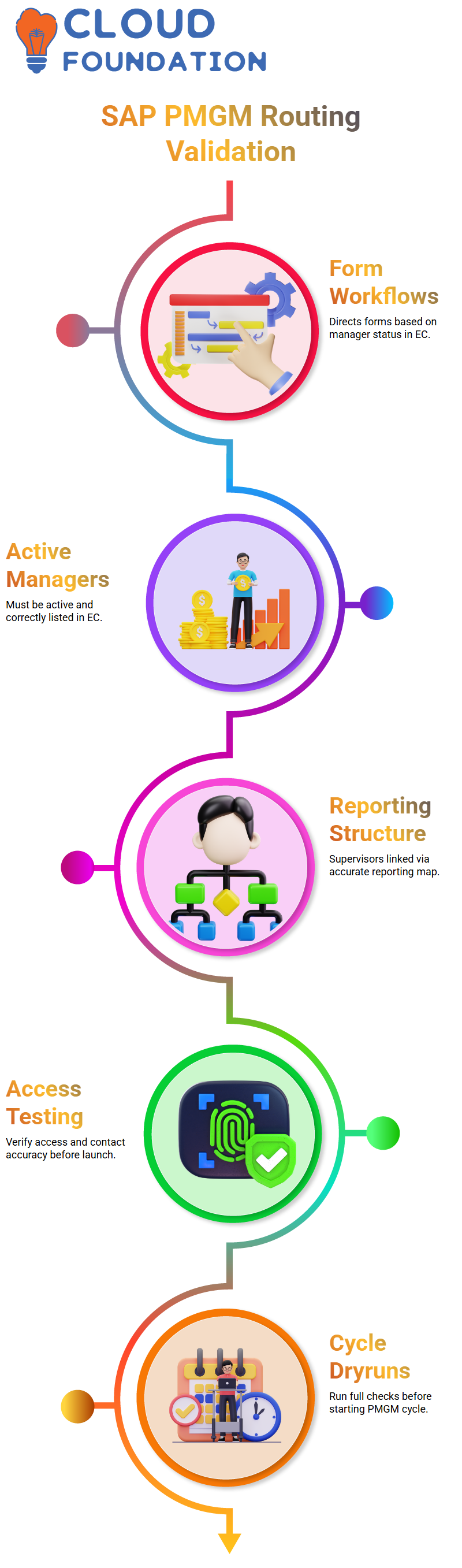
All our routing rules within SAP PMGM are based on this foundational employee mapping.
SAP PMGM Testing
Before launching forms in SAP PMGM, always conduct an extensive test and verify user access.
Are the supervisor and HR contact assigned correctly and present? These checks cannot be compromised, as missing contact data in HR SAP PMGM can prevent forms from reaching specific individuals; similarly, if manager information is inaccurate, the form will not proceed further.
Before initiating the SAP PMGM Cycle, conduct extensive dry runs to ensure that every detail in Electronic Commerce is verified.
Connecting SAP PMGM with Core Employee Data
SAP PMGM relies heavily on Employee Central data. Employee configurations, reporting lines, and role assignments — all live in Employee Central (EC).
Furthermore, when we create template roles in SAP PMGM, we rely heavily on mappings stored within EC to route forms accurately.
Integrating SAP PMGM forms ensures they follow an exact path, eliminating bottlenecks caused by misconfigurations or errors in settings.
SAP PMGM Documentation
SAP PMGM documentation and examples. Message definitions in business rules don’t just serve as labels – they define how your system communicates with users.
These resources, particularly the Employee Central document, are essential. It began with reading them after finishing SAP SuccessFactors, and they helped prepare us as we transitioned to SAP PMGM.
SAP PMGM Screenshots and Workflow
SAP PMGM documents, such as their Workflow Guide. This comprehensive documentation explored email notifications, permission bases, dynamic role creation, and setting workflows with CSV imports.
SAP PMGM material helped expand our live discussions and provided more depth for the theoretical foundation.
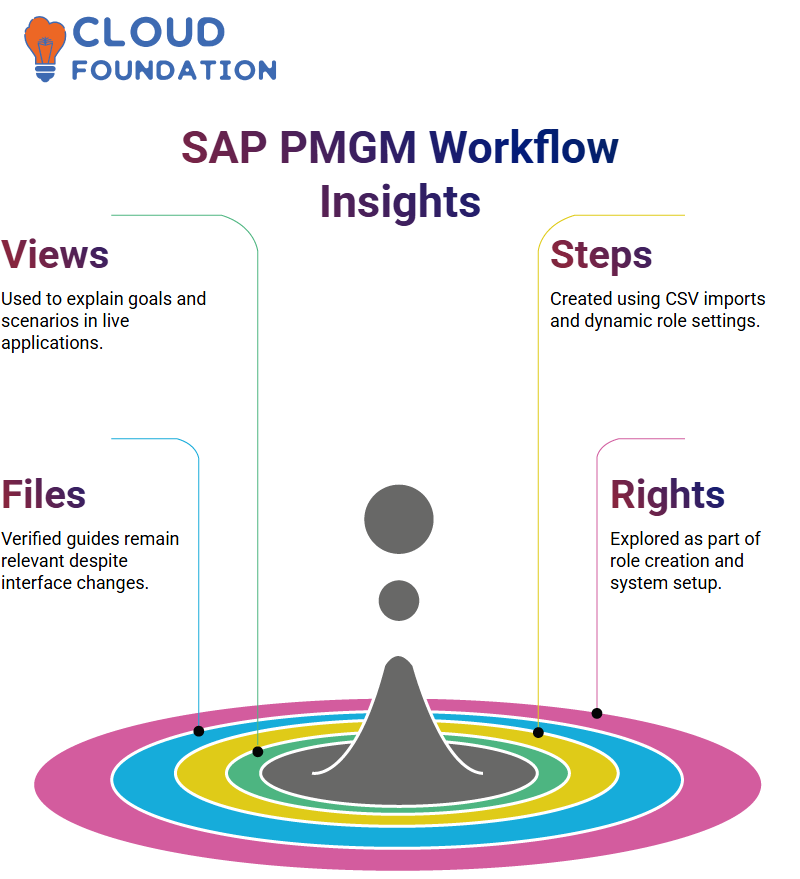
We revisited dynamic roles, verified workflow creation was intuitive through practical screen demonstrations, and even captured challenges of importing multiple workflows within SAP PMGM into documents.
SAP PMGM Document Verification via Screen Sharing
As part of our investigation of SAP PMGM documents, we reviewed various folders labelled with its name. After verifying two primary documents (the implementation guide and another SAP PMGM PDF), which remain applicable due to consistent tool functionality in SAP PMGM, these two remained applicable despite interface changes and self-study attempts (they had been uploaded long before but never properly indexed).
Realising there was no business tools document for SAP PMGM was disappointing, so an action plan was created to address it. These tools, taken directly from real-life SAP PMGM projects and extracted as screenshots to facilitate goal creation and scenario handling, provide viewing examples that make practice smoother while building confidence when dealing with real-world applications.
SAP PMGM Group
The SAP PMGM group is crucial to outline user selection criteria clearly whether by location, business unit, or role when assigning users to SAP PMGM group membership.
Employees from specific locations or departments often need to be added.

SAP PMGM offers the flexibility of excluding specific individuals from groups based on certain criteria, making the setup highly adaptable.
SAP PMGM in Real-Time Training
At live demonstrations of SAP PMGM, always emphasise its real-life implementation.
Not just theoretical concepts are explored; we also examine how HRBPs assign roles, who has access to specific areas, and when access should be restricted.
Role-play interview scenarios often centre around SAP PMGM.
Navigating SAP PMGM: Hands-On Insights from Real Practic
SAP PMGM advises based on their own experiences. When working with permission roles, it is essential to understand how the view summary provides an accurate representation of the current setup, including users, roles, and permissions.
In SAP PMGM, although this summary window cannot be edited directly, it serves as a valuable tool for double-checking the configuration.
Exploration is key when using SAP PMGM; take some time to explore its managed permission rules.
From your configuration, you can explore real history. From the left panel, you’ll see modification timestamps and user identities – not necessarily precise changes, but knowing who made them provides a reasonable basis for internal audits.
SAP PMGM relies heavily on role-based permissions (RBP). Across various modules, RBP helps manage access efficiently, whether for goals, performance, or calibration needs. SAP PMGM ensures that only authorised personnel have access.

Vinitha Indhukuri
Author



