SAP Security Tutorials | SAP Security Courses
Welcome to SAP Security Tutorial Blog: Want to gain expertise in SAP security to protect your company’s data and stay protected in today’s increasingly digital economy?
Organizations need to ensure their SAP systems are reliable in order to protect company assets, so this blog offers knowledge to enhance SAP security. The SAP Security Tutorial Blog features tutorials and guides on securing SAP systems effectively.
At CloudFoundation we provide comprehensive security training courses, covering SAP security fundamentals as well as advanced courses designed to keep you protected.
Authentication of data, authorization, cloud security, audit log, SAP Security Modules, sensitive data permissions are covered here in detail.
SAP Security step by step
Organisations require secure solutions that protect data, prohibit unauthorised usage and keep critical information secret.
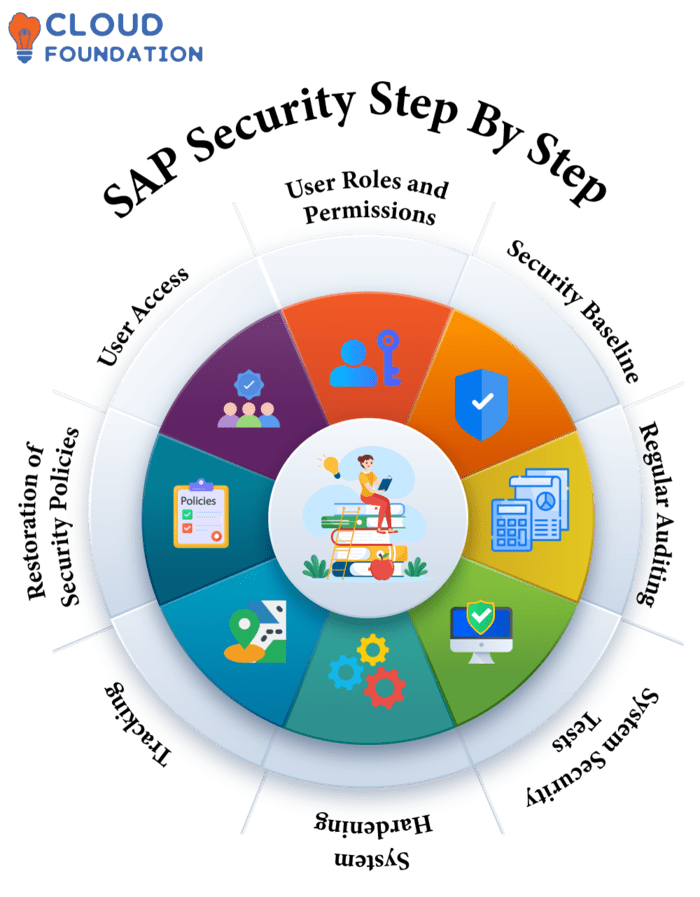
User Access
The system requires users to login using an individual log-in and password for secure access to its systems; minimum, maximum and complex password requirements will help facilitate safe usage of password security features.
User Roles and Permissions
Once user access has been established, configure user roles and permissions.
User roles allow access to certain programs, tables, fields or transactions while user rights vary based on each application’s transaction or table user access rights.
Security Baseline
Establish and document an access control baseline to establish user access levels, then regularly revisit this security level in order to safeguard the system while restricting it only for those that require access.
Regular Auditing
Audits provide critical assurance of system security and prevent unauthorised access. Regular audits should take place to protect user access privileges and baselines as well as identify security vulnerabilities within a system and verify it meets these parameters.
System Security Tests
System security should also be tested regularly, in order to assess vulnerabilities, security baseline levels and user access permissions.
System Hardening
System hardening entails increasing defenses to make systems more resistant, such as disabling unnecessary services, ports and apps as well as setting password policies and creating password policies to secure them more securely.
Tracking
Regularly monitor for system anomalies and security breaches to detect systemic anomalies or breaches; regularly assess assaults or unauthorised access.
Revamp of Security Policies
Security policies should be frequently revised in line with changing needs; review instructions as they pertain to current security issues in order to stay ahead of any emerging concerns and remain compliant. Incorporate regular testing as part of maintaining policy updates.
Security SAP
Security SAP provides end-to-end protection of company resources and processes while supporting secure operations both on-premises and cloud SAP implementations.
With powerful encryption and tokenization technology at its disposal, this tool helps safeguard transactional data while helping combat IP theft.
SAP security authenticates individuals accessing sensitive company assets. User names, passwords, digital certificates and two-factor authentication are built-in methods of authenticating users gaining entry.
Two-factor authentication can prevent unapproved access while more securely protecting company assets than single password authentication alone.
User roles and permissions provide data access controls. SAP security enables administrators to set access levels such as “view only” or “edit”, giving administrators complete control over who can view, read, edit or remove data.
Authorization manages access to key systems, business processes and services while only authenticated users may gain entry. User roles and responsibilities within its security policy determine this authorization.
Advanced SAP security offers intrusion prevention, malware protection and application control technologies which enable organisations to detect and disarm hackers, malware threats and other potential dangers. These tools help organisations detect and combat hackers and threats like them quickly.
Organisations can leverage user access management software to restrict users according to their roles and permissions, protecting data, applications and systems with an all-encompassing security suite.
SAP Security Cloud
SAP’s Security Cloud delivers enterprise-grade protection capabilities within a virtual private network environment protecting data while assuring regulatory assurance while optimizing IT infrastructure to meet business demands.
These services ensure the data which is secured for corporate needs while optimizing IT infrastructure for optimal use.
With its encryption service, companies can set data encryption policies which encrypt data leaving their company, thus protecting it against unauthorized access.
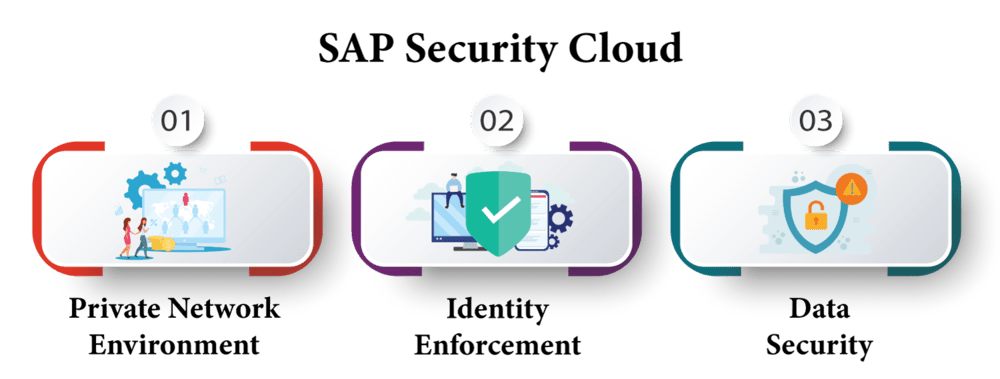
Identity enforcement services enable organisations to implement identity governance standards throughout their organizations and verify user identities before restricting data access only to authorized individuals.
Organisations may further control data usage using access control service for location restrictions as well.
Data security services set restrictions that limit data access. They protect it against unwarranted intrusion. Application security service safeguards applications against any unintended access and analytics solution provides insight into IT security and resource utilization.
Companies can protect data and optimize IT infrastructure using integrated security services provided. Many businesses implement GRC (Governance, Risk, compliance) processes for various reasons.

SAP Security Training

GRC in SAP Security
GRC also helps organisations remain up-to-date with security legislation and best practices, helping to detect security gaps within an organisation and identify any necessary controls that need to be put in place to combat potential breaches.
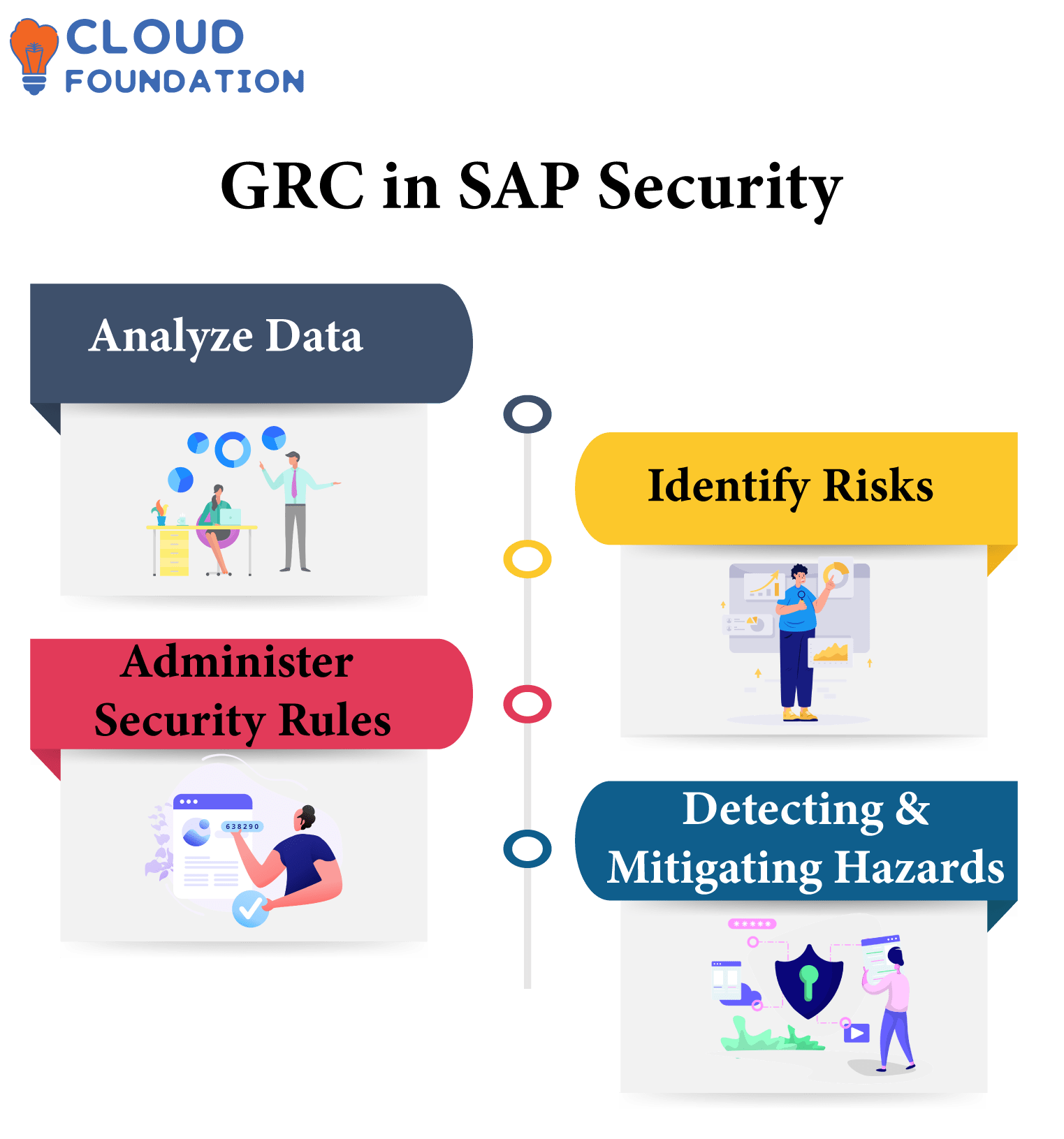
Security needs drive SAP GRC components. GRC aids companies in overseeing system security. GRC tools analyze data, identify risks, administer security rules, assess them and mitigate them as necessary, assess internal requirements as well as best practices and monitor for issues.
GRC solutions assist companies in detecting and mitigating hazards within their organizations, protecting the data with SAP regulations and requirements with ease.
Since internationalizing business operations is now standard practice and enterprises need to prioritize IT security best practices, GRC (Governance, Risk & Compliance) in SAP Security is becoming ever more relevant for enterprises.
A company must maintain an updated GRC strategy in order to keep processes and systems compliant with regulatory standards as well as their businesssecurity needs.
SAP Security GRC ensures an organization’s on-premise and cloud SAP systems follow to existing and developing standards, with tools and techniques for controlling user access, monitoring suspicious activity, discovering security problems and protecting important datain turn limiting identity theft and private data breaches.
Companies should keep all GRC procedures updated and documented for legal purposes.They include risk management, identity management, division of duties, secure storage facilities for incident responses and secure storage areas with safe environments.
SAP Security and GRC
Organisations use various technologies to protect data and ensure staff and stakeholders to follow security policies.
They include prevent unauthorized data access, identify data-security risks early, report any incidents to relevant authorities as quickly as possible providing data security for organisations of any size.
Likewise, security teams may utilize it for auditing systems and data to guarantee safety.
Organizational data and analytics may assist businesses with making strategic business decisions and early risk identification. This helps guide decision-making process while simultaneously improving efficiency of early risk identification processes.
Data security provide organizations with comprehensive protection, helping them meet industry regulations while its user-friendly features allow customers to easily access and analyze their data to make smart decisions. With this collection of technologies ensuring data is safeguarded.
SAP Security Audit Log
SAP’s audit log stands out by collecting more detailed data such as user accounts, activities performed, system failure logs, system problems and critical system changes recorded over time.
The SAP audit log also serves to track fraud and risk. Businesses may comply with industry and government laws by recording system actions within it, while anomalous entries might alert organisations of security breaches as well as problems or inconsistencies for quick resolution.

The SAP security audit log records all system actions to help organisations quickly detect and address security threats and concerns, audit system modifications and monitor regulatory submission.
Organisations using SAP systems require an audit log in order to monitor authorized access and prevent abuse or modification, identify risks or abuse or track system modifications and track system modifications or identify risks or abuse.
SAP Security Modules
There are several SAP Security Modules included, some of them are
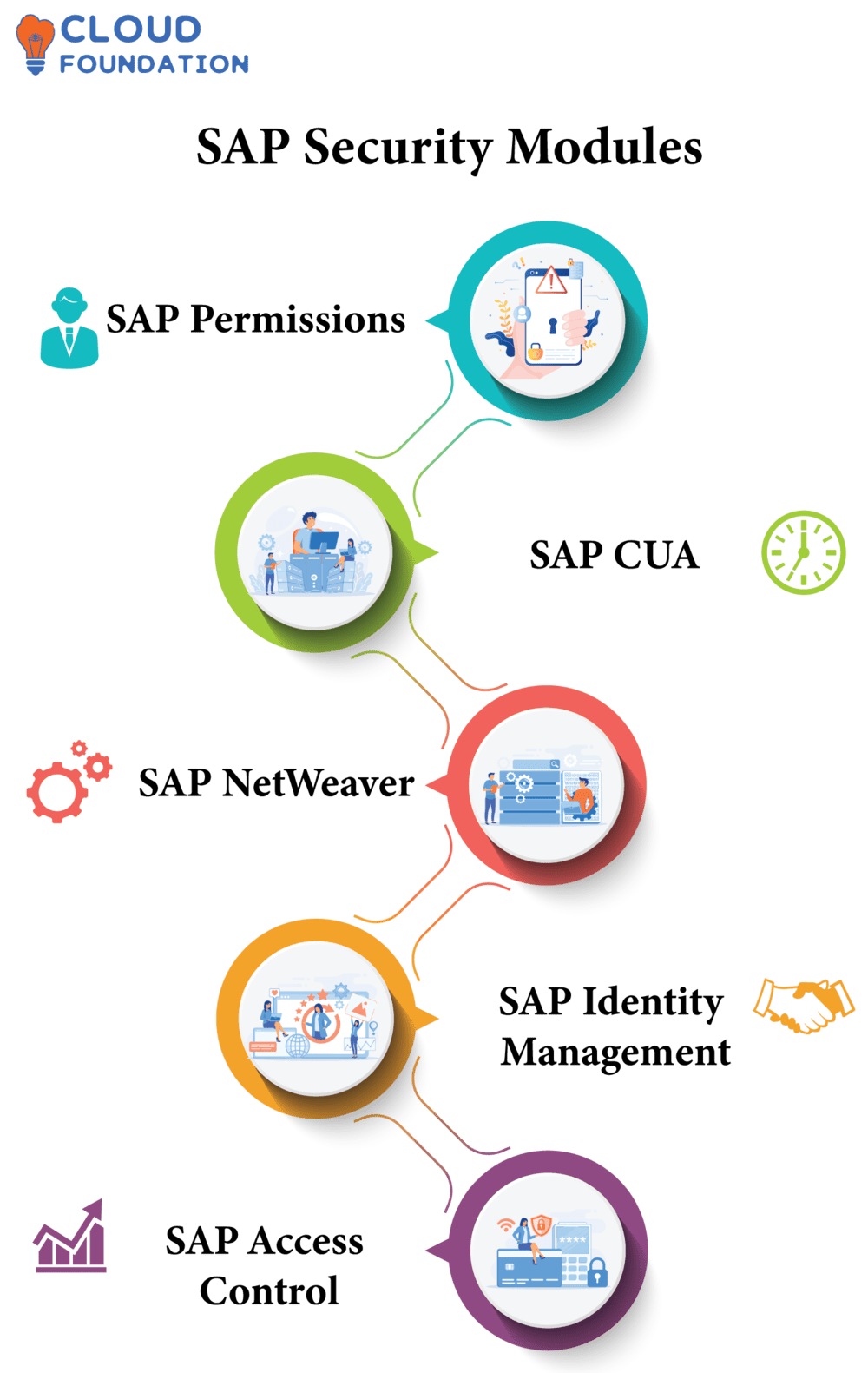
SAP Permissions
The SAP Authorization module allows users to restrict certain functionality within SAP system functionalities. Users, roles and profiles can all be managed, while roles assign authorization profiles directly to users for ease in user permission customization.
SAP CUA
SAP CUA provides users with more power and convenience with its Central User Administration module, centralizing user administration while automating new hire accounts and controlling data access privileges to make sure only authorized individuals gain access to relevant data.
SAP NetWeaver
NetWeaver orchestrates application services across heterogeneous platforms.
SAP Identity Management
SAP security relies heavily on SAP Identity Management for user identities across their systems, restricting resource access only to authorized and authenticated users.
SAP Access Control
SAP Access Control allows organisations to automate resource requests more easily. It features access control lists, certificate-based authentication, and secure activity logs, protecting sensitive information from unintended access by unauthorised users.

SAP Security Online Training

SAP Security TCodes
SAP R/3 Security TCodes provide essential protection. Security TCodes can be tailored specifically to each system or organization for greater granular control over authorizations, roles and access restrictions.
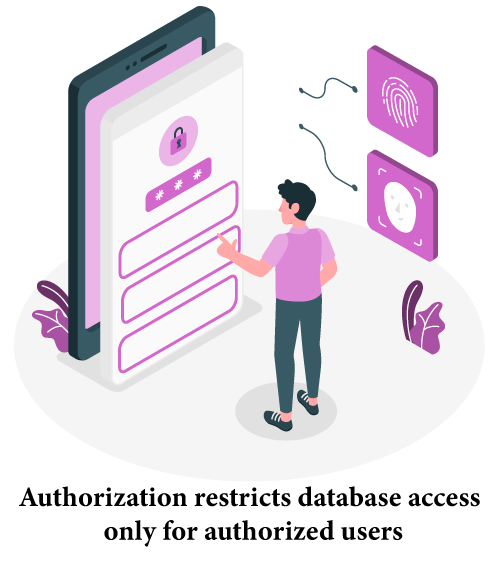

Authorization restricts database access only for authorized users. SAP Systems create roles, assign access privileges to individuals, and authorize database access in order to prevent system abuse.
Roles may organize users by providing access permissions that limit user access to SAP data and regions, protecting both them and the system as a whole. Restricted Access
Access limits help protect systems by minimizing system risk while at the same time safeguarding its access capabilities.
Security TCodes provide and manage permission groups, profiles, and objects which restrict SAP System access.
SAP Security Roles and Responsibilities
Doing this successfully requires having a thorough knowledge of security settings, object management techniques, authorization objects as well as system data tables and values.
Users must adhere to SAP security regulations in order to protect SAP data. Each user possesses an SAP user master record with authorization information and roles assigned. They may have various authorization roles or profiles limiting system access.
Access to data within SAP depends on user security roles. Each position grants them access to certain system functionalities and data items; users may modify system data, perform transactions or write documents depending on their permission profile. SAP Authorization Objects provide more details.
When users request access to system resources, authorization objects provide all of the data necessary for setting their access level.
Authorization objects contain object names, user access rights and permissions associated with specific items. When viewing reports for instance, authorization objects should grant users access and grant any additional permissions necessary for instance allowing amend or remove after viewing etc.
Administrators must specify data type, field values and user range for every authorization object in an authorization role or profile that contains them all.
Tables and values serve to protect system data; each value represents specific pieces of information which must be validated to allow access to system resources by users. SAP security module administrators must understand all tables and values utilized within their security modules.
The user master table contains user information such as authorization roles and access privileges for each individual, while the authorization object values table lists specific objects with details on user access rights, special permissions for their items.
SAP Security Administration or SAP Security Administrator
SAP Security Administration involves safeguarding business applications, systems, data, functions and processes deployed with SAP across an enterprise by applying appropriate plans, practices and knowledge within SAP to their protection.
Access may be granted administratively for IT staff or end user access for workers, contractors and customers. Security administrators develop, implement and oversee security procedures designed to prevent unapproved access or corruption of mission-critical data.
This involves overseeing user roles and profiles as well as data access/authorization mechanisms and organizational security policies.
SAP Security Administration demands Technical, Process, and Risk Management knowledge. Security administrators must possess in-depth understanding of SAP authorizations, functional needs, system configuration options and user preferences in order to manage these aspects efficiently.
Analysis, design and configuration of custom roles, security rules and access restrictions understanding technical documentation writing processes.
SAP Security Administrators collaborate with IT, business teams and end users to assess security needs and set restrictions that restrict access.
After setting policies and roles for security administrators they create user accounts with assigned responsibilities before creating more user accounts if needed.
Security administrators must oversee all user accounts, roles and profiles to edit or remove as appropriate. In addition, the security administrator should monitor, evaluate and update security policies regularly in order to guarantee security maintenance.
Any SAP-based ERP system necessitates SAP Security Administration for optimal operation.
SAP Security Tables
A secure system must exist in order to protect financial transactions, wages and customer records that’s where SAP Security Tables come in!
These tables store information regarding SAP roles, users and permissions that restrict SAP access and safeguard company data.
Some tables contain user security roles for operating various parts of SAP system data and operations. Other tables store user personal data including their ID number, complete name and telephone number.
Permission mappings containing access rights and data access controls for specific functions or data can be stored in separate tables, restricting system access and user operations in ways which prevent unauthorized entry into sensitive locations.
These settings effectively restrict system access while permitting only approved individual’s access.
Organizations may protect themselves against unauthorised system and data access by securely maintaining these tables. This helps companies keep their sensitive information protected against potential breaches.
SAP Security Audit
An SAP Security Audit systematically tests an organization’s SAP system for data protection purposes, helping protect critical enterprise information while uncovering systemic weaknesses. Independent auditors conduct these checks.
First and foremost, legal assurance ensures the system remains legal. Since technological innovations bring with them new security hazards and concerns for data safety. Companies must abide by rules while protecting their own assets.
SAP security audits uncover system flaws such as user IDs, passwords, system access levels and data encryption vulnerabilities that compromise system protections and can compromise data encryption capabilities.
Addressing vulnerabilities protects both systems and their contents typically steps may include: The auditor will conduct an initial system documentation review which includes user IDs, passwords and access levels.
An auditor will evaluate log files and audit trails for suspicious activity, system access and usage safeguards such as Encryption and Authentication and any weaknesses within Security and dataIntegrity rules before testing system components to find weaknesses or identify risks in them.
As part of their auditing service, auditors report results and make suggestions following an inspection. This helps businesses secure and comply their systems; detect weaknesses or any suspicious activities and ensure security among their infrastructures.
SAP Security Tutorials or SAP Security Courses
All SAP Security tutorials and SAP Security Courses provide all of the required knowledge about this cutting-edge technology.
Modern firms often face difficulty protecting their precious data. Organizations must follow regulations while protecting IP.
SAP Security has become an increasing necessity in today’s digital enterprise environment, particularly small firms vulnerable to cybercrime or other security threats.

Role-Based Authorization provides fine control over resource access. Password protection setup is another integral element to SAP Security lessons, while passwords secure data and resources.
Audits provide organizations with early warning of suspicious system activity and SAP Security auditing tracks any unauthorized attempts for entry. They build confidence amongst organisations.
SAP Security jobs or SAP Security and GRC jobs
Security and GRC roles are integral to the successful launch of any SAP deployment and should be filled by professionals possessing both technical and soft skills.
Monitor SAP Security & GRC roles create technical controls over how systems and resources are being utilized and deployed within an organisation, including policies related to use cases such as access control.
Authorization objects, user roles, password complexity rules, division of tasks, data access permissions and data security are included here. Create and implement operating procedures, change controls, emergency response plans and disaster recovery processes as necessary to keep data secure and available when it needs to be.

SAP Security and GRC positions require effective communication with SAP stakeholders; hence strong interpersonal skills are also crucial.
Businesses today need to protect sensitive data while adhering to laws and regulations. SAP systems need experienced SAP Security and GRC personnel in order to remain compliant while handling complexity within data.
Industry norms and job knowledge influence SAP Security and GRC salaries. Security experts with extensive SAP ecosystem knowledge are in high demand as constantly shifting ecosystem demands require constant learning and development for SAP Security/GRC specialists, in return they could expect a rewarding career path ahead.

SAP Security Course Price


Divya
Author