Various types of SAP CRM Modules
Good day to you reader, here we are with another blog in our bucket, so come let us explore more about “SAP CRM MODULES”, before that have a look at “what is SAP CRM” and also know more about “SAP CRM Certification”.
Introduction to SAP CRM
SAP CRM (customer relationship management) allows businesses to organize and monitor customer relationships efficiently. In addition to ERP and CRM applications, the Business Suite also features other applications from SAP that help streamline these customer connections.
SAP Customer Relationship Management helps organizations manage customer retention processes over time.
Customers will be more satisfied and company operations more streamlined with this innovative the program which integrates with SAP ERP and SAP BW (Business Warehouse) for comprehensive customer relationship management.
SAP CRM includes tools for automating sales process automation, marketing campaigns management, customer service operations management, and data analytics. Furthermore, sales force automation software manages leads, opportunities, quotes, orders contracts.
Businesses can easily organize, launch and monitor marketing campaigns using marketing automation modules like Marketing Automation Suite TM (MASS). In addition, service management capabilities enable more efficient handling of accidents, service requests, and issues for accident management needs, and casualty claims processing services requests and incidents more promptly than before.
Businesses may use the analytics module to make decisions based on accurate, up-to-the-moment customer behaviour and preferences.
SAP CRM offers two deployment options to businesses – on-premises or Cloud-Based making the software suitable for organizations of varying sizes in retail, manufacturing, telecommunications, and financial services sectors as well as others.
SAP CRM Basics
SAP CRM is an automated customer relationship solution streamlines business operations while increasing customer engagement and satisfaction. Here is some fundamental SAP CRM terminology:
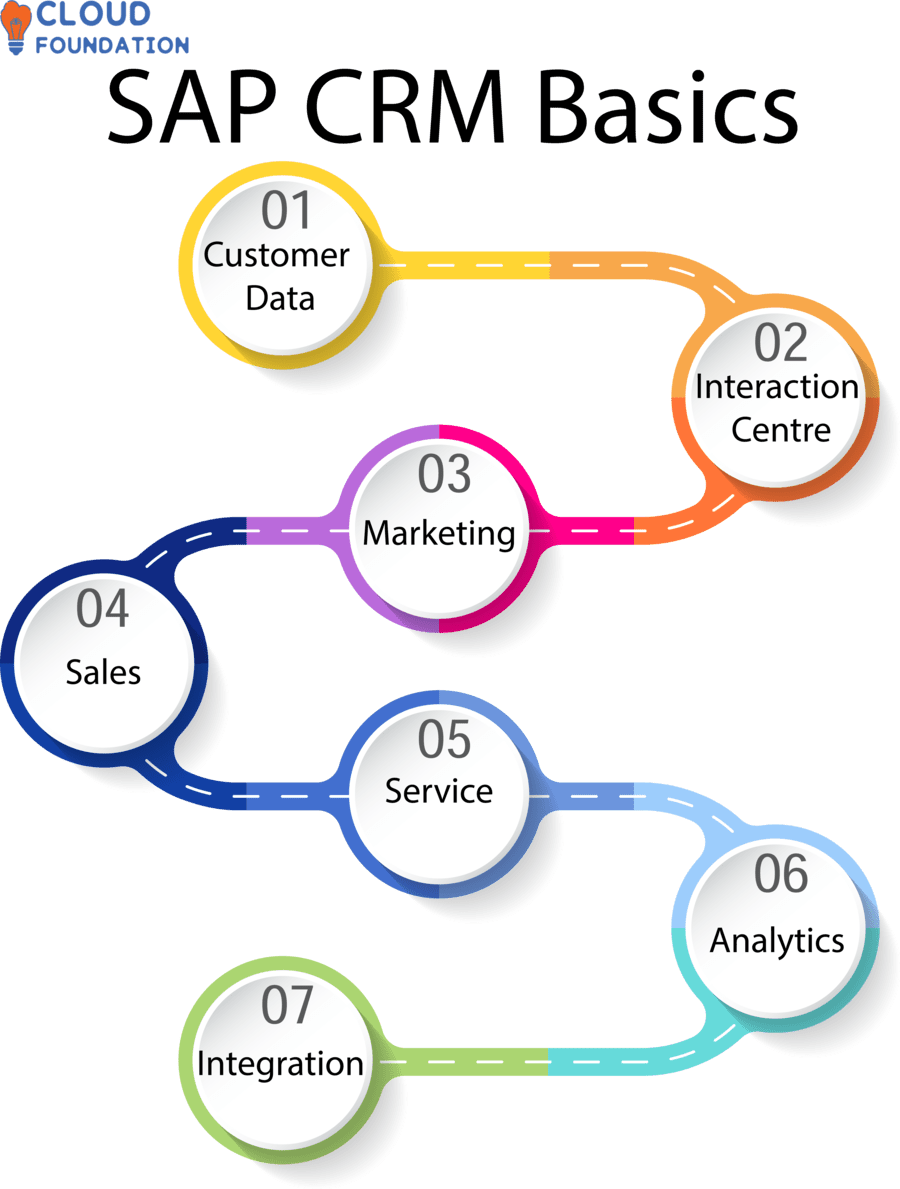
Customer Data: SAP CRM allows organizations to store and administer customer information like contact info, purchase history, and preferences in one central place.
Interaction Centre: SAP CRM allows businesses to manage all consumer interactions through multiple channels – phone calls, emails, chat messages, and social media – effectively and efficiently.
Marketing: Automation Tools from SAP CRM provide businesses with robust automation tools for creating and executing marketing campaigns, managing lists, and measuring the efficacy of marketing initiatives.
Sales: SAP CRM helps sales teams more efficiently manage leads, opportunities, estimates, orders, and contracts and provides forecasting and pipeline management tools.
Service: SAP CRM includes a service management module designed to efficiently handle customer support inquiries such as incidents, service requests, and problems and enable businesses to provide superior consumer care and assistance.
Analytics: SAP CRM delivers real-time consumer preferences and behavior data, helping companies make data-driven decisions and giving companies reporting and analytics tools for measuring the efficacy of consumer engagement strategies.
Integration: SAP CRM integrates seamlessly with SAP ERP and BW (Business Warehouse), creating an all-inclusive customer relationship management solution.
SAP CRM Prerequisites/Skills
Working with SAP CRM requires both technical and functional abilities that complement each other, with both knowledge and skills necessary for making it work optimally:
These include the following technical abilities and knowledge required to use it effectively:
Technical Skills:
ABAP code skills in languages
Understanding of SAP CRM Architecture
Experience configuring and customizing SAP CRM modules
Knowledge of integration with other SAP modules such as SAP ECC, SAP BW, etc.
Knowledge of CRM Middleware, the WebUI Framework, and the IC WebClient.
Functional Skills:
Knowledge of CRM Business Processes
Experience in Sales, Marketing, Service, or E-commerce domains
Knowledge of CRM Data Models and User Roles
Excellent communication skills to interact with business users and stakeholders
Knowledge of industry-specific processes, such as retail, finance, and telecommunications.
Other skills:
The ability to analyze problems and figure out how to fix them
The ability to handle projects and deliverables
Knowledge of the Agile/Scrum project management method
Experience managing and tracking projects with SAP Solution Manager
A combination of technical, functional, and other abilities is required to operate effectively with SAP CRM. To become proficient in SAP CRM, it is suggested that you develop knowledge and experience in both technical and operational areas.
SAP CRM WEB UI Tutorial
The SAP CRM Web UI provides users easy web-based administration of SAP CRM data. Featuring a straightforward menu bar with quick links to its various modules (Sales, Service, and Marketing), users have fast and convenient access to their SAP CRM database functions.
Search, viewing, editing, and creation are now more straightforward for users on any device at any time and location. Users gain easy and direct access to their data whenever needed from anywhere at any time of day or night.

SAP CRM Web UI offers an effective solution for efficiently utilizing CRM data while streamlining processes, providing comprehensive capabilities, and adaptability – essential elements for customer relationship management in any organization. If your firm requires better customer relationship management services, look no further.
SAP CRM Functional Tutorial
SAP CRM offers several modules designed to aid businesses in managing customer interactions and operations efficiently, such as:
Sales Management: With SAP CRM’s sales management module, companies can effectively oversee their sales processes. It provides features like managing opportunities, accounts, quotes, and orders and anticipating sales to help address this aspect of operations more effectively.
Service Management: SAP CRM’s Service Management module assists businesses in managing service operations efficiently, including customer service requests, order processing, ticket administration, and service contract administration.
Marketing Management: SAP CRM’s marketing management module gives businesses powerful tools for overseeing marketing campaigns, such as planning, executing, leading management leads management, and analyzing the market.
Partner Channel Management: SAP CRM’s partner channel management module makes managing business relationships with their partners much more straightforward for businesses, from onboarding and working together to measuring the success of partner collaborations and overseeing them for each.
E-commerce: module equips businesses with all of the tools to successfully operate online sales outlets, with features including creating an online shop with a product catalog and managing orders.
SAP CRM Business Role Configuration
Configuring business roles in SAP CRM is essential in setting the user experience, including how users will engage with and utilize its capabilities. Here are the basics steps for configuring SAP CRM business roles:
Establish Business Role: As part of this first step, it is necessary to identify each role by giving it a name, description, and function in the system. These details allow people to visualize better where each job fits.
Assign Work Centres: After identifying and defining your role within a business job, assign work centers accordingly. Each work center collects transactions and reports related to that specific role within that role and gives users access to particular transactions or information by allocating it as part of a work center assignment for that particular role within it.
Definition of Navigation Bar Profile: A navigation bar profile displays how menus are laid out and allows users to move around freely within an application or website, simultaneously serving multiple business purposes.
Assign Authorizations: Assign authorizations to each business job. Authorization charges establish user access rights, such as which transactions and reports they can view or edit and what data they can view or modify.
SAP CRM Features
Sales and Marketing: SAP CRM contains an arsenal of sales and marketing tools, such as managing service requests.
Customers can create tickets themselves while agents assign keys directly through SAP’s user-friendly self-service options to get assistance with problems quickly.
Other teams within your company also benefit from SAP’s service management features – here are a few critical ones: Service Management.
Analytics and Reporting: SAP CRM’s integrated analytics and reporting tools enable it to glean even more insight from customer data, helping companies track customers’ actions, search for trends and make data-driven choices to enhance service quality and marketing tactics.
Integration With SAP Products: SAP CRM is designed to work seamlessly with other SAP products like ERP to offer organizations an all-in-one customer relationship management solution, streamlining processes while decreasing duplicated information and increasing data quality. It helps organizations simplify operations while streamlining customer management procedures and cutting duplicate data entry costs.
Mobile Access: With SAP CRM’s mobility feature, sales and service teams can operate virtually anywhere with mobile device access. Sales/service teams are more responsive in responding to customer questions or updating information while on the move, becoming more productive and quicker to take action when necessary.
SAP CRM Advantages
Comprehensive Customer Relationship Management: SAP CRM comes equipped with numerous tools for effectively overseeing customer relations, ranging from sales, marketing, and service management.
Businesses can leverage customer data analytics to streamline processes and enhance customer service while gathering valuable customer intelligence.
SAP Products Integration: SAP CRM is designed to interact seamlessly with other SAP products like ERP and BW, helping organizations streamline operations while eliminating data duplication and improving data accuracy. This integration can save organizations time, reduce operational inefficiency and save on resources.
Scalability and Flexibility: SAP CRM’s design ensures it can quickly adapt to meet the diverse requirements of different organizations, making it highly adaptable.
This solution adapts to changing business needs over time while supporting long-term expansion. Furthermore, organizations can host on-premises or via the cloud, granting them a more excellent choice when it comes time for deployment decisions that best match individual and organizational requirements.
SAP CRM Hybris Integration
SAP CRM and Hybris are two software products provided by SAP that work to manage customer relationships and e-commerce activities, respectively. Integrating them can assist firms in providing a consistent customer experience across different channels.
Here are a few critical considerations for merging SAP CRM and Hybris:
Data Integration: one of the primary goals when joining these solutions, since both solutions contain client data that must be synced across both solutions – this can be accomplished using middleware solutions such as SAP Process Integration or Cloud Platform Integration to achieve this sync-up between them.
Process Integration: Integrating SAP CRM and Hybris should also involve harmonizing business processes encompassing client order, return, and refund processes using SAP Process Orchestration (PO). This integration should also take advantage of SAP Process Orchestration as another means.
Customization: Based on your business requirements, customizing both SAP CRM and Hybris platforms might be necessary to meet them. This might entail developing custom fields, reports, and workflows; both platforms must share these modifications evenly.
Testing: Before implementing any integration project, it is critical that testing takes place to make sure it functions as intended. This may include data synchronization testing, business process integration testing, and customizations.
Training your employees on using SAP CRM and Hybris, including learning new processes and workflows, is paramount.
SAP CRM Territory Management
SAP CRM Territory Management can play an instrumental role in streamlining sales operations by organizing sales teams into geographical territories or regions.
Businesses can utilize this capability to establish territories based on customer demographics, sales potential, or geographic location and then assign sales teams accordingly.
Sales teams can then focus on specific accounts and opportunities within their territory, optimizing sales efforts while increasing efficiency.
Organizations may create overlapping regions and backup or auxiliary sales teams to maintain consistency of effort and clarity for customers. Overall, SAP CRM Territory Management can assist companies in improving sales performance while streamlining the sales process.
SAP CRM Career
SAP’s Customer Relationship Management system – used for customer relationship management and interaction between enterprises and customers – presents many promising career opportunities.
SAP CRM Consultant: Your role as an SAP CRM Consultant involves customizing SAP CRM to fit clients’ unique requirements and working collaboratively to understand and address their sales and marketing operation needs. You will work alongside them closely to craft practical solutions that improve processes overall.
SAP CRM Developer: your responsibility will include developing custom applications within the SAP CRM system – creating workflows, reports, or user interfaces as needed while integrating them with other systems.
SAP CRM Functional Analyst: your focus will be collaborating with business stakeholders to understand their needs and devise solutions. You are also accountable for training users of SAP CRM and testing/support of users of this system.
SAP CRM Project Manager: your primary duty will be overseeing implementation projects from start to finish. In collaboration with clients, consultants, and developers, you must work diligently towards doing projects on schedule while staying within budget – much to their delight!
The CloudFoundation will provide thorough online training classes on SAP CRM, as well as lifetime access with video access. If you have any questions, you may ask the instructor, and the support team will be available at all times a day.
On their official website, they offer SAP CRM training videos and SAP CRM related blogs.

Saniya
Author
“Life Is An Experiment In Which You May Fail Or Succeed. Explore More, Expect Least.”



