SailPoint training on IQ Services
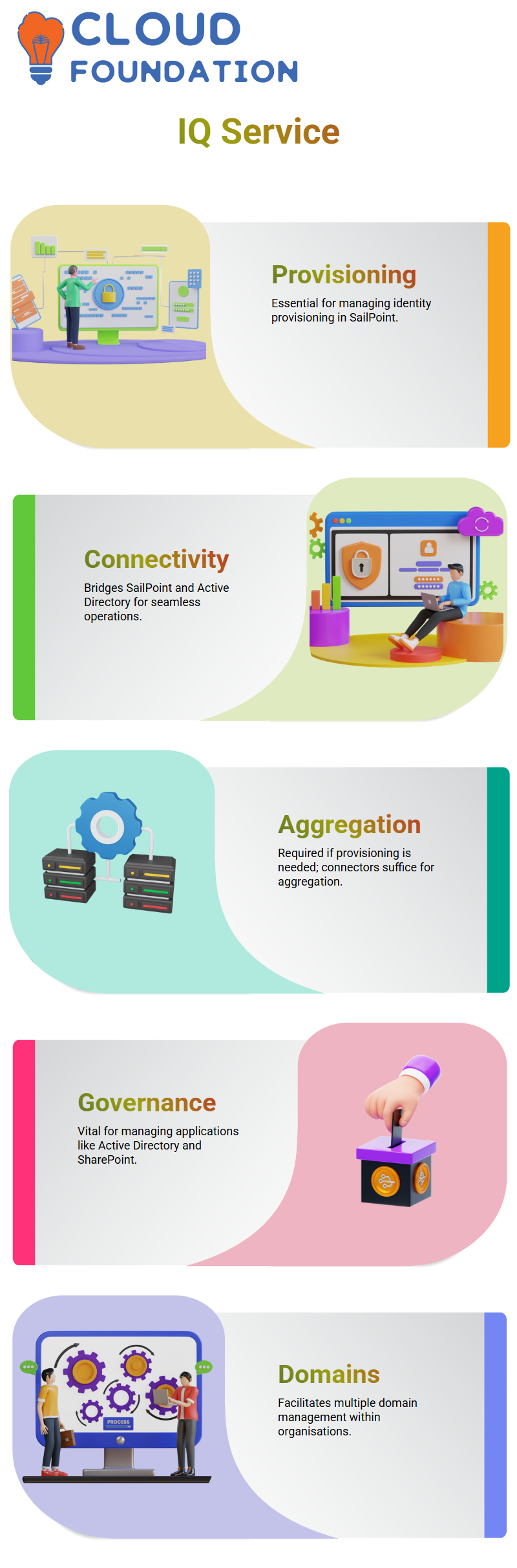
SailPoint IQ Service
Before joining our company, you may be interested in learning more about SailPoint IQ Service.
It is imperative to deliberate and realise its usefulness as well as the reasons for its value. SailPoint IQ Service is not just a simple component but rather a required provisioning tool in SailPoint.
People often have a question about the need for IQ Service. The reason lies in the situation that SailPoint has with AD and others.
The AD connector excels at data aggregation, but its provisioning capability is only available on SailPoint.
The SailPoint application is a Java and XML-based product, while the Active Directory is built on the .NET framework.
IQ Service is introduced to bridge this very gap.
The connectivity between SailPoint and Active Directory is made possible by the SailPoint IQ Service, a role that enables provisioning operations within the organisation.
In other words, a connector is sufficient if the requirement is only for aggregation. Yet if provisioning is the demand, the IQ Service is a must-have.
For an organisation, IQ Service is a vital element for governing different applications, such as Active Directory and SharePoint. While the facilitation of the IQ Service details field is provided, it is not the only one.
In other words, it is not only the operation whereby the provision is facilitated and the operations made smooth and resourceful through providing the required target details by I Quality Service.
Domains in the SailPoint IQ Service
Most organisations very often manage more than one domain, and SailPoint IQ Service facilitates the process.
Conduct is the easier option if we have a permit, say five domains, but the Street ones are indispensable to be managed through SailPoint.
The domains must be set manually in the system for SailPoint only to have the necessary configurations to operate.
For example, if two domains are input and their permissions differ, then correlation at the application level determines how user entities are created.
Systems establish operating the application-wide domains only if it is required to do so, which paves the way for smooth domain management.
Modifying permissions in SailPoint
The configuration in every SailPoint instance is not a complicated detour and is, at its core, very simple.
The SailPoint podium encompasses the entire application, including all available permissions; the user can only aggregate and describe the entitlements.
The catalogue of entitlements supplies a view for people on which permissions they can request.
Specifically, those users who have a need can fill out the forms for various permissions. If there is a requestable entitlement, the user may choose it and be sure that the access is controlled according to the organisational guidelines.
SailPoint is a key player in not only the application admission process but also in the context of user access and enterprise environment security.
As a result of setting the entitlements correctly, not only can organisations provide users with reduced ways to manage permissions, but the security of the systems is also maintained.
Bulk Alterations in SailPoint
Bulk access right alterations are very often required, and SailPoint integrates this through the import/export mechanism.
Instead of manually changing the entitlements, end-users can export the records into a spreadsheet, inspect them, and re-import the updated records.
This function is the most productive way to enrich entitlement modification of ownership and descriptions, reduce administrative workload, and keep all data well-organised.
Access Requests in SailPoint
SailPoint entitles us to do that quite simply, as the automation of access requests can be achieved through workflows, a straightforward method that involves avoiding unnecessary approvals and seamlessly integrating new entitlements.
Any access request, alteration in entitlement, or protocol for user group transition within the organisation, SailPoint’s automation captures them all. Thus, we guarantee that we comply with the law while maintaining uninterrupted process efficiency.
With the right tools, we can implement events that facilitate the desired workflows for automating the identity lifecycle.
SailPoint’s Native Change Detection
In the business sphere, the features of an identity may change without leveraging the SailPoint method.
Through native change detection, the identity revisions performed in the target applications are kept in sync with SailPoint.
Through the utilisation of native change events, SailPoint can automatically identify unauthorised alterations, generate alerts that correspond to the situation, and simultaneously certify compliance with country regulations.
Whether provisioning or deprovisioning, native change detection is essential for protecting the security and clarity of identity management.
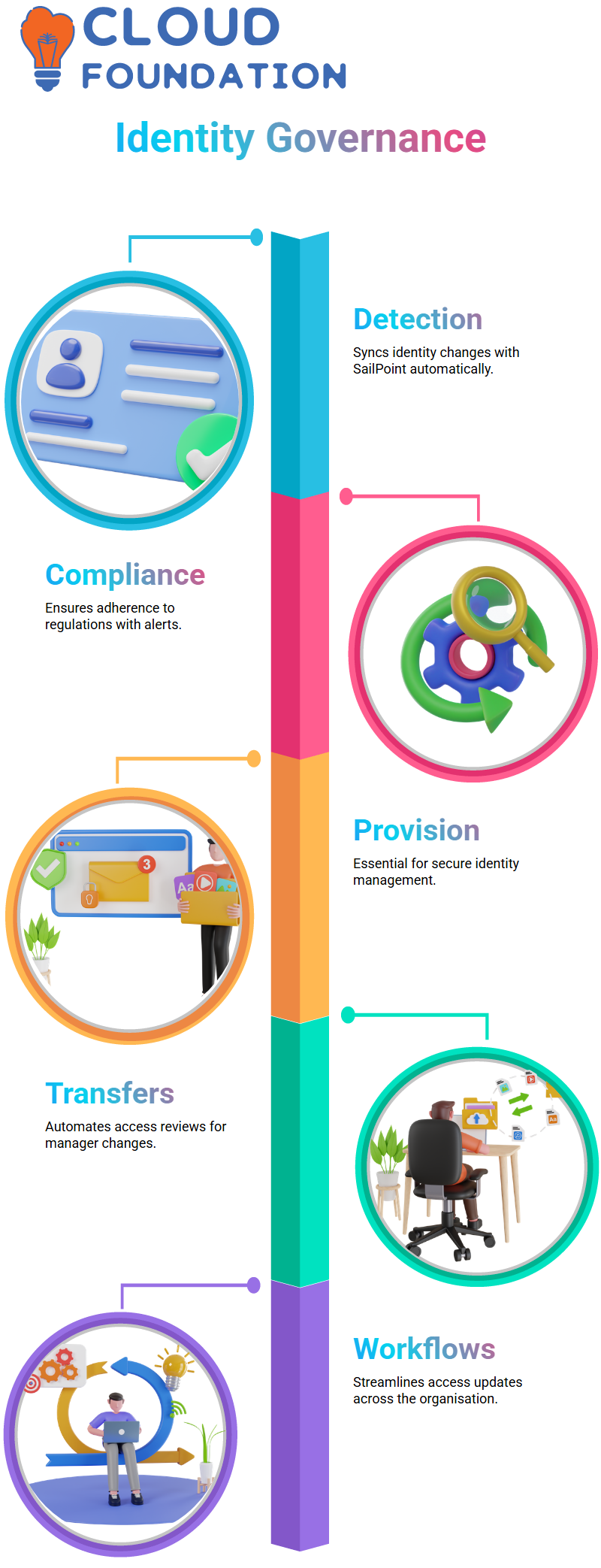
SailPoint Manager Transfers and Role Reviews
If an employee’s manager changes, SailPoint ensures that all access rights are reviewed in an automated manner.
Thus, the user will have no unauthorised access, and the issues of rights and business needs will be kept in step.
SailPoint, by setting up manager reassign events, will not only drive workflows to assessment and automatically update access rights, but it will also be the primary piloting ingredient in the identity governance area and certify respect on an organisation-wide level.
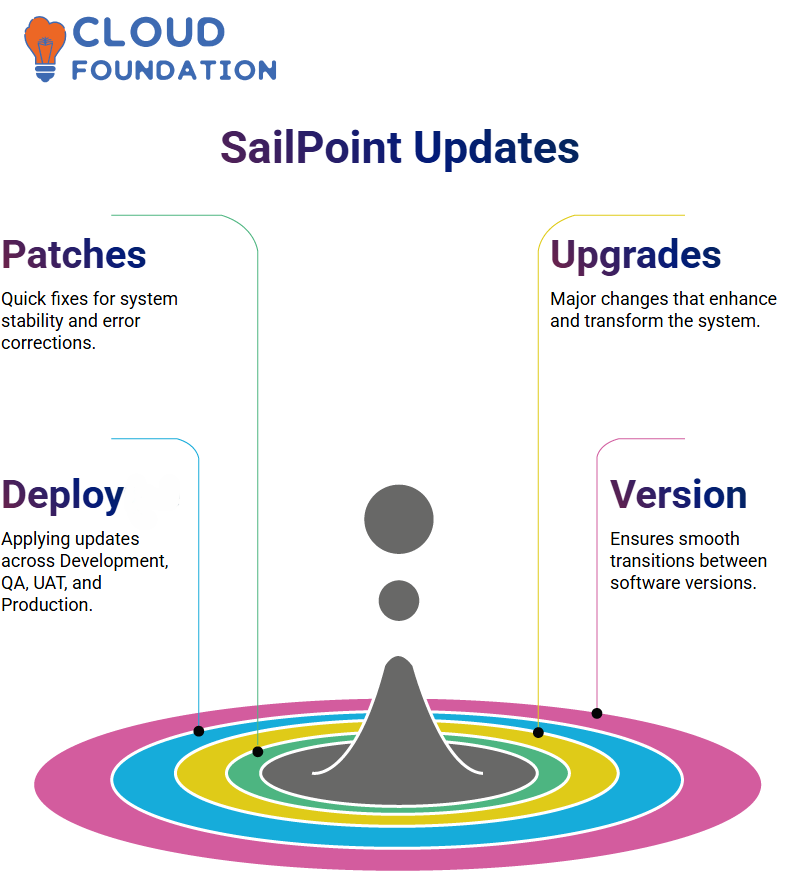
Discernment SailPoint: Patching, Updating, and Deployment
The entire process of identity governance would be simply unattainable without SailPoint – not only the administration of it, but also the continuous addition of updates and patches, which carry out program refactoring, keep it safe, enable new operations, and other tasks.
In the world of SailPoint, patches are minor corrections that focus on specific errors, such as software system flaws.
Think of them as correctness solutions—quick to deploy and vital for conserving stability. Instead of showcasing improvements, patches are intended to optimise the existing framework.
In SailPoint, we do more substantial upgrades. Major upgrades, modernised options, and momentous revisions are included. Patches can be compared to tuning adjustments. In contrast, upgrades are the kind of change that completely transforms the system for the augmented.
These are the ones that require the utmost caution when carrying out, as they may disrupt existing workflows.
Deployment, conversely, involves applying these patches and upgrades to the various contexts that the company uses—Development, QA, UAT, and Production.
The entire process concludes with the application running properly in each phase, and it then transitions to the business-facing Production environment.
Comprehending the difference between patches, upgrades, and deployments is crucial for maintaining a robust SailPoint implementation, and this is also a key aspect of identity governance, as updates are necessary for the proper functioning of these operations.
SailPoint Versioning and Patch Management
Versioning in SailPoint determines the way upgrades and patches are installed. Suppose, for a prototype, you are on version 82; then the transition to 83 will be an orderly one, ensuring that there are no compatibility challenges.
In contrast, patches address specific issues, while upgrades introduce more general enhancements.
Patch management implies that there will be no significant downtime, as a small number of interruptions that do not affect the primary functions would be a quick and straightforward solution.
They mostly fall into the category of vendor-provided solutions that will be passed to you in the form of packages, and they will be installed painlessly.
On the other hand, the upgrades necessitate a thorough plan.
Upgrades are large-scale operations that provide or make available additional capability. Still, at the same time, they involve some risks, such as data loss and bugs, which can sabotage the entire procedure, unfortunately.
For example, updating Hygieia from version 2.0 to 2.1 is a potentially hazardous operation that can lead to data loss and introduce new features that deviate from the original concept.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting Events in SailPoint
SailPoint supplies different ways to link events and workflows. Through the debug page, lifecycle workflows can be rigorously reviewed, and all the details can be entered to ensure that the right events trigger the right processes.
Additionally, we can follow the audit logs, which provide a history of touched events, thereby granting us the indispensable reports for monitoring and control throughout the lifecycle. This will make us honest and open people over time.
Deployment in SailPoint: Safeguarding Consistent Integration
One of the key success factors in the current process of integrating updates in the SailPoint dais is deploying the alterations through multiple and diverse platforms.
The dev team assure there is a proper testing process to build a bug-free production of the amendments by following the passage: the testing of the code in the environment for QA, next the deployment in the out of the space for UAT, it follows that the final one will be placed in the production system.
Every step, from debugging to the final release, is organised in such a way that there are hardly any disruptions while the performance is being boosted.
If there are any glitches, they must all be duplicated in the development environment to achieve stability.
Thus, not only were the end-users not bothered, but they were also working on the same project, according to the CEO.
Awareness of SailPoint Deployment
It’s the rostrum where the production environment, the backbone of the system, decides what you are working on.
The bug-checking process involves running tests on the production environment, identifying issues, and, when found, removing or mitigating them.
Imagine that there is a requirement to onboard an application, develop policies, install patches, or upgrade the product.
Those SailPoint developers, with whom the issue is resolved in development, will serve as the initial filter for any requirements.
This could be a new attribute or simply a resolution to an existing issue.
The deployment involves several steps, including approval from the relevant teams. The downtime for the process has been set mainly between Friday and Sunday, so that the number of affected users is minimised.
Installing a comprehensive document, known as an installation packet, before deployment is an excellent idea. This document contains the timeframes, engineer tasks, and Plan B.
The deployment receives support from interested parties, including the database team and SailPoint support engineers. It is a stepwise method that involves backups, service stops, and upgrades.
How does Code Flow from App to User in SailPoint?
Following the developers’ job completion, the amendments are pulled from the Dev environment to the QA environment.
In the other world, the QA engineers are responsible for authentication work and the documentation process, thereby completing the goal.
It is worth noting that after authentication is completed, the support and development teams, as well as QA engineers, are relieved of many duties.
Only when the go-forward is given to apply the transitions and they are then evaluated by the business teams in the next environment, if all goes well, can the modifications be positioned.
SailPoint Application Upgrades
The upgrade of the SailPoint application is a methodical approach to achieving missions. For example, organisations employing version 80 are not able to move directly to 84; they will need to go step by step from 80 to 81, then 81 to 82, and so on.
Two tactics can be adopted: namely, following the migration procedure one after the other or performing the migration task simultaneously.
Furthermore, the migration procedure involves extracting objects from the existing version and importing them into the new version.
That being said, sequential upgrades are usually a lot.
Migration vs Upgrade in SailPoint
Remember that migration is not an upgrade. The upgrade involves transitioning from an older version of SailPoint to the latest one.
On the other hand, migration is the process of transferring data from one product to another.
One prototype of the migration is the switch from OIM to SailPoint, which would be a migration assignment. The organisations need to review all applications and objects that have been onboarded and ensure they are all migrated to SailPoint.
SailPoint Business Process
One of the most typical mistakes is the misunderstanding of the difference between SailPoint’s workflows and business processes.
While lifecycle events trigger workflows, business processes set the rules and automation for identity governance.
For example, SailPoint’s LCM provisioning system is triggered when a user submits an access request, and, similarly, a procedure relevant to the joiner activity is activated without manual intervention, thereby ensuring the right level of approvals and proper provisioning.

Navya Chandrika
Author



