Workday Organization Tutorial – The only HCM course you need
📣 3145 Participants |🎓 2185 Reviews | 4.7 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
Workday Organization & Design
Organizations in Workday
- Organize workers into groups that serve a common purpose
- Typically represent how work is done and how the workforce is structured; can serve many other purposes and are used across the entire platform
- Workers are tied to multiple independent organization types, each with a different purpose.
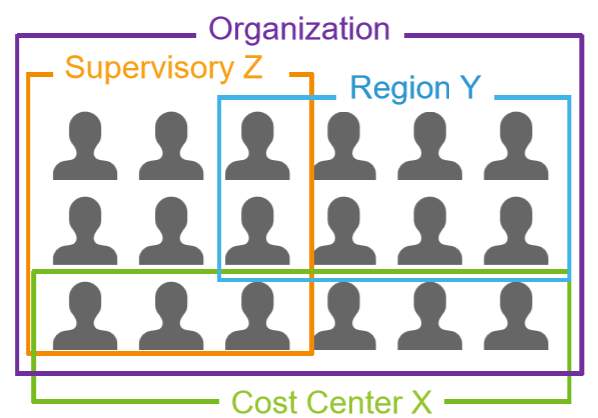
What are Organizations used for?

Key Organization Principles
- Core component of Workday’s unified platform
- Different organizational structures meet specific needs but are shared across the entire platform
Efficiency and Effectiveness
- Default and dynamic assignments minimize manual data entry and improve data integrity
- Each organization can have its own processes and characteristics
Governance and Compliance
- Seamlessly integrated with security, reporting and business process frameworks
- Changes are auditable
Organization Types
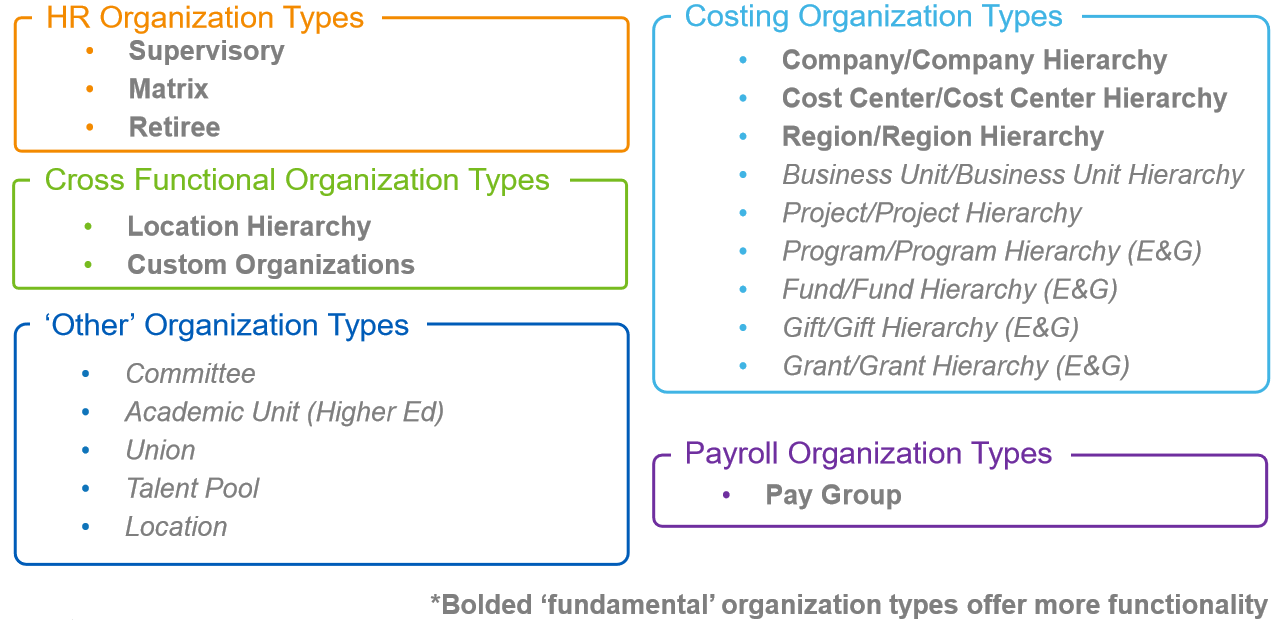
Key Behaviours across Organization Types:
- Staffing Assignments: Workers are assigned to organizations during staffing events or on an ad-hoc basis
- Organization Hierarchies: Organizations can be combined into hierarchies to represent how organizations roll up to one another.
- Role Assignments: Workers are assigned to organization roles, which are tied to security access.
- Financial and Payroll Workbags’: Organization assignments are defaulted on transactions and used for reporting purposes
Hierarchies
- Some types of organizations have a corresponding hierarchy for grouping organizations into a hierarchic structure
- Hierarchies establish parent/child relationships. They don’t store the definitions of individual objects, such as positions, workers, or financial accounts
- Hierarchy structures can be defined with the order of subordinate organization subtypes within a hierarchy ‒ When a hierarchy structure is in effect, you can only create subordinate organizations of sub-types that are valid according to the hierarchy structure
- Organization hierarchy roll-ups can be changed at any point
- Organizational roles can be inherited down the hierarchy ‒ Roles are filled once at a higher level and inherited by those below
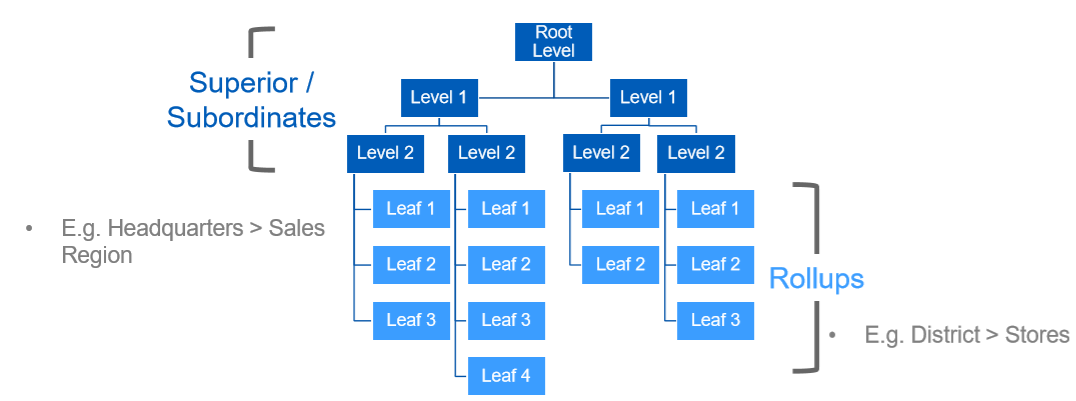
Organization Sub-Types
- Organization subtypes are created by customers to enable a delivered organization type to be further categorized
- For example, Supervisory Organizations could be categorized as Divisions, Groups or Departments ‒ Subtypes can be also be used to define levels in a hierarchy
- For example, a cost center hierarchy could include organizations with sub types of Area and Function
- The Organization Subtype can be appended to the organization name if configured (e.g., Benefits Department, Executive Management Group)
- All Organization Subtypes are tenanted data (customer-owned)
Fundamental Organization Characteristics
‘Fundamental’ Organization Types have the following characteristics:
- Reorganization Tasks
- Availability Date
- Visibility Configuration
- Sub-Types are allowed
Reorganization Tasks
- A Reorganization Event enables:
‒ Grouping reorganization activities with a common effective date into one event for viewing and reporting purposes
- The following activities use a Reorganization Event:
- Create a new organization (except for Matrix Org)
- Assign Included Organizations (e.g., Region or Location in a hierarchy)
- Assign workers to a custom organization
- Move Retirees
- Other organization maintenance activities require an effective date vs. a reorganization event and cannot be reported as part of the reorganization
- Change Organization Assignments process changes organizations for workers in a supervisory organization on the same date but is not a reorganization event
Organization Availability Date
- Defaults as Reorganization Event date when an organization is created; can be updated to an earlier date
- Informational only – not used in any delivered validations
‒ Workers can be assigned to organizations prior to the availability date
- Custom validations can be written to prevent the organization from being used in a transaction with an earlier effective date
- If date validations are not going to be used, consider always using reorganization with an effective date of 01/01/1900 to prevent confusion.
Visibility
- Visibility setting on an organization controls who can view details and members of an organization
- Everyone
- Role Assignees
- Role Assignees and Members
- Role Assignees of Current and Superiors
- Visibility is inherited from the superior organization and cannot be updated on subordinate organizations.
Supervisory Organizations
- Are required and critically important to HCM – all workers are hired into a Supervisory Org
- Group workers into a management hierarchy to specify who reports to whom
- Supervisory Organizations report to one another to form the Supervisory Organization Hierarchy
- Each Supervisory Organization has one and only one superior (parent) organization
- Provide the context for staffing actions
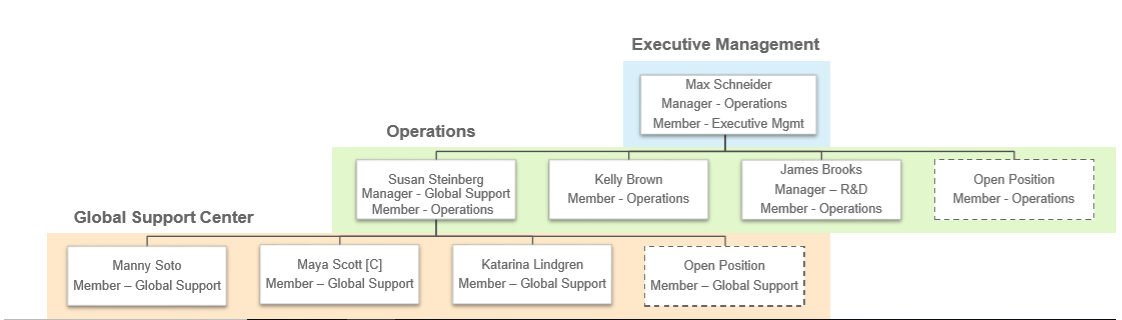
- Each worker is a member of a Supervisory Organization
- A Manager (role) is assigned to a Supervisory Organization, or may be inherited from a superior organization
- A Manager is NOT a member of the organization(s) they manage
Locations & Location Hierarchies
Location
Locations are used to track business assets and physical work spaces
- Locations are also used to default data values, prompts, date formats, and time zones
- Each location is configured with one or more delivered ‘usages’ types
‒ E.g., Business Asset, Business Site, Campus, Par Location, Work Space, Payroll Tax
- Every position or job must be assigned to a Location with ‘Business Site’ usage
- A location may roll up to another location
Locale
Enables control of display of multinational date, time, and number formats
- To determine a self-service user’s language display, Workday evaluates (in this order):
- User’s language (user preferences)
- User’s locale (user preferences)
- User’s Location language
- User’s Location Locale
- Tenant’s language
- Tenant’s Locale (the default is US English)
- Specify Locale for each business site (worker location)
Work Space
- A work space is mapped to a location and allows for more granular location tracking, like building, suite, cubicle, etc.
- Work space levels are hierarchical (up to 10 levels) and must roll up to a ‘Business Site’ type of Location
- Optional configuration based on customer requirements
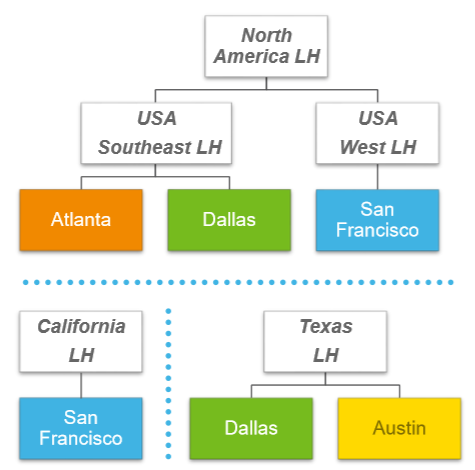
Location Hierarchy
- A rollup of ‘included’ locations
- Often used to define geographical regions for regulatory reporting
- Often used for security role assignments (not enabled directly on locations)
- A location can belong to more than one location hierarchy but only once within an individual location hierarchy
- Workers are dynamically included as members of a location hierarchy based on the location their location assignment
Costing Organizations
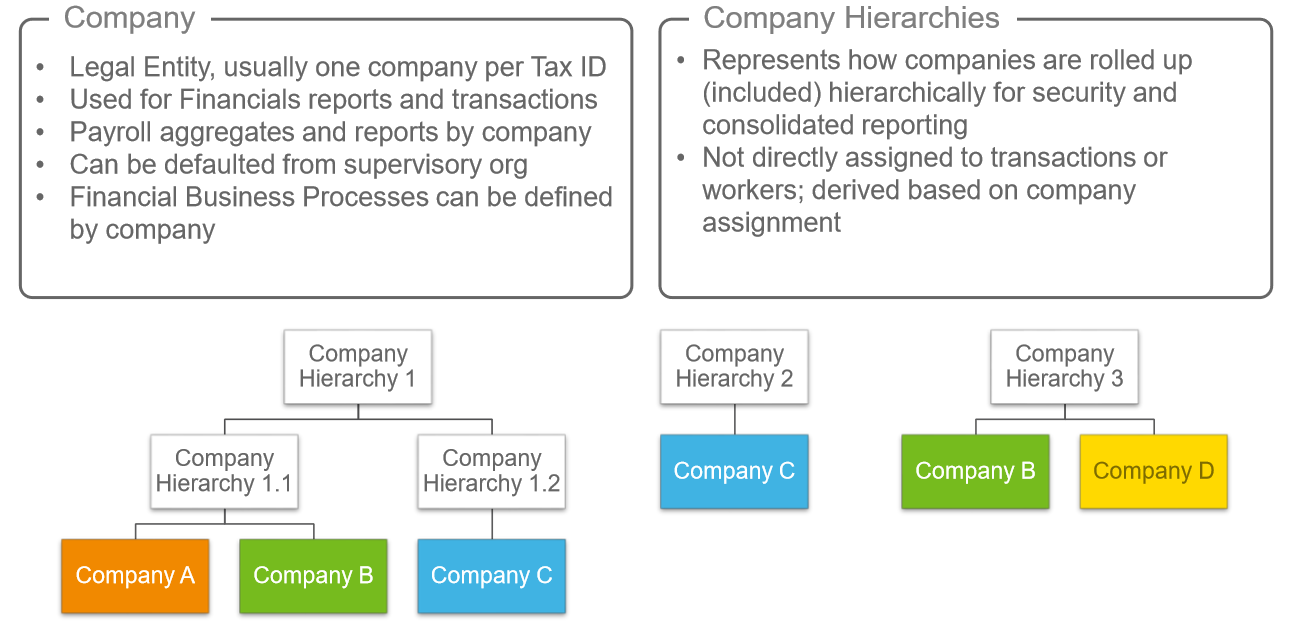
Company & Company Hierarchies
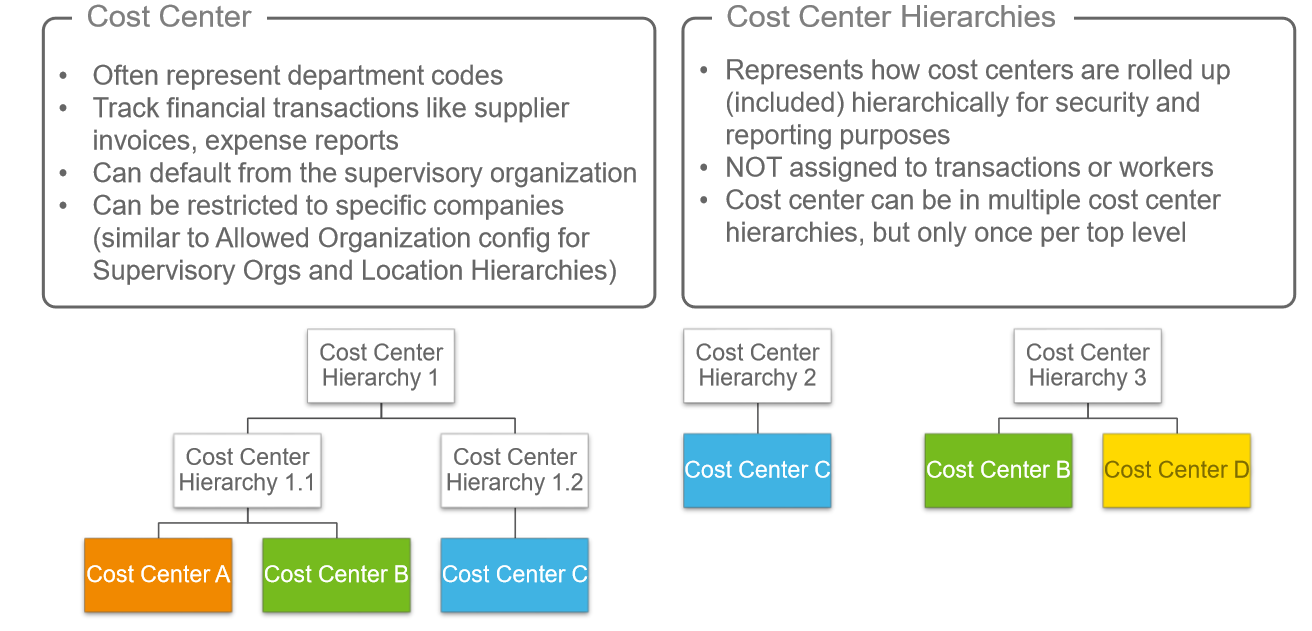
Cost Centre & Cost Centre Hierarchies
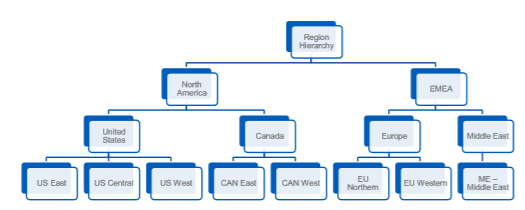
Region & Region Hierarchies
- Optional – Reflect area of responsibility rather than physical work location.
- Regions can be rolled up into Region Hierarchies, often used to track geographic or sales region.
- Often used to facilitate financial reporting; can be used to attribute cost or revenue separately from where it originated ‒ For example, a worker in a U.S. location who supports the UK office can have their costs tagged to a UK region.
- Generally, not used HCM-only purposes.
Optional HR Organizations
Matrix Organizations
- Reflect dotted-line relationships to a second manager
- Are non-hierarchical and are not related to a supervisory organization
- Workers are manually assigned to a matrix organization
- Matrix relationships are reflected in organization charts
- Can be used in eligibility rules and conditional logic across the application
- The Matrix Manager might be given security to: ‒ View a member’s compensation, past jobs, skills and experience, time off and leave and worker history ‒ Participate in processes related to the matrix members
Retiree Organizations
- Used for grouping terminated workers who have retired
- Commonly used in benefit eligibility rules and conditional logic across the application
- Retiree organizations can be hierarchical (roll up to another Retiree organization)
- Retiree status is assigned to the worker using the Assign Retiree Status business process and a termination reason code identified as a retiree reason
Other Organization Types
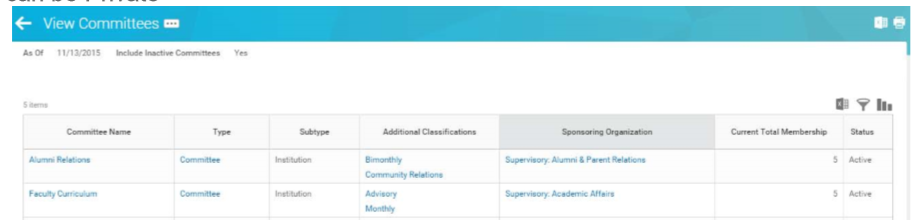
Committees and Committee Hierarchies
Allow you to track committee types, committee classifications, committee classification groups, committees, membership types, membership type targets, members, inviting committee candidates, meetings, agendas, and record votes.
- Committee membership is assigned to workers, Academic Affiliates and External Committee Members
- Committees can be sponsored by Supervisory Orgs, Companies, Grants or Academic Units, Search – Job Requisition
- Committees can be grouped in hierarchies
- Committees can be Private
Unions
- Allow you to track unions and their members
- Workers are assigned to Unions
- Can be used in eligibility rules and conditional logic across the application
Custom Organizations
- Like other organization types, these are used to group workers for: ‒ Reporting ‒ Costing ‒ Eligibility ‒ Business Process condition rules ‒ Security
- Unlike other organization types, membership rules may be created and used to assign groups of workers to custom organizations based on certain criteria
Custom Org Common Use Cases
Acquisitions
- Workers in the acquired company have special compensation or benefits eligibility
Planning and Budgeting
- Headcount / worker spend based on org type relevant to your organization
Rollups of other org types
- Pay groups for external payroll vendors
- Matrix orgs
Other custom org types
- Exclude workers from view
- Hide workers from self-service view (FERPA, under-cover workers, etc.)
Payroll Organizations
Pay Groups
Logical grouping of employees for payroll processing
- Note: Payroll journals are created based on Company, not pay group
- Determine pay frequency and pay schedule
- Used to facilitate security for payroll purposes
For example, a de-centralized payroll department may have multiple pay groups in order to secure employees for payroll purposes
Worktag Introduction
Used to “tag” transactions for reporting and analysis purposes
- Key words, or tags, that can be reported upon within the system
Found in:
- Financial transactions
- Payroll
- Time tracking
- Academic period pays
- Budgeting and workforce planning
- Closely linked to worker organization assignments
- Organizations can default from worker organization assignments to be used as worktags for reporting purposes
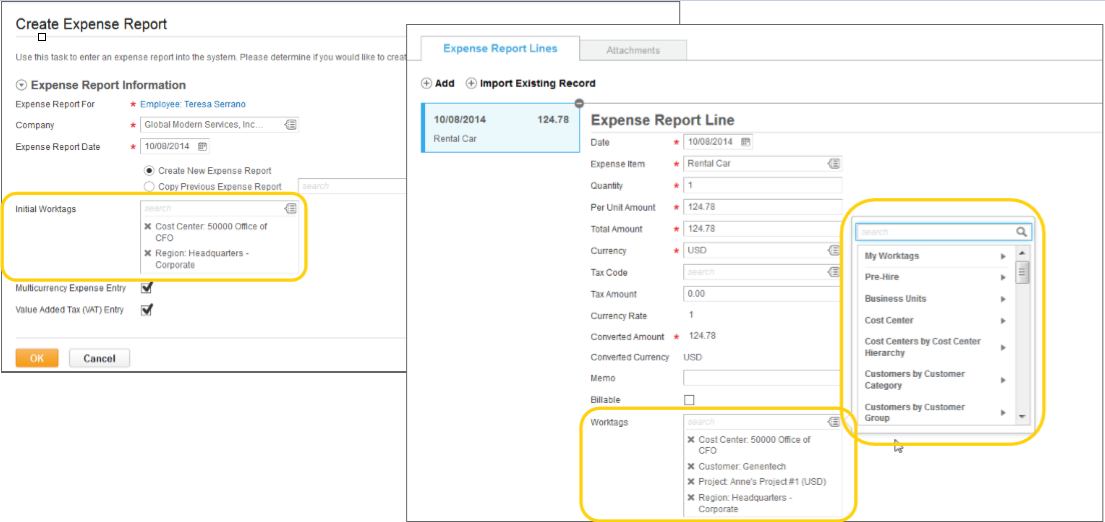
Organization Assignments Worktags

Organizations as Worktags: Expense Report Example
Staffing Models in Workday
Staffing models in Workday are the tools and capabilities in the HCM system that help firms plan, manage, and monitor their workforce. These models help companies make hiring, training, and personnel management decisions by providing a complete workforce view.
Conclusion: I hope with this above information you will get the idea about organisation design in workday.

Rajesh
Author
