SAP PMGM training
Goal Management in SAP PMGM
Goal Management in SAP PMGM exists to ensure all employees are aligned and focused on what matters. SAP PMGM helps organisations set, track, and measure goals more efficiently.
SAP PMGM stands out with its goal library, which contains over 500 SMART goals – these goals being Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic, and Time-sensitive.
They are designed for specific business situations and timescales. SAP PMGM uses this framework to ensure goal clarity and accountability.
SAP PMGM, its potential to align employee performance with organisational strategy, became clear. Performance Management and Goal Management are designed to help employees work more efficiently and effectively, serving as a link between strategy implementation and execution, ensuring everyone moves in unison towards accomplishing organisational goals.
One key aspect of SAP PMGM was how easy goal setting can be with employees, thereby strengthening accountability while tracking performance.
If an employee meets their goal, it shows progression; otherwise, it highlights areas for improvement – all this takes just minutes per employee.
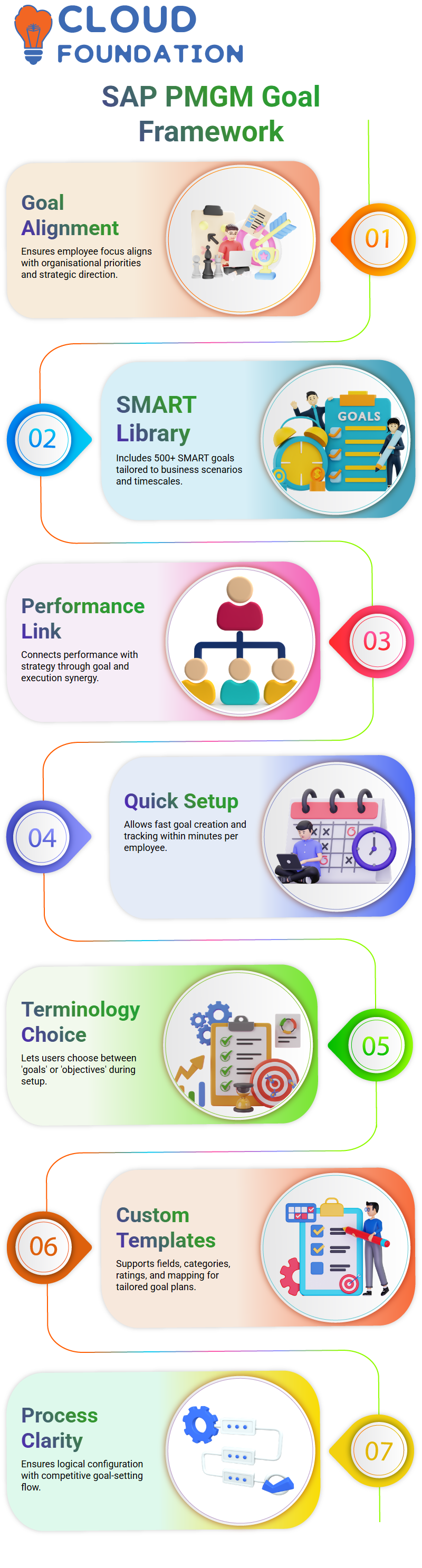
SAP PMGM uses both objectives and goals interchangeably when setting up systems. During implementation, customers select one term to use at setup; this choice can be later altered via provisioning settings.
Comprehensive Goal Management in SAP PMGM
During our session, we thoroughly explored goal creation in SAP PMGM.
We reviewed all available methods, including creating goals via provisioning or the front-end instance, as well as adding custom fields, categories, and ratings to templates. We then focused on discussing group mappings as a topic of interest.
SAP PMGM allows us to set meaningful goals. From setting field definitions to configuring categories, every step strengthens the goal-setting process. Furthermore, competition tools provided a logical and practical flow.
SAP PMGM Components and Goal Planning
SAP PMGM includes many components, and one of its core elements is its goal plan. Think of this tool as an online worksheet similar to Excel sheets where goals are created, managed, and tracked throughout the year. Since performance evaluation occurs over time, this device helps keep everything organised and under control.
Different clients utilise SAP PMGM differently; some conduct performance cycles twice annually, while others do so only once, depending on their requirements and company culture.
When asked in interviews how often performance cycles occur, my answer consistently returns to client needs.
SAP PMGM supports multiple goals, including organisational, business, and personal objectives.
Organisational goals typically apply across all employees of an organisation and are established by it; their achievements depend on team effort; no single employee can accomplish them alone – everyone plays their part in reaching these objectives.
SAP PMGM Goal Creation and Goal Plan Management
Setting goals in SAP PMGM is a crucial first step. When setting your first goal in the system, you are laying the foundation for efficient performance tracking and goal management. In SAP PMGM, you can delete goals that no longer serve their intended purpose. This way, you ensure that all goals in the plan align meaningfully.
SAP PMGM Goal Plans
At SAP PMGM, we must recognise the significance of goal plans. Every organisation operates under different business rules, which determine how we configure SAP PMGM goal templates.
Therefore, ensure that each employee receives one explicitly tailored to meet organisational priorities.
SAP PMGM enables us to easily create multiple goal plan templates, allowing clients to activate numerous plans throughout the year.
This often involves copying goals between plans for consistency purposes. Furthermore, these highly flexible templates can easily be tailored by consultants as necessary.
SAP PMGM Goal Templates and Categories
SAP PMGM configurations begin by emphasising goal categories. Each goal must fall under at least one category whether business, personal, or organisational so choosing them is user-friendly and straightforward through dropdown menus in SAP PMGM.
SAP PMGM enables organisations to easily define essential fields, such as goal name, start and end dates, status, and visibility, to track progress effectively.
Every SAP PMGM goal template supports multiple categories to maximise adaptability without restricting business operations.
Smart Goals Inside SAP PMGM
Setting practical objectives within SAP PMGM involves setting SMART goals. These specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time-specific objectives allow employees to clearly and precisely express their desires—an invaluable feature.

SAP PMGM supports up to 100 such objectives, allowing employees to outline their aspirations with clarity and precision, while always emphasising the importance of these goals in creating tangible success within an SAP PMGM environment.
Private and Public Goals in SAP PMGM
SAP PMGM handles private and public goals differently. A private goal, created by an employee and accessible only to them or someone with proxy access, such as an admin, remains private.
In contrast, public goals can be viewed by all within an organisation, making this distinction in SAP PMGM essential for maintaining visibility and collaboration around objectives.
Managing Private and Public Goals in SAP PMGM
SAP PMGM gives users the power to set goals either privately or publicly. These options often remain within an employee’s own space, although managers may still view some, depending on permission settings.
Public goals, however, can be seen by a wider audience if granted access.
SAP PMGM enables employees to adjust visibility settings at any time, whether creating or reviewing goals, to ensure privacy or facilitate collaboration as needed.
Goal Visibility and Sharing in SAP PMGM
Your visibility may be considered as part of SAP PMGM goal-sharing features; public goals are visible to all, while private goals require explicit sharing permissions from their owner(s).
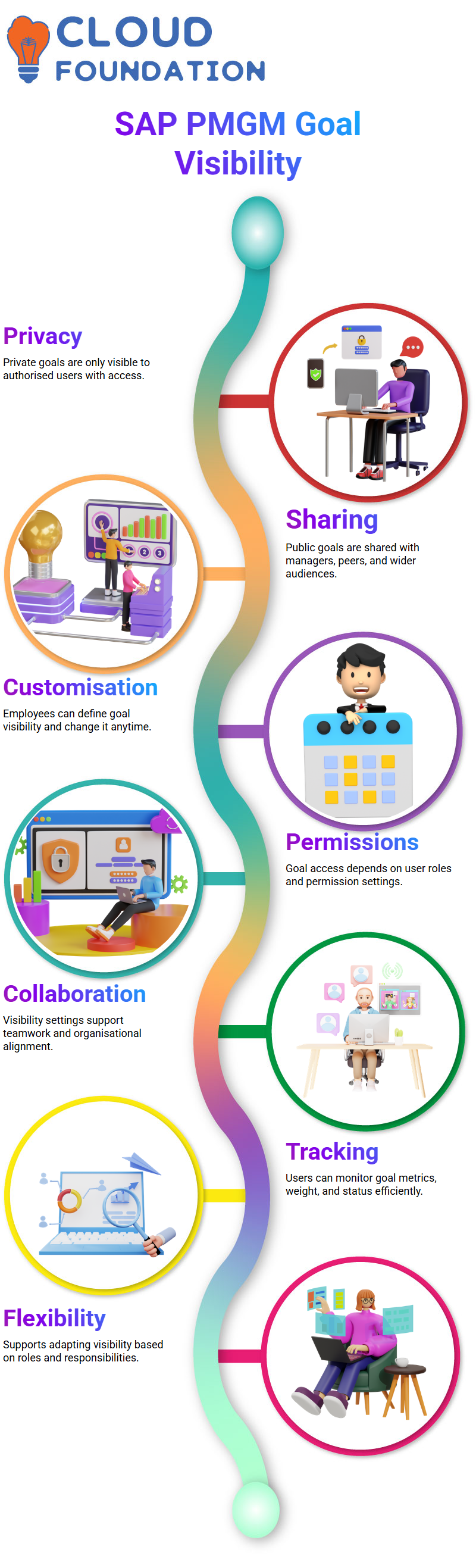
This ensures information security while also supporting collaboration when necessary.
Goal Visibility and Customisation in SAP PMGM
SAP PMGM allows employees to categorise goals as either public or private. Public goals are visible to managers, colleagues, and peers, while private goals are only visible to employees and specific administrators with special access permissions.
It is vitally important to distinguish between private and public goals. The latter allows all authorised personnel access, whereas with private goals, only those authorised can view it.
With public goals, anyone in your organisation will see your efforts. SAP PMGM provides you with the flexibility to choose what is most suitable for you, based on your role and responsibilities.
Employees can track goal metrics, weight, and status using SAP PMGM. With customer-specific fields designed to keep employees on target without missing deadlines, this comprehensive tool supports both transparency and privacy.
Managing Private and Public Goals in SAP PMGM
SAP PMGM gives users the power to set goals either privately or publicly.
These options often remain within an employee’s own space, although managers may still view some, depending on permission settings. Public goals, however, can be seen by a wider audience if granted access.
SAP PMGM enables employees to adjust visibility settings at any time, whether creating or reviewing goals, to ensure privacy or facilitate collaboration as needed.
Goal Visibility and Sharing in SAP PMGM
Your visibility may be considered as part of SAP PMGM goal-sharing features; public goals are visible to all, while private goals require explicit sharing permissions from their owner(s).
This ensures information security while also supporting collaboration when necessary.
Goal Visibility and Customisation in SAP PMGM
SAP PMGM allows employees to categorise goals as either public or private. Public goals are visible to managers, colleagues, and peers, while private goals are only visible to employees and specific administrators with special access permissions.
It is vitally important to distinguish between private and public goals. The latter allows all authorised personnel access, whereas with private goals, only those authorised can view it.
With public goals, anyone in your organisation will see your efforts. SAP PMGM provides you with the flexibility to choose what is most suitable for you, based on your role and responsibilities.
Employees can track goal metrics, weight, and status using SAP PMGM. With customer-specific fields designed to keep employees on target without missing deadlines, this comprehensive tool supports both transparency and privacy.
Goal Permissions in SAP PMGM
Configuring goal permissions in SAP PMGM is of utmost importance and relies on role-based settings, XML templates and system tools for access management purposes.
Assist clients with configuring SAP PMGM according to their industry, culture, and governance standards when providing advice about its configuration.
A financial institution may require more stringent privacy controls, while an IT firm may prefer an open environment for sharing goals and information.
SAP PMGM Permissions and Role-Based Access
Permissions play an instrumental role in SAP PMGM. There are two principal permission types: template-level (managed with XML files) and instance-level (controlled via role assignments), designed to protect sensitive information while allowing authorised personnel to make updates.
SAP PMGM ensures sensitive data remains safe from prying eyes while permitting those responsible to make necessary updates quickly and securely.
SAP PMGM role codes, such as E (for Employee) or EM (for Employee Manager), provide access control, delineating who is accountable for setting, reviewing, and approving goals, ensuring everything is managed responsibly.
Proxy Access in SAP PMGM
SAP PMGM enables super admins to fill the role of unavailable individuals when urgent matters need attention, through proxy access.
While managers or employees usually cannot act in this capacity for others, super admins possess this unique power.
With SAP PMGM’s proxy functionality, continuity is guaranteed: no longer do essential tasks have to be put off because someone is out. Our workflow remains efficient and accountable!
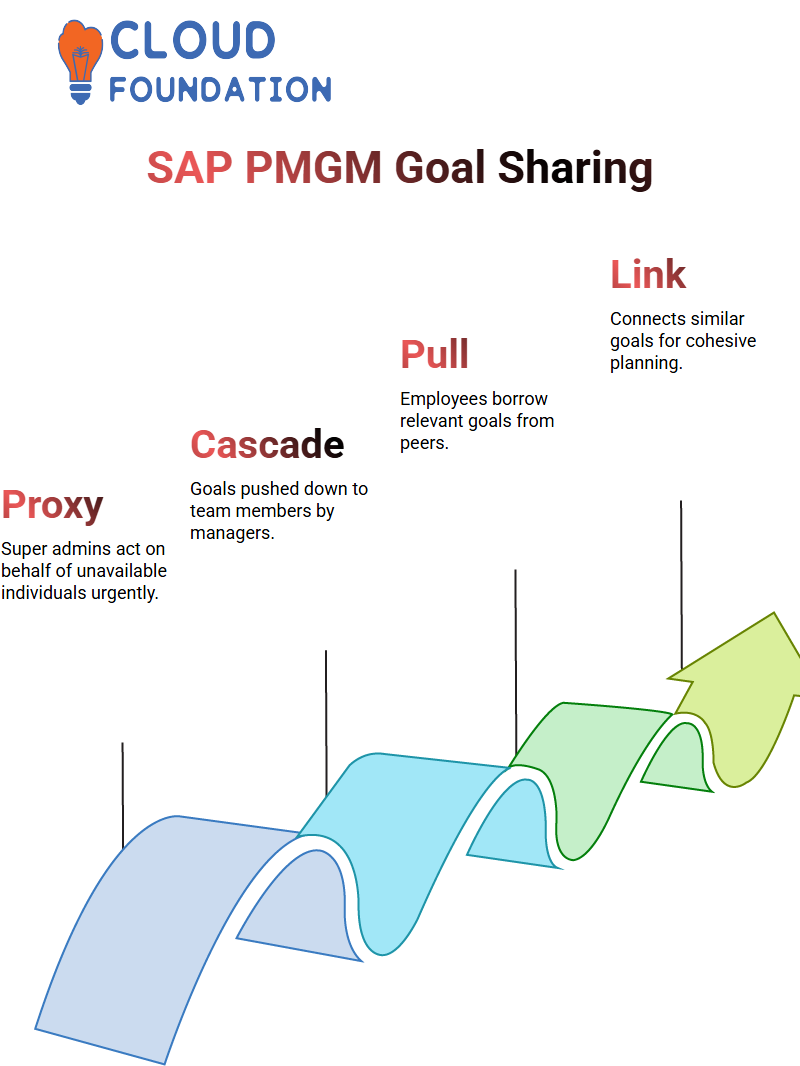
Understanding Cascade, Push, Pull, and Alignment in SAP PMGM
SAP PMGM stands out with its innovative goal-cascading functionality. Cascade Push allows sending goals downward through an organisational structure for instance, from managers to team members — while Pull will enable employees to borrow relevant goals from peers.
SAP PMGM calls these borrowed goals ‘Cascade Capable,’ which simplifies alignment while building out goal networks within the platform.
Goal alignment within SAP PMGM encourages collaboration across departments. When you align goals in any of the available ways—cascading, pushing back, pulling, or directly linking you create an atmosphere in which personal objectives seamlessly align with organisational strategy.
Furthermore, SAP PMGM enables you to link two existing goals that share similar activities, creating a cohesive goal-setting experience.
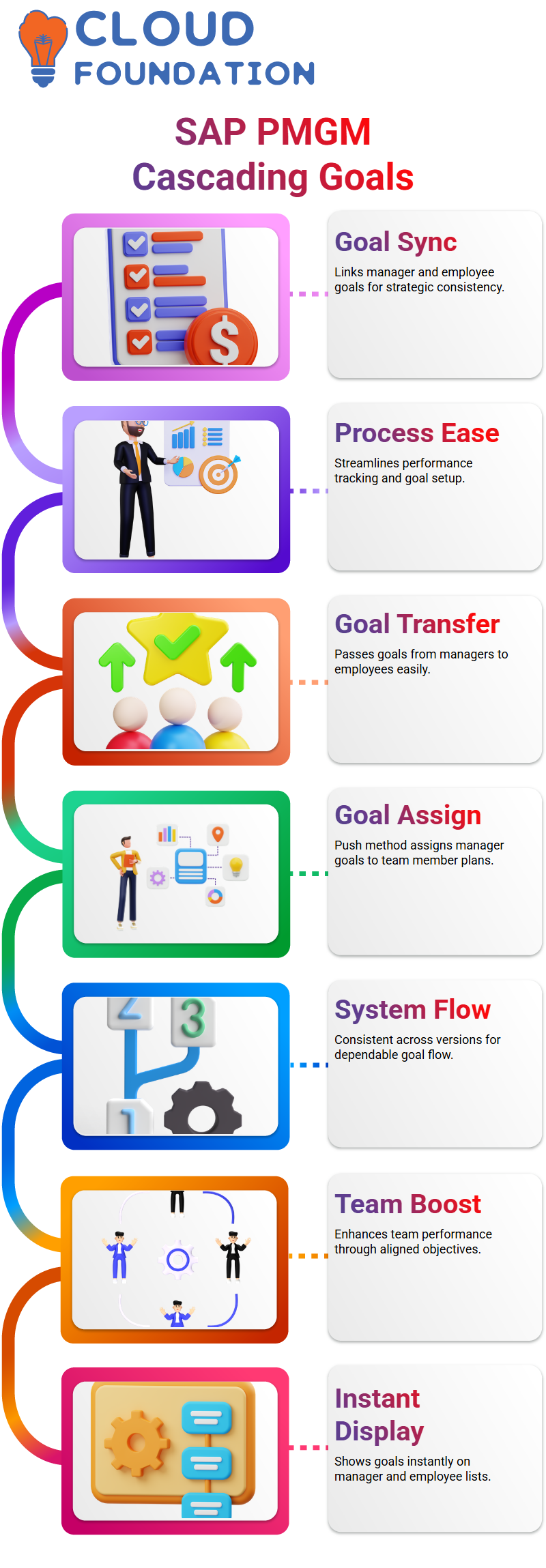
Cascading Goals in SAP PMGM
SAP PMGM, one of the first things that quickly became clear was how cascading goals streamline alignment between managers and employees.
A manager only needs to open SAP PMGM, select their goal, select their employee(s), click the source link, confirm it matches, click ‘Cascade Successfully’, and it will appear on both goal lists instantly in SAP PMGM.
SAP PMGM makes my work smoother by prompting me if my assignment doesn’t meet relevant standards, which makes tracking performance more accurate and easier for all involved.
Cascade Push in SAP PMGM
Once began exploring SAP PMGM, the Cascade Push method stood out immediately. Imagine that Mona wants to pass down her goals to employee Edward.
She logs into SAP PMGM, selects her goal(s), clicks the cascade button, and confirms the action. The system displays the goal in Edward’s plan as a newly aligned goal.
SAP PMGM interface may differ between versions, yet its process remains constant. As soon as Mona completes her cascade push, Edward’s goal plan now incorporates Mona’s objectives for team consistency and productivity.
Cascading goals is an invaluable way to translate organisational strategy into actionable team-level goals, leveraging SAP PMGM’s intuitive software platform and providing visibility across goal hierarchies.
Cascade Pull Works in SAP PMGM
Cascade Pull can have a significant impact on SAP PMGM. Imagine Mona’s scenario. She wants to pull one goal from Donna, her director.
To accomplish this task, Mona uses an employee search that even detects inactive users to locate Donna’s goals and retrieves them.
SAP PMGM prompts Mona to confirm this action; once complete, Mona’s goal plan will be updated with Donna’s goal, allowing editing or modification as per the permissions granted by SAP PMGM.
 SAP PMGM makes it simpler for all levels to align upward or across hierarchies and encourages strategic ownership across the entirety.
SAP PMGM makes it simpler for all levels to align upward or across hierarchies and encourages strategic ownership across the entirety.
Linking Goals with SAP PMGM Cascade Align
SAP PMGM goes beyond cascading; it also lets users link goals. Witnessed Edward linking his goal with Amy’s on a similar project using the Cascade Align feature of SAP PMGM; by using Amy’s goals, he successfully established their connection and linked them.
After linking, Edward and Amy could see their shared goal path on their goal plans. SAP PMGM empowers teams by improving collaboration across departments working on related initiatives.
SAP PMGM linking capabilities enable goals not to remain isolated; when working across reporting lines with different peers, linking provides transparency and context as to why each objective matters.
Goal Relationships in SAP PMGM
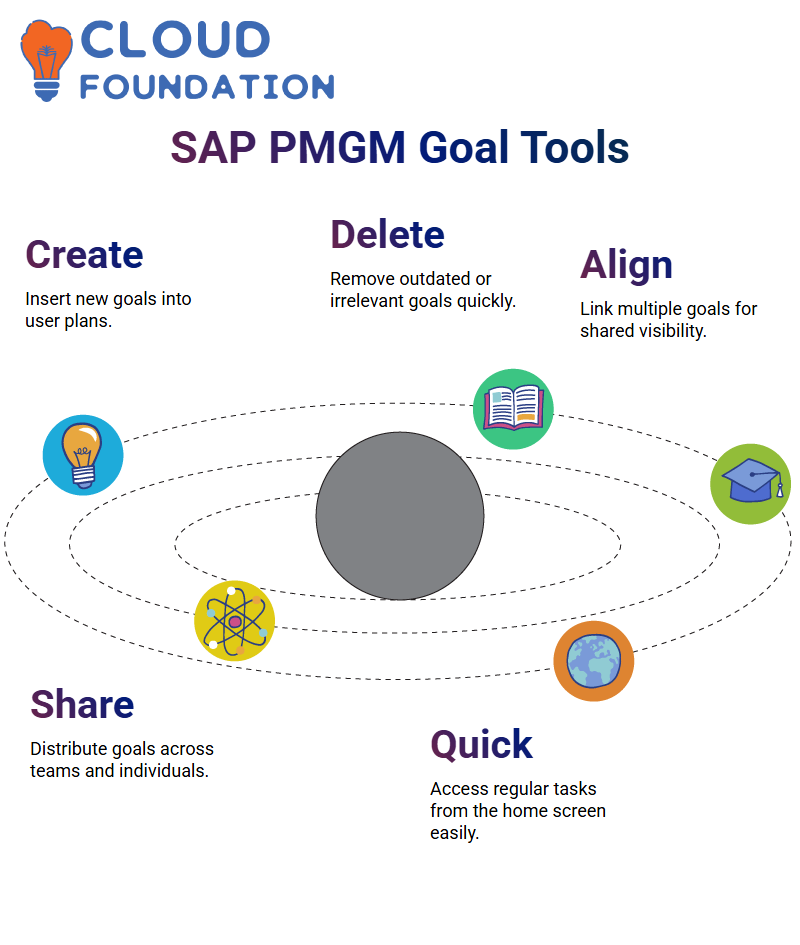
Within SAP PMGM’s interface, you will encounter action buttons such as Create, Delete, Align, and Share, which enable users to insert new goals, remove outdated ones, or link multiple goals together.
SAP PMGM also features a parent-child goal structure, where one main goal branches out into subgoals for easy viewing by teams. Teams can see where individual efforts fit into this larger picture.
SAP PMGM Team Goals
SAP PMGM facilitates team goals across departments or project groups working toward common objectives.
For example, if finance, marketing, and accounting departments each employ 20 workers on similar tasks that require aligned efforts across departments, then assign team goals via SAP PMGM so that all efforts align in harmony.
Goal management across departments and team cohesion are optimised using this method.
Quick Actions in SAP PMGM
Often use quick actions in SAP PMGM for shortcuts to tasks that are performed regularly. These aren’t editable by employees they’re set up in advance by SAP PMGM super admins based on what our organisation needs.
This design makes SAP PMGM’s home screen both flexible and focused. Without digging deep into the navigation, you can find what you need in just a click or two, which is particularly helpful on busy days.
Goal Management Features in SAP PMGM
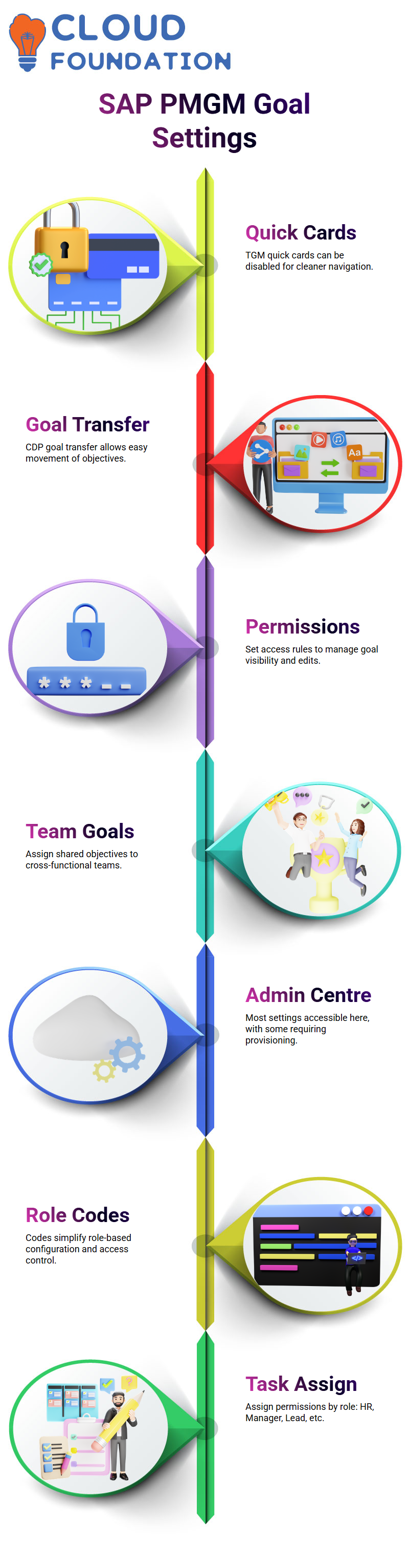
SAP PMGM offers an array of goal management features. Some key settings for goal administration include disabling TGM quick cards, enabling CDP goal transfer, and setting permission controls to manage goal access.
Other features include supporting large target populations, team goals and initiatives – each setting can be toggled on or off depending on organisational needs.
SAP PMGM makes these features accessible through an Admin Centre; however, some features require provisioning access. Because working in a demo system, could only explore instance-level settings.
Breaking Down Roles in SAP PMGM
As part of your SAP PMGM configuration process, pay particular attention to roles. Typical examples include employees, HR representatives, Managers, Project Leads, and even Matrix Managers each role affects what can or cannot be seen inside SAP PMGM.
SAP PMGM makes role-based configuration seamless by offering role codes such as EMM (Employee Manager’s Manager) or ED (Employee Direct Report). Can assign tasks and permissions logically and efficiently using SAP PMGM.
SAP PMGM Integration and Performance Tracking
SAP PMGM stands out with its integration capabilities. It easily syncs with Microsoft tools like Outlook and Teams, helping me stay organised by providing direct access to calendar events through SAP PMGM, keeping my schedule intact.
SAP PMGM supports both internal and external integrations. Internal connections occur within SuccessFactors modules, while external connections link to third-party tools.
Data from Employee Central can potentially flow into other modules, ensuring consistency throughout the platform.
 SAP PMGM makes managing performance data exceptionally straightforward: all pertinent information is readily available and up-to-date, facilitating progress evaluation and enabling informed decisions to be made more quickly.
SAP PMGM makes managing performance data exceptionally straightforward: all pertinent information is readily available and up-to-date, facilitating progress evaluation and enabling informed decisions to be made more quickly.
SAP PMGM and Goal Execution
Goal execution is where SAP PMGM excels. Managers assign goals to team members and track their progress toward these goals using this system; regular monitoring is carried out through structured follow-up.
By setting goals together and understanding everyone’s role in meeting them, this helps ensure successful goal achievement.
SAP PMGM: Uploading and Verifying Goal Data
Once your CSV file is complete, upload it back into SAP PMGM using the import section and select it to initiate the upload.
Once the upload is completed, SAP confirms and schedules the processing of data within 24 hours; you should receive an email alert once the process is complete.

Sometimes changes appear immediately; other times, it takes longer. Check back with SAP PMGM’s goal section periodically until your new goal has been added; once complete, the goal should appear under its appropriate category for tracking and evaluation purposes.
Release Cycles and Feature Updates in SAP PMGM
On an annual basis, SAP releases updates that may include feature enhancements or retirements for their PMGM release cycles typically in April and October during which users can submit enhancement requests.
If enough customers request changes simultaneously, SAP could remove or enhance an important feature altogether.
Therefore, it’s vitally important that users remain up-to-date with SAP PMGM release notes, as you never know when something you rely on will get discontinued.

Vinitha Indhukuri
Author



