SailPoint Task Management Tutorial
Tasks in SailPoint
SailPoint has the practicality to merge multiple account aggregations and administer them in sequence through a series of tasks. For a task that requires daily performance, we can establish a run-to-rule task to achieve it.
To move items from one SailPoint illustration to another, we use specific tasks. Nonetheless, instead of relying on the default data export task, we are the ones who carry out the installation of the required plugin and, ultimately, export the data.
SailPoint Task Scheduling
We discussed creating and running usage tasks in SailPoint over the past 24 hours. Today, we will discuss how to monitor and schedule these tasks instantly. To meet the duration and frequency of any job, we can use the cron parameters.
In SailPoint, we can perform various tasks, such as creating communication groups, identity refresh tasks, and providing certification support. Additionally, we can modify our functions as needed and run them as required.
When we have already made sequential tasks in SailPoint, our concern now is how to schedule them to get executed automatically. For illustration, if we want a sequential account aggregation task to run daily, we can set up its schedule.
The initial step in creating a scheduled task in SailPoint involves selecting the frequency of execution—daily, weekly, or monthly. It is unnecessary to schedule the task if it only needs to be run once.
SailPoint organises tasks into three categories: task definitions, task results, and scheduled tasks. Task definitions retain all the tasks created and thus are the repository.
Task results save the outcome of the task’s execution. If a task is not responded to and remains in a hung state, we can only delete it from the task results table, not from task definitions, so that we can guarantee the normal functioning of the system.
SailPoint Task Execution
What about the situation when you are required to perform a SailPoint task immediately, without waiting for it to be scheduled? The good news is that it is feasible.
While you run a task in SailPoint, a scheduled execution time is visible. If you wish to initiate it without expanded delay, then you just need to delete the ‘subsequent execution’ value from the object. Once this is done, SailPoint proceeds with the task and completes it instantly.
Setting Up Scheduled Tasks in SailPoint
Executing scheduled tasks in SailPoint involves determining the time frequency and the server on which the job will run. If a clear-cut server is to be executed in, we shall provide the host.
It is essential to have a backup server in case the primary server goes down, so that scheduled tasks are not disrupted, which ultimately helps prevent disruptions.
SailPoint Cron Expressions
To schedule a task in an exact manner in SailPoint, we will use cron expressions. A business may use the cron expression to describe a time pattern that can produce a task every five minutes.
If we decide to change the cron expression of a scheduled job in SailPoint, then the task will be run according to the frequency set in the new cron expression.
If in doubt, we can utilise online cron makers to obtain the correct expressions.
SailPoint Cron Expression Management
When setting up tasks in SailPoint, key factors to consider include execution frequency, server availability, and cron expressions.
Schedules with distinct deadlines will help us achieve the best results from our identity management operations.
SailPoint confirms the uninterrupted execution of the system by creating and running a configuration check, which is central to our duty management strategy, as it enhances the system’s capability and predictability.
Scheduling and Surveillance in SailPoint
SailPoint has made scheduling tasks so manageable that they appear effortless. You may want to certify and schedule reports to run automatically; doing so will make everything more expedient.
What happens if a task does not end up being a success? One essential aspect of every finished or failed task is knowing the outcome. For a few tasks, manual checks can be easily performed, but in a real-world environment, those implementing the system need to run thousands of functions every day. By leveraging SailPoint’s database queries, you can simultaneously retrieve failure data and other relevant information.
(It should be a techy term to call a person who gives a system a concrete action, and I don’t remember this word or phrase in tech.) Similarly, all your troubles can be fixed with the aid of writing DB concerns.
SailPoint Entitlements and Group Aggregation
Entitlements make a central focus of the SailPoint application, especially in the context of the integration with Active Directory. I assign users’ entitlements, provided their security groups remain intact.
You can opt for a more resourceful approach to leveraging group aggregation functionality, rather than manually creating entitlements.
SailPoint products clone Active Directory’s defined security groups, allowing them to be easily imported in bulk.
Before I kick off anything, I always check the connections. If something goes wrong in the first place, the collection will refuse to be completed. After running a test connection, I can be assured that there will be no follow-up issues.
Configuration in SailPoint
Exemplary configurations are the make-or-break element in SailPoint. Without them, neither entitlement aggregations nor group aggregations will be executed properly. Therefore, I must ensure the details are described explicitly.
Both tasks are required for the development of Active Directory. It is essential to settle the domain name (DN) of a group when integrating with Active Directory in SailPoint. Additionally, if SailPoint brings groups into reflection, explicit configuration ensures the accuracy.
I have conducted numerous experiments, and I can confirm that missed configurations can lead to unexpected results.
To ensure a smooth SailPoint implementation, being well-versed in settings is a crucial element.
SailPoint Recovery Steps
Once the process is killed, the right way to start over with the SailPoint is very required Though some people might be influenced and try reinstallation, doing so is not required at all and even brings several problems to the users So I do this first thing: I launch the start service file or run a terminal command.
When I want to establish that SailPoint is operational, I usually do that through localhost or another defined monitoring method. If I encounter issues, I know that there is still a lot of troubleshooting before
Moreover, a critical issue is preventing Java from updating automatically.
The spontaneous updating of Java can cause severe damage to the regular operation of SailPoint, which is why this is a production environment, and Java configurations must be locked.
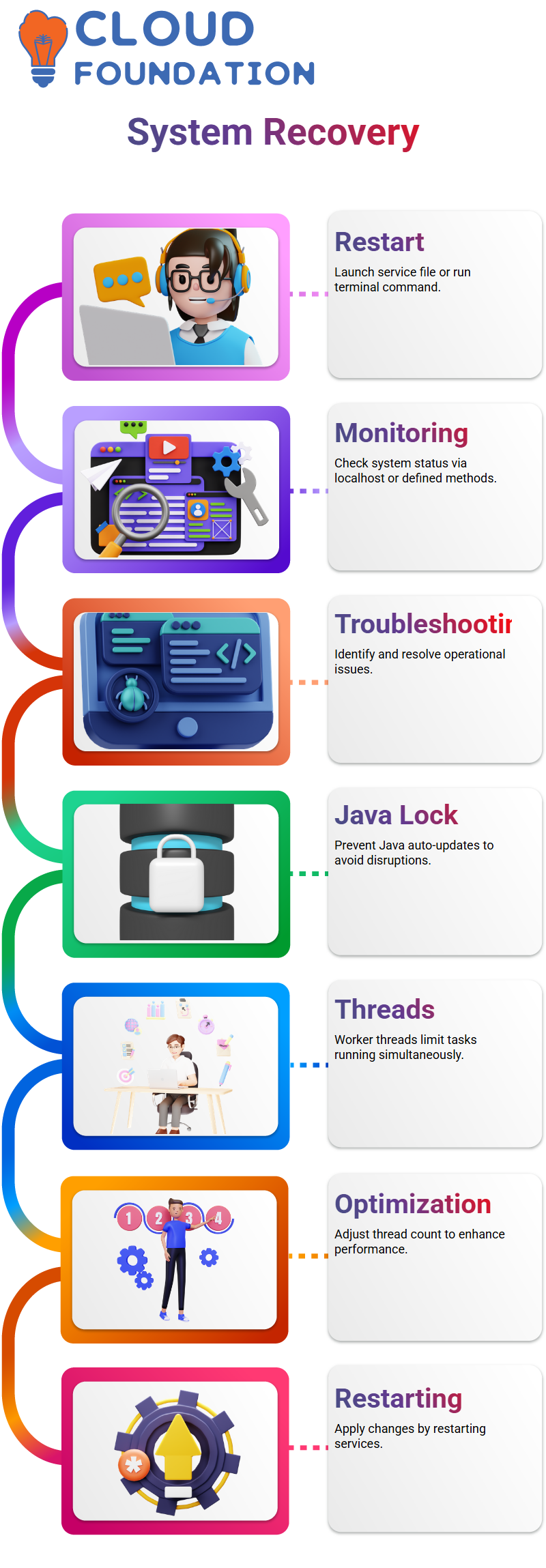
Worker Threads in SailPoint
Do you ever wonder why it takes a lot of time for one task in SailPoint? The primary reason for the task’s prolonged duration lies in the worker threads. For each task, a worker thread is assigned by SailPoint to execute the task’s execution. If we have only five worker threads, only a maximum of five tasks can be done at one time, while the others are in the waiting list.
Therefore, running additional worker threads simultaneously is the best action you can take.
You can tune this in the SailPoint identity properties file by changing the values, and then you can further optimise performance by restarting services.
SailPoint and Server Issues
Have you ever experienced a situation or problem where SailPoint unexpectedly stopped responding? You try clicking, but nothing happens.
The service appears to be stuck, and it seems as though no matter what you do, you’re unable to resolve the issue. I’ve been at that point, and the least I can say is that it is infuriating.
If such situations occur with SailPoint in a production environment, it is inappropriate to restart a server without first examining the process. Otherwise, I always verify the process. First, I open the Task Manager and then search for the SailPoint-related process to obtain its ID.
Every time the service runs, we find the most recent ID, so I\’m able to get that very one.
After procuring the process ID, manually stop the service. I use the Windows shell with administrative rights and type the command line to kill the process. However, if access is forbidden, I repeat the action after checking my permissions.
SailPoint Job Scheduling
One of the most significant challenges of executing SailPoint tasks is scheduling them at five-minute intervals. SailPoint provides a daily schedule, but planning your tasks to perform at five-minute intervals requires some methodical approach.
A case in point here is a management task that is supposed to be performed every five minutes. Through the availability of system threads, the frequency of execution can be planned and configured accordingly.

Navya Chandrika
Author



