Forgerock Authorisation and Identity Essentials
Resolving Authorisation and Token Issues with Forgerock
I attempted to reach the endpoint once again when I returned to Postman, but Forgerock promptly returned an error stating that the exchange token was invalid.
That informed me that there was a mistake in the request headers.
I then inserted the appropriate content-type after opening the headers tab.
I could plainly observe how Forgerock handled the call differently when I pushed the request button once again.
I have now verified the body, parameters, and authorisation one last time.
Although everything seemed to be in order, Forgerock still required a suitable redirect URI.

I returned to Forgerock’s Auth Provider settings, made the necessary changes, and saved them.
It was only after that that the registration process began to function as I had anticipated.
Using Forgerock to Create and Manage Clients
Every client in Forgerock requires distinct identifiers, and I constantly remind learners that the values they offer at the time of creation are important in the future.
As long as the request is legitimate, Forgerock automatically updates this information anytime you need to.
We can do the same process to clients who ask us how they may find their own application in ForgeRock.
Either they provide us with the necessary information, or we construct the client for them.
We return the client ID and client secret when the client has been formed.
Everything is logged by Forgerock, making it simple to follow up with each customer later.
Using Forgerock APIs to Read & Update Client Information
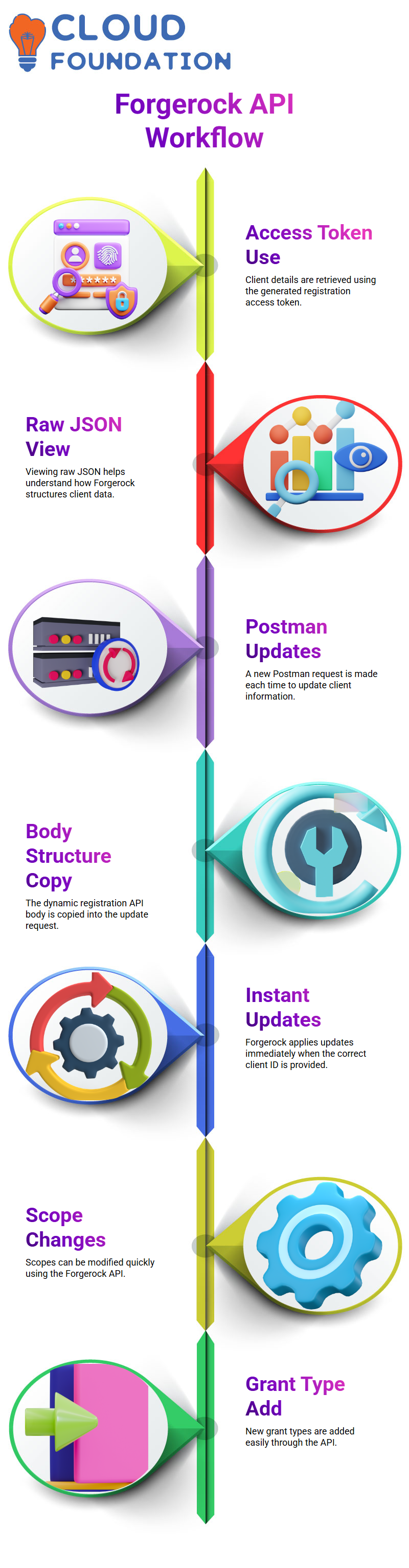
After I submitted the request, Forgerock provided me with all the client information I needed using the registration access token that it had produced.
You may better understand how Forgerock organises client data by seeing these variables in raw JSON.
I constantly make a fresh request in Postman to update a client.
I put the dynamic client registration API’s body structure into the update request after copying it.
Forgerock acknowledges the update and instantly applies it to the client when the right client ID has been entered.
For instance, I prefer to utilise the Forgerock API if I need to change scopes or add a new grant type since it’s quicker, clearer, and simpler to evaluate.

ForgeRock Training

Session Management, OIDC Claims, and Forgerock Scopes
I went back to the Forgerock interface and went through the advanced settings when the client upgrades were finished.
In order for Forgerock to save OpenID Connect sessions as part of the token system, I enabled session management.
When creating authentication processes, this feature, which allows you to reuse the ID token as an SSO token, is crucial.
Additionally, I added the OIDC claims script to Forgerock. You may alter the claims that are returned for each scope using this script.
Forgerock automatically adds the relevant claim values to the ID token or userinfo response when you add scopes like profile, phone, email, or address.
Every step of this claims process may be expanded, tailored, and improved using Forgerock.
When dealing with complicated applications that largely depend on identification traits, that flexibility becomes crucial.
Identity Federation and Advanced Forgerock Topics
SAML setup in ForgeRock entails establishing federation entities, identity providers, and service providers.
Cross-domain authentication is made available when SAML entities are added to Forgerock’s Circle of Trust.
Interviewers often inquire about how Forgerock manages the Circle of Trust, token issuance, client registration, and identity federation.
OIDC and SAML are both essential identification protocols within Forgerock.
For this reason, I ensure that each learner has immediate access to these functionalities in Forgerock.
You get the confidence to handle Forgerock integrations in the real world by continuously practising these operations.

ForgeRock Online Training

Forgerock Authorisation Flow
Once you see authorisation in action, you’ll learn why it seems so natural by relating each stage to actual situations, particularly those involving Forgerock.
Consider yourself the proprietor of the resource. You are at the centre of every system I teach, including Forgerock-based systems.
Before accessing your private information, the client application, such as a payment app, needs your consent.
I usually draw attention to this point because Forgerock emphasises user-controlled consent as a fundamental concept.
And I want you to see how effortlessly the flow occurs when you adopt this perspective.
Imagine now that the client is any third-party application that wants safe access.
Every time I use Forgerock to illustrate this in class, I explain how the client never obtains any data directly from you.
Rather, a structured authorisation request is sent.
The platform’s ability to maintain a clear division between user, client, and server is one of the reasons so many organisations have faith in Forgerock.
You determine whether the client’s request for your authorisation is sincere when they make it.
The system generates an authorisation grant after your approval.
This section is usually the turning point when the client obtains restricted and regulated authorisation, whether I’m utilising OAuth examples or showcasing an actual Forgerock setup.
ForgeRock Authorization Process
The authorisation grant is then sent to the authorisation server by the client.
The authorisation server reviews the grant, confirms the user’s identity, and determines if the request matches what you allowed in a lot of the configurations.
I teach, particularly those based on Forgerock Access Management.
One of the reasons I continue to suggest Forgerock in workplace learning sessions is this verification phase.
An access token is issued by the authorisation server if everything checks out.
To help students understand the hexadecimal-style structure, I often show a genuine token created in a ForgeRock test environment.
The token serves as a temporary credential, demonstrating the client’s entitlement to proceed without disclosing personal information.
The client contacts the resource server after obtaining the token.
To demonstrate that the fundamental reasoning is the same, I often switch between basic OAuth examples and a complete Forgerock implementation in our training lab.
Forgerock makes sure that the token specifies precisely what the client can and cannot access.
Regardless of whether the resource server contains balance data, profile information, or transaction history.
The resource server and authorisation server don’t have to be the same system, despite what many students believe.
Depending on how the company plans its surroundings, they may coexist or function independently in a Forgerock architecture.
I bring this up because, in my experience as a Forgerock solution instructor, flexibility is one of the main benefits.
I want you to look how the token moves through each system without disclosing raw credentials.
Whenever we try this flow in real-time practice, particularly with Forgerock Access Management.
One of the best things Forgerock teaches me is that authorisation should be strong but never invasive.

Vanitha
Author
