Amazon Web Services certification training
Understanding Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services (AWS)offers an effective way to manage cloud services efficiently. In today’s session, we explored how AWS facilitates global service management and resource allocation.
Amazon Web Services excels at offering scalable storage solutions; therefore, we explored S3 buckets as part of this investigation, where naming conventions play a crucial role.
However, due to its global operation, specific restrictions exist regarding how these buckets should be called.
Amazon Web Services stands out with its Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) feature, making instance creation and management an essential aspect of cloud computing.
During our session, we discussed region-specific configurations and best practices for launching instances via AWS.
Amazon Web Services’ IAM services ensure secure access control by offering Identity and Access Management (IAM).
Creating roles and permissions is integral when working with multiple users or services simultaneously; we discussed how best to configure IAM using Amazon Web Services efficiently.
Optimising services and understanding deployment strategies with Amazon Web Services becomes vitally important. We investigated various techniques for resource allocation and service integration using this cloud service provider.
Amazon Web Services remains one of the leading players in the cloud computing industry, making its features essential in improving productivity and streamlining processes.
At SCM Group, we collaborate with Amazon Web Services to refine our technical skills while expanding our skill set.
Amazon Web Services Cloud Solutions
Amazon Web Services (AWS), where we explore the power of cloud computing and how AWS services can help businesses maximise their potential.
Amazon Web Services offers an expansive suite of cloud solutions spanning storage to database management. In this session, we’ll focus on key elements, such as AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), Amazon S3, and security credentials, that make up this array.
Understanding IAM (Identity and Access Management) when working with Amazon Web Services is vitally important. IAM allows for the secure management of user permissions and policies across AWS accounts by configuring IAM settings accordingly, controlling access to resources while ensuring secure authentication of those accessing them.
Amazon S3, one of the most acclaimed services within Amazon Web Services. With it comes effortless data storage and retrieval; recently, we even created two buckets to demonstrate just how efficient Amazon Web Services storage management solutions can be used to meet organisational storage demands.
Amazon Web Services takes security extremely seriously. By configuring IAM policies, we establish security credentials, such as access keys and multi-factor authentication, that strengthen the defences of AWS accounts.
Utilising Amazon Web Services, we seamlessly tie policies to users and groups to provide controlled access, preventing unauthorised actions while safeguarding our cloud environment.
Amazon Web Services’ regions and availability zones allow administrators to distribute workload efficiently. When setting up AWS environments, choosing the optimal region ensures lower latency and enhanced performance.
Amazon Web Services also offers dynamic scalability capabilities. From managing databases with Amazon RDS or setting up computing resources with EC2, AWS ensures services scale dynamically.
IAM configurations to S3 storage, to better master cloud security and management. By practising these concepts, we hoped that cloud security and management would become second nature.
Understanding Amazon Web Services IAM
IAM users in Amazon Web Services (AWS). If you need help managing user access and permissions in AWS, this will serve as a great starting point for your journey.
Establishing an IAM user in Amazon Web Services begins by choosing whether they’ll have access to the AWS Management Console, which is an entirely optional step. Should they grant this privilege, they’ll be able to log in and interact with services accordingly.
Establishing an IAM user is straightforward. I navigate to the IAM section and click ‘Create User.’
When setting a password, I prefer creating my unique version rather than opting for autogenerated options; this ensures more control and security for my password.
Amazon Web Services provides users with the flexibility to change their password upon first login, although this is not always necessary.
If a user logs in with an assigned password, they will be prompted to update it based on predefined security settings. Grouping users on Amazon Web Services streamlines permission management.
Roles in Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services Roles allow for specific services to act on behalf of their users.
When creating roles in AWS, such as Amazon EC2, I choose the service and outline my trust policy with the necessary permissions.
Assigning roles ensures users can gain access to necessary resources without jeopardising security.
I select the necessary permissions, create custom policies for all relevant users, and apply these to Amazon Web Services to facilitate smooth navigation for users within the Service.
Managing Custom Policies in Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services facilitates the creation of tailored policies specifically to my requirements.
I create these by selecting appropriate permissions and assigning them to users while also ensuring proper enforcement of access controls. Once I create a policy, I attach it to user accounts to grant access.
Filtering policies ensure that only necessary permissions are assigned, protecting security while simultaneously increasing efficiency within Amazon Web Services.
Multi-Factor Authentication in Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services takes security very seriously, so adding multi-factor authentication (MFA) provides another layer of protection.
To set it up, I select my authentication method, such as an authenticator app, and follow the on-screen instructions to link my account.
Once Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) has been enabled, users must authenticate themselves using an authenticator app-generated one-time code for instant verification.
This helps prevent unauthorised access even if their password becomes compromised and prevents any potential abuse against Amazon Web Services.
Amazon Web Services Security
Maintaining security when working with Amazon Web Services is of utmost importance, especially when using RDS databases.
Enabling public access could leave them vulnerable to threats, such as hackers who could misuse data stored therein; as a result, all public access must be blocked entirely.
Amazon Web Services offers cloud foundations and security groups to manage access. When setting up an RDS instance, ensure that you select the appropriate configurations and authentication settings.
Additionally, backup schedules protect data by making snapshots readily available when needed.
Amazon Web Services Storage Solutions
Amazon Web Services offers a range of storage solutions tailored to various needs. Object storage, with S3, and block storage, with EBS, are among the many offerings, making selecting the right option key to success.
Understanding Amazon Web Services’ storage architecture is crucial, and here at D4E, we explored scenarios in which S3 is ideal and when alternatives should be considered within AWS.
Amazon Web Services users often encounter challenges when configuring storage resources. Amazon Web Services takes data security very seriously, employing encryption and access controls that protect our information.
During this session, we focused on securing storage solutions within Amazon Web Services.
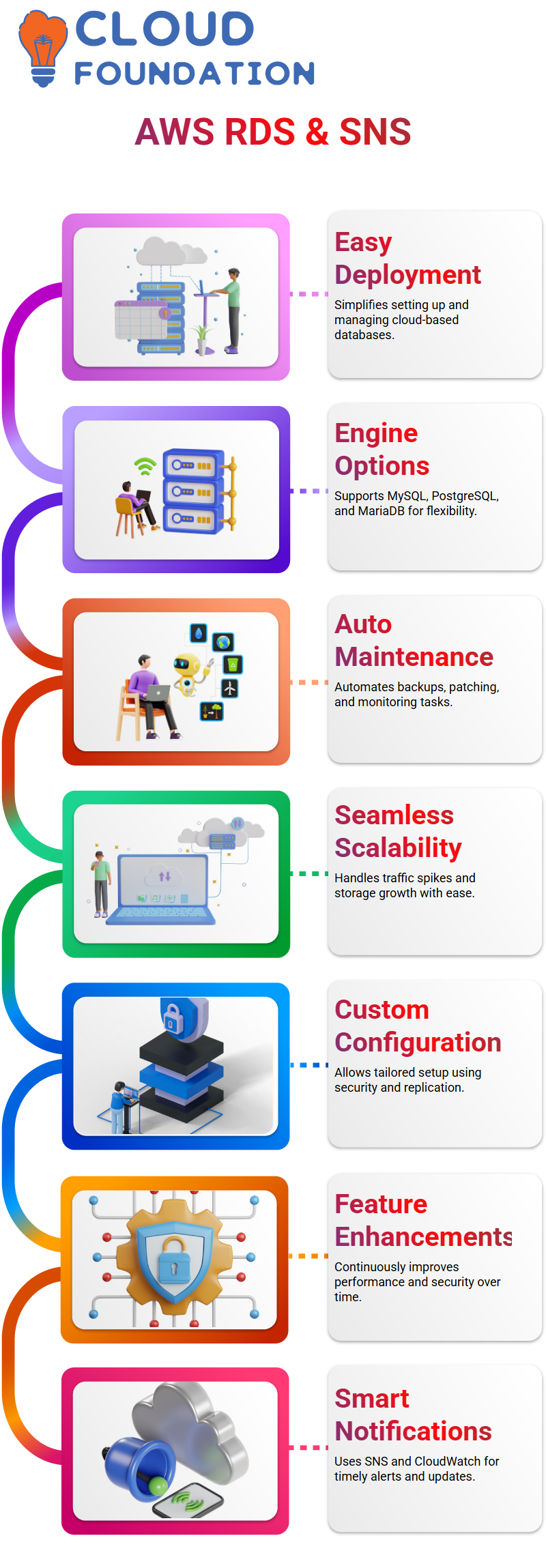
Amazon Web Services RDS
Amazon Web Services RDS. Managing databases can be intimidating, but Amazon Web Services makes deployment and management much simpler.
Amazon Web Services offers various database engines, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MariaDB, to ensure optimal performance and reliability in applications.
Choosing one depends upon your application requirements to achieve optimal performance and reliability.
One significant advantage of Amazon Web Services RDS is its automated database maintenance, which makes tasks such as backups, patching, monitoring, and optimisation seamless, freeing up valuable time for development and optimisation efforts.
Amazon Web Services allows for seamless scalability. From handling spikes in traffic or growing storage demands, RDS ensures your database infrastructure stays agile and responsive.
 Implementing Amazon Web Services RDS is simple. By selecting a database engine, defining security policies, and configuring replication, we establish a reliable environment tailored to our specific needs.
Implementing Amazon Web Services RDS is simple. By selecting a database engine, defining security policies, and configuring replication, we establish a reliable environment tailored to our specific needs.
As Amazon Web Services evolves, new features continually enhance database performance and security. Staying abreast of these advances ensures that we maximise cloud-hosted databases to their maximum potential.
Simple Notification Service (SNS) in Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services SNS plays an invaluable role in notification management. It helps customers track changes and updates across AWS services, while topics allow users to organise notifications effectively.
Setting alerts with Amazon Web Services CloudWatch helps ensure issues are quickly addressed by notifying when CPU usage, memory usage, or other metrics exceed predefined thresholds. Notifications may also be configured to occur if these thresholds are reached again in future periods.
Monitoring Services in Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services provides powerful monitoring tools that enable users to track system performance.
Alerts can be configured to notify users when key thresholds are met, enabling proactive management and giving them time to take necessary actions before performance degrades further.
Understanding how Amazon Web Services manages data security can ensure a more positive user experience.
Encryption policies, access controls and the proper configuration of notification services all play key roles in providing a safe environment.
Amazon Web Services: Setting Up Your Site-to-Site VPN
A site-to-site VPN using Amazon Web Services, and explore how secure connections between networks are established. If this topic interests you, then read on!
First, we create a customer gateway. This entry point determines how our on-premises network connects to Amazon Web Services and assigns an IP address accordingly, ensuring a stable communication channel between this gateway and virtual private gateways.
Next, we link our virtual private gateway with Amazon Web Services by configuring its virtual private gateway and selecting either static or dynamic routing protocols to ensure efficient data flow and effective network communications with Amazon Web Services.
At this stage, selecting an optimal routing protocol could make all the difference when communicating between networks that operate over Amazon Web Services.
Once we’ve completed our VPN setup, the next step should be to download our configuration file, which will allow us to integrate our settings seamlessly. Amazon Web Services’ robust networking options make this step straightforward and effective.
Understanding subnets and security groups is of vital importance in Amazon Web Services, as their access control features enable finely tailored control that applies rules either across an entire VPC or to specific instances. This ensures adequate security without complicated administrative processes.
Amazon Web Services: Automating Backups
Amazon Web Services enables backup automation by allowing users to schedule backups to S3.
Automating these processes ensures data integrity while mitigating risk, and setting permissions correctly makes exporting and importing seamless.
Manage DB instances through Amazon Web Services by selecting engine types and configurations.
Users can optimise resources based on long-term needs by choosing reserved instances with upfront or partial payments, which provide cost savings.
Practical Exercises with Amazon Web Services
To expand our knowledge, we conducted hands-on exercises. Mastering Amazon Web Services requires real-world practice; thus, we focused on creating and managing services within Amazon Web Services.
Launching and monitoring Amazon Web Services instances provides valuable experience with their capabilities.
Troubleshooting issues and refining configurations allow cloud operations to run more effectively with Amazon Web Services.
Working with Amazon Web Services across multiple scenarios enables more effective decision-making. We conducted tests of various setups to learn all aspects of managing services within this platform.

Vinitha Indhukuri
Author



