Workday P2P Tutorial for Beginners
Company Hierarchy: Setting Up Structures, Roles, and Security
In today’s business landscape, organising company information into a structured and secure system is no longer optional—it’s essential.
From setting up company hierarchies to defining roles, reference IDs, and document management, a systematic approach ensures that businesses remain efficient, compliant, and secure.
In this article, we’ll explore the process of setting up a Re Organisation (an audit page for company details), creating company hierarchies, assigning roles, and managing document IDs.

The goal is to provide a clear understanding of how to streamline operations while maintaining the highest level of security.
Setting Up a Workday Re Organisation
The journey begins with creating a Re Organisation that captures key company details such as:
X Company (company-specific data)
authorised collaborators
Reference IDs
A Re Organisation can be named—for example, Pandemic—and is designed to store data in a specific format (e.g., 0.01.99). Once created, the reference ID is adjusted to match the company’s requirements, ensuring consistency across records.
Creating the Company Hierarchy in Workday
After setting up the Reorganisation, the next step is to establish a company hierarchy. This hierarchy defines the relationships between different entities, roles, and departments.
A short code (e.g., MVNP) can be added to company names for easier identification.
Dates are linked to reference IDs, serving as anchors for hierarchy creation.
The hierarchy accommodates everyone in the system—contractors, employees, and content workers alike.
Visibility Options
When configuring access, four visibility modes are available:
Everyone (default)
External URLs (shared links)
Subtype-based visibility
Complete access
These settings strike a balance between transparency and security, tailored to meet the specific needs of each business.
Understanding Workday Role Assignments
Role Assignments indicate which roles a person holds within a hierarchy:
Current role: Assigned directly to the hierarchy.
Superior role: Linked to parent hierarchies.
This ensures that employees only see what’s relevant to their responsibilities while maintaining accountability across the hierarchy.
The Concept of a Holding Spot in Workday
A holding spot acts as a safeguard for data. When set with a specific date (e.g., today’s date), any activities linked to the company after that date are automatically deleted.
 This helps organisations manage temporary or test data effectively.
This helps organisations manage temporary or test data effectively.
Adding Company Details in Workday
A company setup isn’t complete without its essential details. These include:
Legal company name (not just a registered document name)
Currency (USD by default, for transactions and business operations)
Reference ID (to quickly locate records)
Contact information (billing, procurement, and shipping contacts)
Effective date (backdated or adjusted to meet business rules)
Address history (valid for 1, 5, or 10 years)
Ownership information and member details (e.g., employees or shareholders) are also added, ensuring the company’s structure is fully documented.
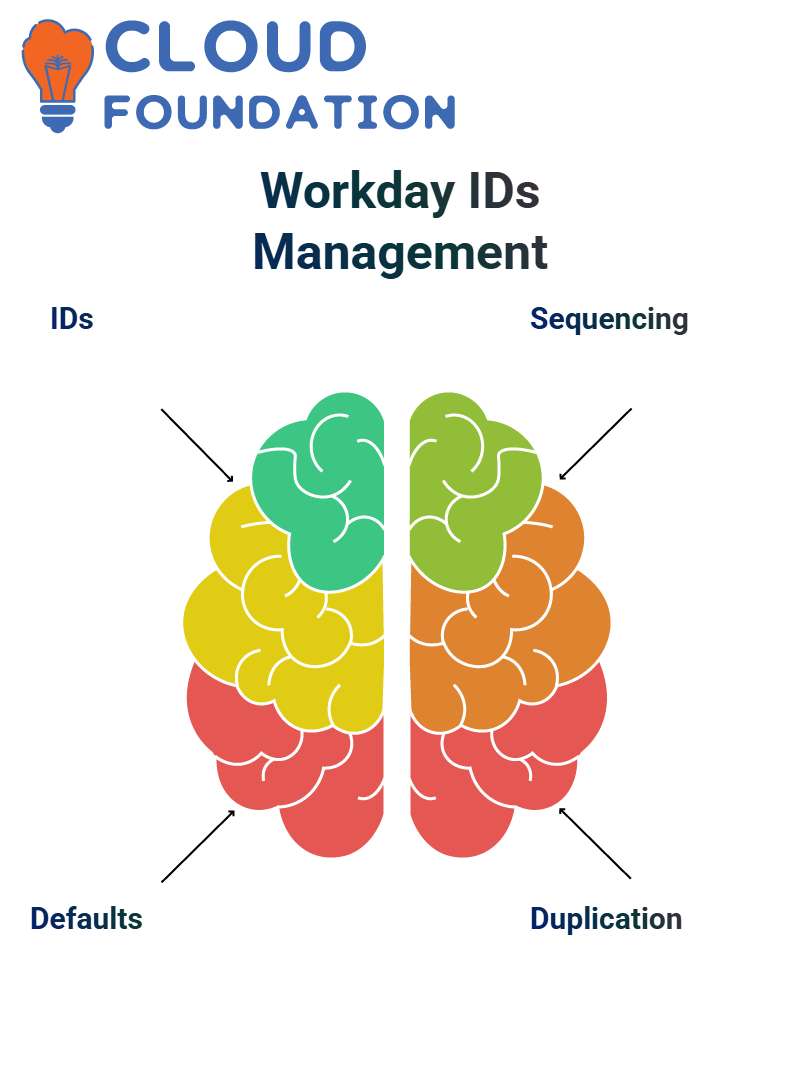
Workday ID Definitions and Document Sequencing
Every company generates and manages large volumes of documents, including purchase orders, invoices, contracts, and other related documents. To streamline this:
ID definitions assign document numbers (e.g., Invoice #1234).
Default tenant settings apply formats universally (e.g., for customer messages or voice logs).
Sequence IDs ensure numbering consistency, with customizable formats like (EQ) CustomerVoice#10.
This eliminates duplication and keeps audit trails clean.
Assigning Roles and Responsibilities in Workday
Security is a cornerstone of any hierarchy. Roles are assigned strategically:
Accounting Manager: Oversees financial entries and compliance.
Content Manager: Manages business content and documentation.
In large organisations (100+ companies), assigning roles only at the company level becomes impractical. Instead, roles cascade from the parent hierarchy, ensuring consistency and avoiding administrative overload.
Creating Cost Centres in Workday
To manage financial and operational accountability, cost centres are established. Examples include:
Double Cost Operations – Focused on internal operations.
Transport – Dedicated to logistics and mobility.
Each cost centre can be tagged with business unit locations, regions, or predictive centres, making it easier to allocate costs and measure performance.
Workday Security and Efficiency: The Key Takeaways
The process of setting up a company hierarchy is not just about creating records—it’s about building a secure, efficient ecosystem where roles, responsibilities, and data align seamlessly.
Key insights include:
Always define a holding spot for temporary data.
Use reference IDs and short codes for easy navigation.
Assign roles strategically, keeping scalability in mind.
Create cost centres to track and manage operational spending.
Ensure document IDs follow consistent, logical patterns.
Building a Robust Procurement and Supplier Management Framework in Workday
In today’s competitive business environment, procurement is more than just acquiring goods and services—it’s about building reliable systems, maintaining financial accuracy, and fostering inclusive relationships with suppliers.
A well-structured procurement system ensures efficiency, transparency, and compliance while enabling organisations to adapt to changing market dynamics.
This article examines how companies can develop a procurement framework that encompasses fiscal schedules, supplier classifications, payment terms, and inclusive supplier practices.
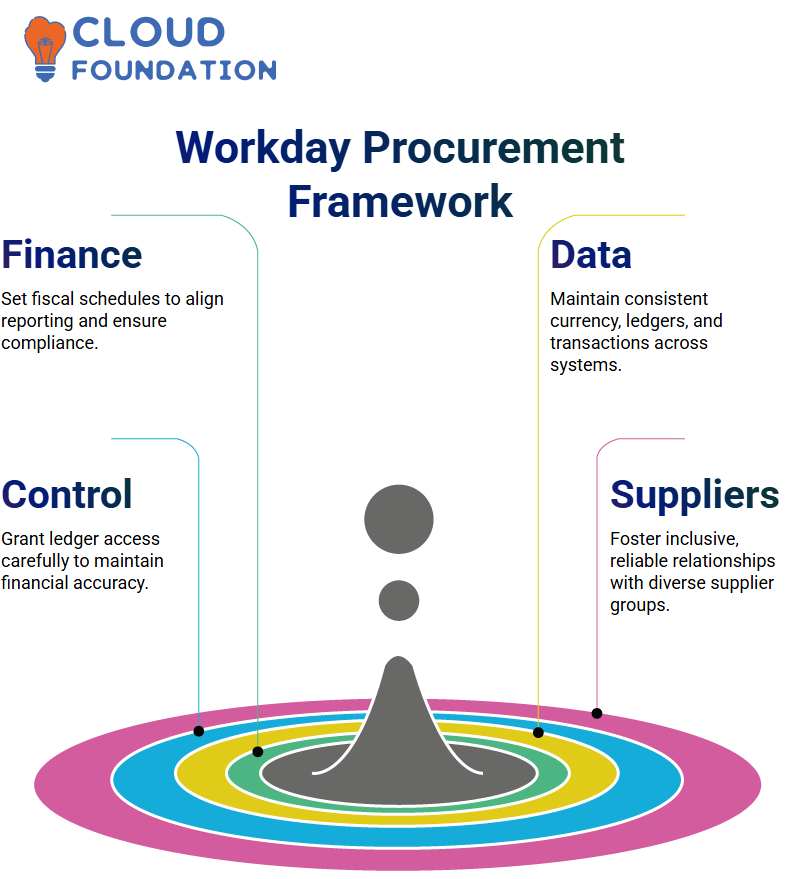
Establishing a Solid Financial Foundation in Workday
Every company’s operations begin with a well-defined fiscal schedule. For U.S. companies, the fiscal year often runs from April to March, aligning accounting and reporting periods with compliance requirements.
When setting up a fiscal schedule:
Use a standard corporate template for efficiency.
Ensure that all financial data (currency, ledgers, transactions) remains consistent.
Assign administrative roles carefully, as accounting managers often hold broader rights to open ledger periods.
By securing financial structures at the outset, businesses can maintain clarity in reporting and streamline audits.

Workday Online Training

Workday Configurations for Efficient Procurement
Before procurement activities can run smoothly, three key configurations must be in place:
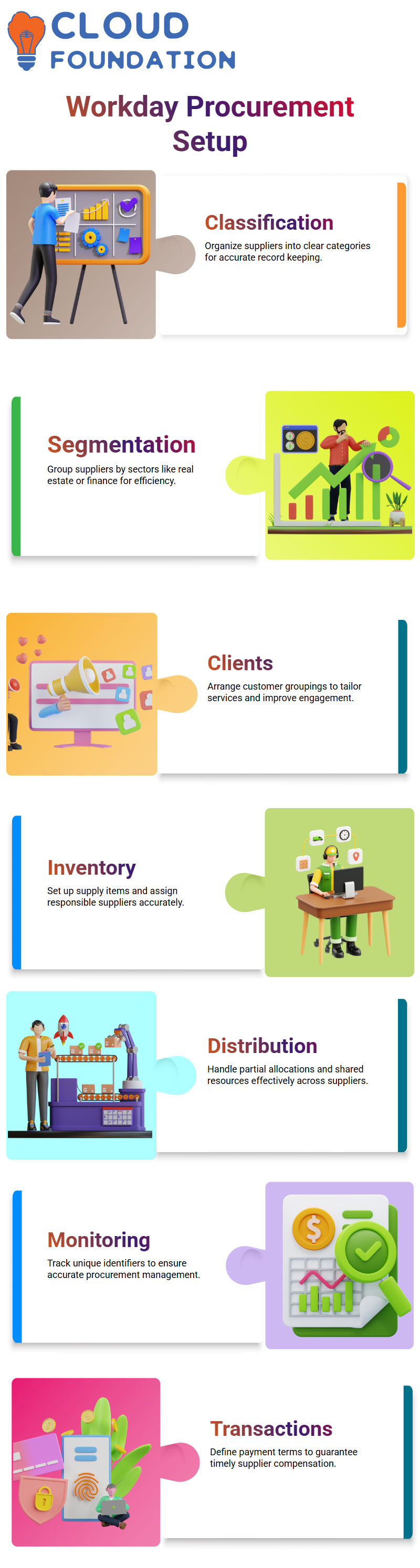
Supplier Categories: A mandatory classification for every supplier, ensuring clarity in procurement records.
Supplier Groups: Optional but helpful in grouping suppliers by sector—such as real estate, chemical industries, or financial services.
Customer Groupings: Helpful in organising client interactions and tailoring services to specific industries.
These configurations create a structured environment, minimising errors and supporting better supplier management.
Understanding Supply Creation and Payment Terms in Workday
Supply creation is the foundation of any procurement system. It involves setting up categories, defining payment terms, and assigning suppliers for various items.
While some supply names may be undefined, systems typically manage partial allocations, such as one-third portions for shared resources.
For example, tenants like X may operate with rapid procurement processes and unique identifiers, such as minus C.I.N., which require careful tracking.
Defining payment terms—whether via purchase orders or direct payments—ensures suppliers are compensated correctly and cash flow is managed efficiently.
Defining Supplier Payment Terms in Workday
Payment terms are a cornerstone of supplier relationships. Clear agreements prevent disputes and foster trust. Common practices include:
Standard Terms: Example: Net 30—payment due 30 days from the invoice date.
Discount Terms: Example: 2% 10 Net 30—a 2% discount is applied if payment is made within 10 days.
Flexible Due Dates: Systems can automatically calculate due dates to match business needs.
Additionally, features such as “Do Not Pay During Bank Account Updates” safeguard transactions from fraud or errors, ensuring funds are transferred securely.
Inclusion Through Special Suppliers in Workday
A growing trend in procurement is the recognition of special suppliers, including businesses from underrepresented communities (e.g., Black-owned, LGBTQ+-owned, or women-owned suppliers). Governments and corporations are increasingly encouraging diversity by:
Creating categories for classification, certification, and vision.
Assigning special events and reviews to validate supplier activities.
Ensuring fair treatment and equal access to procurement opportunities.
This approach not only drives social equity but also fosters innovation and strengthens community relationships.
Leveraging Technology for Supplier Management in Workday
Modern platforms, such as Workday, offer an integrated view of procurement processes, encompassing supplier creation, review, approval, and payment. Such systems offer:
Ease of navigation with user-friendly dashboards.
Supplier review roles to ensure checks and balances.
Electronic payment integration, enabling direct account-to-account transfers.
By embracing these platforms, businesses can streamline their procurement workflows, enhance transparency, and minimise manual errors.
Purchase Orders and Procurement Efficiency in Workday
Purchase orders (POs) are central to procurement control. A robust system should include:
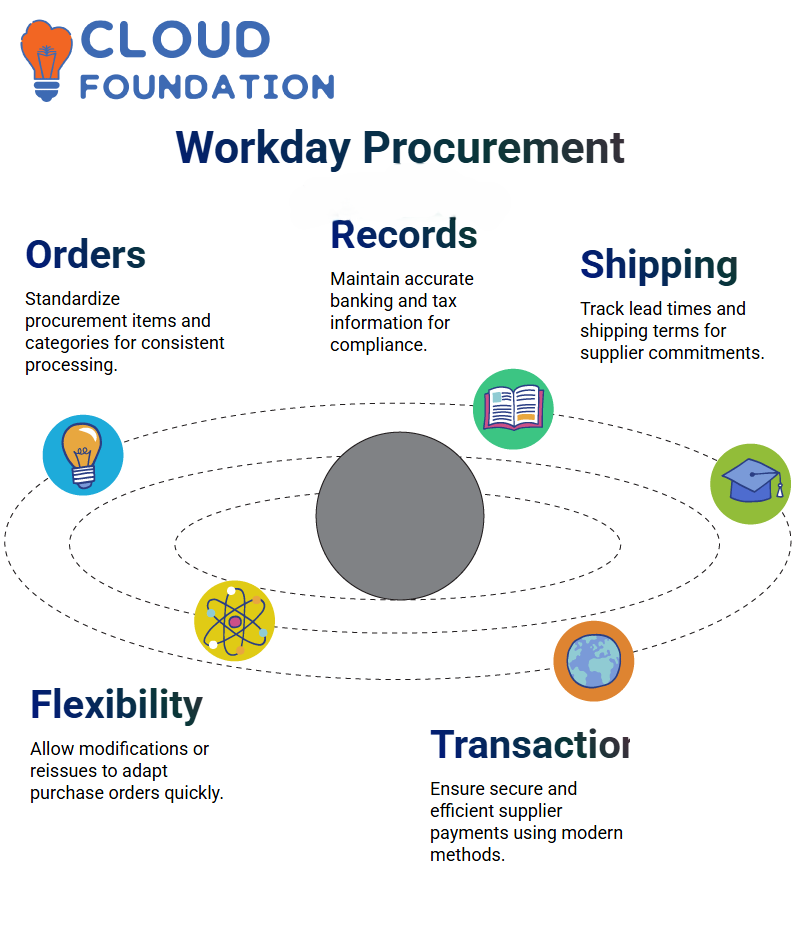
Default procurement items and categories to standardise orders.
Banking and tax details to simplify compliance.
Lead times and shipping terms to track supplier commitments.
Order modification options, allowing flexibility in changing or reissuing POs.
Features such as advance shipping notices help companies prepare for incoming goods, while structured review processes ensure suppliers consistently meet expectations.
Workaday Payment Methods and Future Trends
Companies today use a mix of cash, checks, debit/credit cards, and EFT. Looking ahead, cryptocurrency may become the default reference type for global suppliers, offering faster and borderless transactions.
Grouping suppliers by region or security segment enables large corporations to manage their diverse supplier bases effectively. Meanwhile, remittance memos, tax information, and secure integrations protect against compliance risks and payment delays.

Workday Course Price


Vinitha Indhukuri
Author