SAP FICO Business Partner online course
Why Master Data Centralisation Matters in SAP FICO
SAP FICO centralises master data so it can be shared among various modules, whether finance, materials management, or customer service is involved.
A BP structure lets data freely move through it without interference; general and company code data were separately created depending on roles within SAP FICO.
Structure provides businesses with more flexibility; for instance, when creating business partners with only general data roles, such as GADM01, all data becomes publicly accessible.
However, once assigned an FLVN00 role within SAP FICO, specific financial attributes become accessible.
SAP FICO Master Data Segmentation
As part of their configuration process, they ensured that they segregated vendors and customers not only by function but also geographically or by service type.
SAP FICO supported this level of granularity through BP groups and AP account group configurations.
Segmenting SAP FICO accounts to maintain traceability between each segment’s number range. Segmentation can also facilitate collaboration with international vendors or service providers, providing traceability across their relationships.
Understanding SAP FICO Business Partner Master Data
Working in SAP FICO, one of the primary concepts that was essential was understanding the role of Business Partners (BPs).
Within SAP FICO, a BP serves as a centralised master record where we maintain details for both customers and vendors. Redundant copies of customer or vendor details were stored; now, we maintain a single record that integrates across all modules.
Allow me to illustrate with an easy example. A vendor in SAP FICO and need to maintain their name, contact details and address information; simultaneously this vendor could also be used by the MM team for procurement without SAP FICO’s .
Business Partner concept, entering similar data twice could potentially create inconsistency across departments; instead it allows us to use Business Partners as shared entities between teams.
SAP FICO makes it simple and accessible to access general Partner data such as name, address and language preferences of Business Partners with ID 1001 easily and instantly across Finance, Procurement and HR as needed – it acts as one central hub for master data in SAP FICO.
SAP FICO Business Partners
SAP FICO provides me with an effective tool for accurately configuring business partners. From setting number ranges and assigning groupings, every step plays a crucial part in structuring my data.
Double-check to ensure that my routings match those intended by vendors or customers before finalising configurations.
By categorising business partners effectively using SAP FICO, such as domestic vendors versus service vendors, streamlining processing and improving traceability becomes much smoother, making reconciliation and reporting simpler down the line.
SAP FICO Business Partner Configuration
We explored SAP FICO to establish business partner (BP) configurations. One of the key tasks was setting up Business Partner groups.
SAP FICO enables vendors and customers to organise themselves under these categories for a smooth operational flow.Starting by creating Business Partner roles and Groupings.
SAP FICO simplifies connecting business partners, vendors, and customers by helping to synchronise data among these groups; these setups play a pivotal role in maintaining master data as a single central repository across modules.
SAP FICO Roles
SAP FICO defines different business partner roles, such as FLVN00 for financial vendors and FLVN01 for materials management vendors, to efficiently structure data while controlling access by responsibility.
Business Partner Roles have also been divided into domestic vendors and service vendors for easier management.
SAP FICO enables businesses to organise data into multiple groups, such as ‘BP Domestic’ (code V001) and ‘BP Service’ (V002), with unique number ranges starting at 5000 for B1 and 6600 for B2, making data maintenance systematic and traceable.
SAP FICO Business Partner Rules
As you use SAP FICO, take the time to familiarise yourself with its preconfigured business partner roles.
These rules form the backbone of how we create and manage partnerships, including those with vendors and customers, as well as freelancers and contact persons.
SAP FICO provides well-defined regulations that allow us to structure our information appropriately.
The Business Partner Section in SAP FICO, it becomes apparent that an extensive set of default rules already exists to meet most situations, ranging from service platforms to internal company contacts.
 Therefore, it’s usually preferable to stick with this preexisting setup unless there’s a compelling reason to add new contacts or change existing ones.
Therefore, it’s usually preferable to stick with this preexisting setup unless there’s a compelling reason to add new contacts or change existing ones.
Linking Business Partners to AP Groups in SAP FICO
One of the more insightful steps of SAP FICO was learning how to connect BP groups and Accounts Payable (AP).
This means that any vendor registered under AP will also appear under its respective procurement and finance groups, ensuring data consistency between the procurement and finance departments.
SAP FICO also assigned number ranges for these vendor groups–beginning at 3000 in one group and increasing gradually with each subsequent one.
Its systematic approach to number management prevented overlaps and simplified audits.
SAP FICO Business Partner Integration
SAP FICO requires integration between business partners (BPs) and accounts payable (AP) and accounts receivable (AR), one of the cornerstones of which is their connection with accounts payable and receivable, as well as vendors, customers, and other relevant entities.
I’ve spent considerable time configuring and explaining this linkage between vendors/customers/BPs in SAP FICO to ensure all financial transactions are accurately recorded and reconciled.
SAP FICO starts by creating master data for vendors and customers, which we then associate with business partners through synchronisation settings.
When we add vendors into our system, corresponding business partner accounts are also created – these BPs will later become linked via cross-application component features using master data synchronisation features.
SAP FICO allows us to choose whether the integration flows from Business Partner (BP) to Vendor (Vendor) or from Vendor to Business Partner.
When undertaking new implementations, starting with BP and then transitioning to Vendor should generally be preferred. However, during migrations, it’s sometimes necessary for the process to go from Vendor back towards BP. This flexibility is one of SAP FICO’s core advantages.
As part of using SAP FICO, one of the primary focuses should be creating the appropriate connections.
Establishing business partners through SAP FICO involves more than simply producing numbers; it encompasses all necessary groupings that represent your organisation’s financial structure.
As soon as you open the SAP FICO Business Partner screen, navigate directly to Supplier Finance.
This section contains company code data relating to company codes as well as an automatic allocation of both Business Partner and Vendor numbers by SAP FICO, which sets the stage for data synchronisation in subsequent stages.
Master Data Synchronisation in SAP FICO is essential in connecting vendor groups and Business Partner groupings seamlessly.
When entering into Master Data Synchronisation mode, focus on customer and vendor integration within SAP FICO for maximum impact – this is where relationships thrive.
Vendor Integration in SAP FICO
Always start by accessing SAP FICO’s Business Partner Settings for vendor or customer integration settings. In our case, selecting ‘Settings for Vendor Integration’ was key to meeting our synchronisation objectives.
Gain more insights into vendor integration settings within SAP FICO by studying field assignments.
There are two core direction flows available when assigning numbers – business partner to vendor and vice versa. Understanding these paths helps your business establish vendors on SAP FICO.
SAP FICO Vendor Master Data
Let me walk you through an interactive, practical session of SAP FICO, specifically focused on vendor master data management and business partner integration.
Have you ever wanted to understand more about how business partner (BP) numbers connect to vendor numbers within SAP FICO? This session can help.
SAP FICO allows us to configure different number ranges that impact vendor numbers and BP numbers differently. For instance, starting with 3000 and 5000 are two distinct starting numbers for either vendor or BP accounts.
As these should line up appropriately in specific configurations of data storage systems, groupings of data must be created before saving your information to avoid system malfunctions due to unexpected expectations.
Vendor Master Records
Let’s say you also need to add Reliance as a vendor in SAP FICO, following a similar strategy: select “Organisation”, then the relevant role, and then V002 vendor group, as appropriate for service vendors.
Enter all mandatory fields for Reliance–city, state, postal code, country and reconciliation account–into SAP FICO to maintain consistency across vendor data entries by mandating specific fields and creating logical grouping structures. This helps keep data entry consistent across vendors.
Financial Data to Vendor Master
Now comes the financial side. In SAP FICO, we must input key financial data regarding company codes. This involves assigning vendors to specific company codes (mine was 1100-) and specifying reconciliation accounts.
SAP FICO stresses accurate data entry. You’re required to specify reconciliation accounts as non-negotiable items, including short keys, payment terms, and account management data.
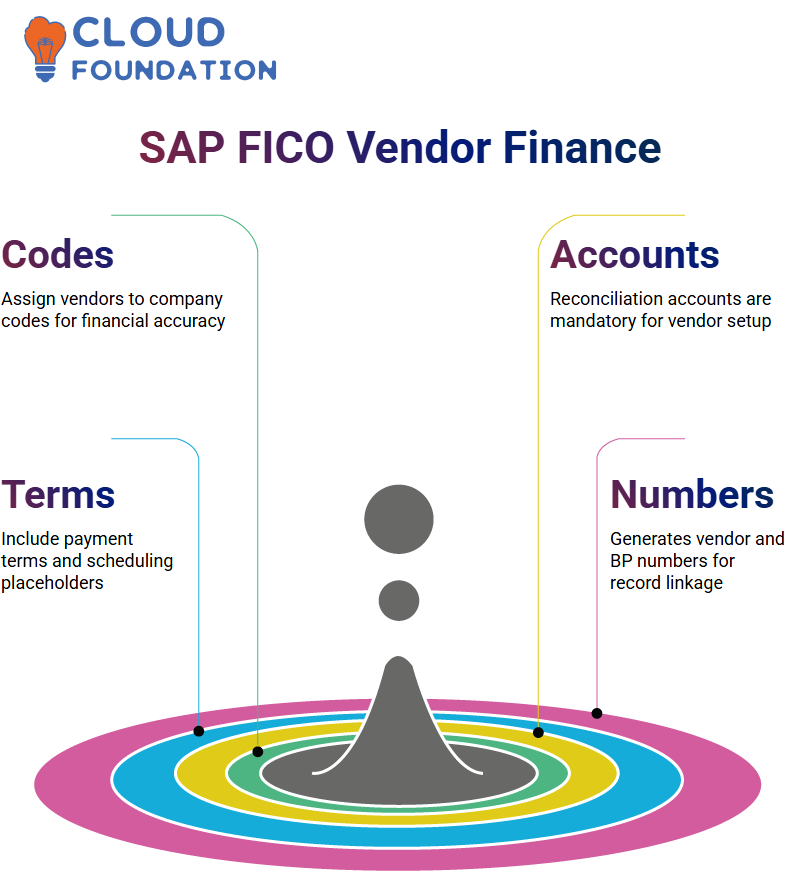
Even if you aren’t ready to configure payment schedules in detail yet, placeholders such as ‘payment immediately’ help save master record space.
SAP FICO: Why Two Numbers Are Generated
After saving vendor data in SAP FICO, it may produce two separate numbers — one for the business partner and the other for the vendor.
This occurs because SAP FICO internally links these master data records for improved integration and management.
Labcare may utilise SAP FICO’s backend system, ensuring seamless financial operations.
Their Business Partner number starts with 5000, while their Vendor number begins with 3000; both numbers can be connected seamlessly for efficient financial operations.
Number Ranges in SAP FICO
One of the key configurations within SAP FICO is the number range configuration.
To set these, navigate through SPRO – SAP Reference IMG – Cross Application Components – SAP Business Partner – Basic Settings- Number Ranges.
This gives us complete control over how business partner numbers are generated, whether internally or externally.
Example: I created number ranges, such as B1 from 5000 to 5999 and B2 from 6999 to 6999, in SAP FICO to organise business partners, including domestic vendors and service vendors, into categories. When dealing with multiple partner groups, it is vitally important that these ranges remain accurate.
SAP FICO Document Entry and Validation
After setting up master data and synchronisation settings in SAP FICO, always verify the setup by posting a sample transaction. This allows me to ensure everything works as intended.
SAP FICO simplifies posting transactions through the document entry screen in financial accounting, so we recommend starting with single-entry postings to keep things manageable.
When the system accepts your entry without errors or rejects it altogether, then your configuration is most likely accurate.
SAP FICO provides error messages that point me towards any configurations that require modification, helping ensure my system is ready for real-time business operations. This iterative approach ensures optimal system functionality.
Drilling Deeper with SAP FICO Tools
SAP FICO screens from document flow visualisation and balance sheet checking through to entry analysis using different accounting modules, to show just how comprehensive SAP FICO’s solution for handling transactions and maintaining vendor information is.
Once you become proficient with SAP FICO’s posting keys, number ranges, vendor/customer BP concepts and vendor/customer balance sheet concepts, it becomes incredibly intuitive. Every click showcases its structured yet integrated environment, from account setups to master data maintenance.
No questioning SAP FICO provides superior tracking, visibility and compliance features. From managing invoices and tracking cost centres to reconciling vendor accounts, SAP FICO remains an indispensable solution in enterprise financial operations.
Future Plans with SAP FICO Vendor and Customer Modules
Currently, my focus in SAP FICO is on vendor transactions; customer data configuration and transactions will follow once finish setting up the vendor-side setups.
SAP FICO provides tremendous flexibility, but to maximise its advantages, it must be structured methodically.
Everything, from BP groupings and document types to accounting entries and document approval, must align with existing financial processes and work smoothly together.
Planned Activities in SAP FICO Modules and Enhancements. To continue exploring SAP FICO modules and delving deeper into Business Partner (BP) enhancements.
It also intend to share PPTs and reference documents for anyone who wants to dive deeper into setting up Business Partners within FICO.

Vinitha Indhukuri
Author



