What is FortiManager
In today’s fast-paced, security-conscious digital world, businesses must efficiently manage and secure network infrastructure to be competitive.
Enterprises of all sizes rely on Fortinet’s FortiManager centralised management platform for comprehensive network security solutions.
With its enhanced scalability, centralised control, and real-time monitoring, FortiManager lets organisations manage their Fortinet firewalls, switches, and wireless access points from a single interface.
FortiManager provides a robust foundation for managing essential security infrastructure together with operational continuity and protection against emerging threats in financial institutions, healthcare providers, telecoms, and major organisations.
FortiManager improves corporate agility and security with policy automation, device configuration management, and integrated firmware updates.
For enterprises to optimise network security while minimising complexity and operational overhead, FortiManager offers safe, dependable, and performance-driven solutions including centralised logging, high availability, and disaster recovery.
What is FortiManager?
FortiAnalyzer is a powerful tool for centralized network security and reporting, offering a single pane of glass for securing devices and devices.
Its features include device manager, AP manager, fabric view, custom tunnels, and system settings.
The FortiManager is a user-friendly tool that integrates with the analyzer, offering comprehensive reports to strengthen security posture.
The manager includes device manager, which contains policies for devices and objects, and AP manager, which allows for VPN configuration.
The fabric view is used to tie to third-party cloud applications, such as Guard, Guard Overall, and Switch Manager.
The FortiManager is worth it for its ability to control a large list of things, such as 4D Wi-Fi, Forti for carriers, affordable email, forti analyzers, and virtual versions of these devices.
It can be broken down into administrative domains (ADOMs) or administrative domains, which can be deployed in a way where multiple tenants can be managed, or leased as a service to customers.
The high level of FortiManager allows for various tasks to be done right high. It is important to note that the Fortinet Analyzer is not for management, but rather for managing other appliances or VMS on a large scale.
Forti Analyzer in FortiManager
FortiAnalyzer, a device that can manage other appliances or VMS on a large scale.
FortiAnalyzer is a centralized network security and reporting platform that provides a single pane of glass for centralized security.
It offers a single pane of glass for securing devices, providing a single pane of glass for analyzing network security and reporting.
The platform also includes machine learning, event triggers, and security analytics reports.
Fortinet Analyzer can also be broken down into administrative domains or administrative domains, allowing different levels of administrative capability to employees or peers.
This is useful for managed service providers who can deploy the device in a way where they can have multiple tenants and lease it as a service to their customers.
Maintenance process in FortiManager
The maintenance process in FortiManager allows users to manage devices and their configurations. By grouping devices based on group, users can easily identify the configuration status and policy status.
Device discovery is a powerful tool for managing devices, as it allows users to define system templates, such as predefined SNM, DNS, and more.
To import policies and objects from a device, users need to import them into the FortiManager. Once the device has been provisioned, they can import the existing policy set and create new standardized policies over time.

FortiManager Training

This process can be done by choosing “import now” or “import all,” with “Policy Dash 01” being the default option.
After importing all policy address objects, users can choose whether to use local CA, certificates from Fortinet, Fortigate, or FortiManager.
A rating list is generated, showing that 12 out of 12 items have been imported, including an application list, authentication setting, antivirus profile, and man DNS profile.
The device is synced with the policy package, and yield signs indicate whether the configuration is different or completely gone.
Columns are customizable, and users can double-click on the device to view its connected interfaces.
Maintaining devices and their configurations is crucial for efficient management.
By grouping devices based on group and enabling FGM, users can easily identify and update their policies and objects.
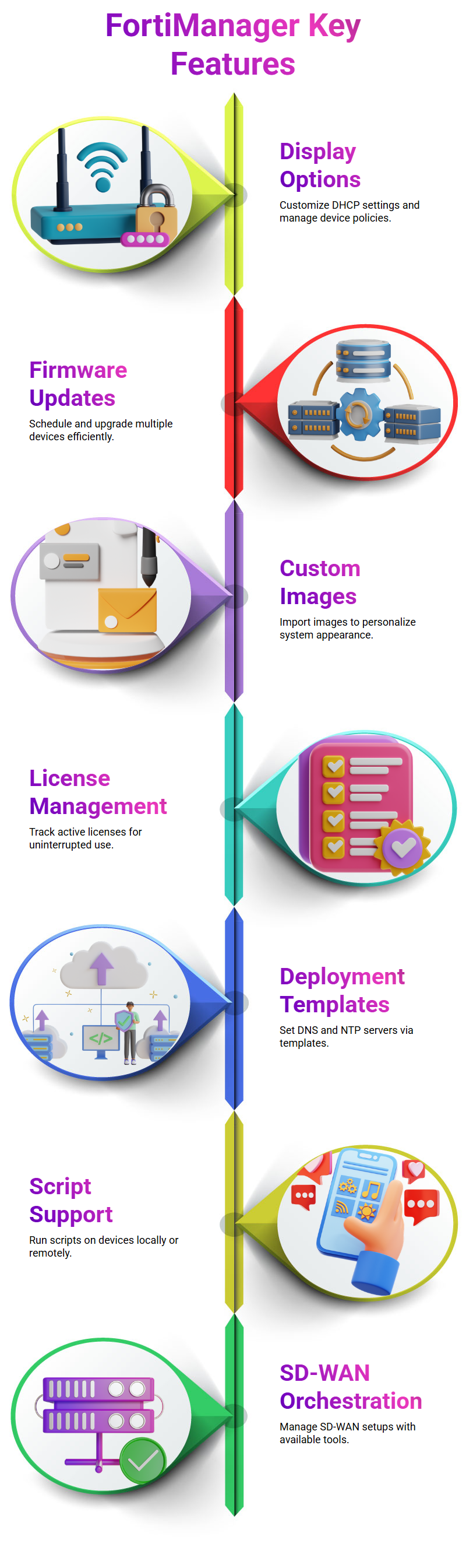
Features of Managing Devices in FortiManager
The FortiManager allows users to customize display options, including DHCP server DNS settings, and manage policies and devices. Users can also access global display options that go back to the same settings.
Users can schedule firmware updates from their fleet and upgrade devices as needed. This feature is particularly useful for those who need to update multiple devices at once.
Additionally, users can import custom images to avoid getting a call at six in the morning.
The license tab allows users to check available licenses, ensuring they don’t have to keep a rolling table that may or may not be active.
Deployment templates allow users to set DNS, configure management settings, and push messages to specific NTP servers. Customized FortiGuard block pages can also be created within the template.
The system is scaled at scripts, allowing script writers to write scripts that can be run on device objects within the FortiManager or remotely via a cli.
SD-WAN orchestration is also available, although it is not used by many users.
The FortiManager offers a variety of features for managing devices, including display options, firmware updates, and deployment templates.
Users can customize their settings, schedule updates, and work at scale with SD-WAN orchestration.
However, it is important to note that the system does not support SD-WAN orchestration and may not be suitable for all users.
VPN management and the process of creating a VPN community.
It begins with the use of a Dom, which is turned off, but the user can edit the content and enable VPN management.
The user then decides to take AP off, as they don’t need it and don’t have access points. Which is then enabled.
The FortiGate is then given its settings from the photo manager, and the magic happens from the FortiManager, also known as the VPN manager.
The user is then encouraged to download the 4-day manager administration guide and the FortiGate administration guide from help for new Netcom.
The user is then directed to create a community, which is another way of describing a VPN topology. The community is created, not the actual endpoints, but the VPN.
The user is advised to download the FortiGate administration guide and the FortiGate administration guide from help for new Netcom.
The VPN community is then created, and the user is instructed to create the VPN endpoints.
It revolves around VPN access to headquarters and a star hub-and-spoke topology.
The endpoints are discussed, including the use of pre-share keys that are auto-generated and pushed down via the configuration from the FortiManager.
This allows users to identify themselves without seeing them. Other options include using a CA or a domain environment, and using a public one to identify themselves.


FortiManager Online Training

Managed and Unmanaged gateways in FortiManager
A managed gateway has four gates, two of which are managed by the for DES manager.
Unmanaged gateways have 40 gates not managed by the FortiManager and other third-party applications that support IPSec.
These gateways are not managed by the FortiManager and other third-party applications.
The creation of new gateways and manage to gateways. The first step is to create a new gateway for each device, ensuring that all devices are under essential management.
This process is straightforward but requires careful consideration of the specific devices and applications involved.
The first gateway in this is about protected subnets. This is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution.
Before using the “tricky” method, there were issues with selecting the right IP addresses for different targets.
When using dynamic mapping in quick mode, selectors would appear due to the fact that when a local lands on a remote site, it would turn to a different IP address depending on the target.
To address these issues, it suggests using a policy and objects approach. They will create the headquarters IP address.

For the protected address, will use the “is” command to cancel the previous step and create the headquarters IP.
For the protected subnets, then will use the “protected subnets” command to create subnets that are encapsulated inside an IPSec tunnel.
These subnets are LAN IP addresses, which are used to manage the network traffic between the two locations.
It emphasizes the importance of maintaining the same object as the target, rather than creating dynamic IP addresses for every address or branch office.
This approach allows for more flexibility and control over the network’s routing and communication.
It emphasizes the importance of careful planning and execution when creating protected subnets and ensuring that the network remains secure and efficient.
Conclusion
FortiManager technology provides a centralized, efficient, and scalable solution for managing Fortinet’s security devices and infrastructure.
By offering features such as unified management, automated workflows, and seamless integration with FortiGate firewalls and other Fortinet products, FortiManager ensures improved visibility, control, and security posture across distributed environments.
Its ability to streamline network configurations, simplify policy management, and enhance overall operational efficiency makes it an essential tool for organizations seeking to strengthen their network security.
As enterprises continue to evolve and expand, FortiManager remains a critical asset in maintaining a robust, agile, and secure IT infrastructure.

FortiManager Course Price


G. Madhavi
Author