Veeam Replication Techniques training
Understanding Veeam Replication
Veeam replication is an integral component in maintaining business continuity. When working with virtual servers, selecting an appropriate datastore is crucial.
My advice is to log onto ESX02 to view existing ones before creating new ones.
Veeam Replication
Veeam replication goes beyond creating backups; it also ensures fast recovery.
 At the same time, backups store their data in formats such as.VBK,.VRB or.VIB files are used for storage purposes, while replication creates exact copies of virtual machines at another site for fast restoration.
At the same time, backups store their data in formats such as.VBK,.VRB or.VIB files are used for storage purposes, while replication creates exact copies of virtual machines at another site for fast restoration.
Veeam Backup Retention Policies
Retention policies in Veeam are of vital importance; my configuration keeps backups for seven days, though continuous replication may also be available depending on business requirements.
Setting Up Veeam Replication
Replicating virtual machines using Veeam begins by selecting our production VMs in Veeam and choosing their respective target hosts (typically located at disaster recovery sites), followed by selecting our destination host(s).
This ensures that, in the event a primary server goes offline unexpectedly, its replicated counterpart is ready and waiting to take its place instantly.
Veeam can then be configured for replication tasks to ensure minimal downtime and seamless failover in the event of a failure.
We set schedules and recovery points accordingly to achieve our objective of smooth failover operations.
Why Use Veeam Replication?
Replication is ideal for virtual machines where downtime cannot be tolerated, providing reliable near-instant recovery solutions such as Veeam’s Continuous Data Protection (CDP).
Veeam replication helps IT teams ensure system availability by maintaining system redundancy, even in the face of unexpected disruptions or malfunctions, thereby keeping essential services up and running without disruptions or outages.
Setting Up Datastores in Veeam
Setting up a datastore requires manual creation; once an attached disk has been attached, its datastore configuration must be completed before it can be used in Veeam replication.
When I encountered issues where my new datastore wasn’t showing immediately upon Veeam discovery, manually configuring its configuration solved my problem.
VM for Veeam Replication
Veeam can handle virtual machine replication for only selected virtual machines, ensuring optimal resource use and time savings.
In my setup, multiple VMs were chosen rather than individual replication jobs to save both time and effort when selecting my replica targets.
Storage in Veeam Replication
Storage capacity plays a pivotal role in successful replication. I recently witnessed a VM with a size of 1.6TB that failed to replicate because my host only offered 500GB of storage.
For this reason, proper management must be executed when dealing with significant storage needs, primarily because replication cannot function effectively without adequate capacity management in place.
Veeam Replication for Hyper-V
Veeam replication is not limited to VMware environments; it also works well in Hyper-V environments, provided the version and available resources are compatible.
Compatibility may vary depending on the individual version and environment.
 Hyper-V replication jobs may fail if resources become scarce or concurrent tasks exceed predefined limits; therefore, optimising proxy settings can significantly enhance replication performance.
Hyper-V replication jobs may fail if resources become scarce or concurrent tasks exceed predefined limits; therefore, optimising proxy settings can significantly enhance replication performance.
Veeam Snapshot Management and Restore Points
Veeam replication creates restore points to ensure quick recovery in case of data corruption, up to seven of which you can configure as rollback options for your environment.
Retention policies ensure storage efficiency by automatically deleting old restore points according to defined retention policies, thereby maintaining optimal storage utilisation.
VMware and Hyper-V have different snapshot limitations, so replication configuration is key in meeting each platform’s specific constraints.
Veeam Guest File System Indexing
Veeam offers guest file system indexing capabilities. When setting it up, indexing allows for creating a catalogue of guest files to enable quick file recovery and browsing/searching capabilities.
Indexing isn’t mandatory, but it makes the recovery experience smoother overall.
When it comes to indexing settings for virtual machines (VMs), you have several options available: individual VMs, as well as indexing for Windows and Linux, are supported.
Filtering options are also available, but we won’t delve into them further here.
It is essential to remember that for indexing to function effectively, it requires credentials with administrative rights; otherwise, the results won’t match up as anticipated.
Application-Aware Processing in Veeam
Veeam offers another key component, Application-aware processing. Specifically designed to protect servers hosting databases such as Exchange, Active Directory, or SharePoint, activating this setting ensures database integrity during recovery.
Otherwise, database inconsistencies could arise, rendering mailboxes or user data inaccessible.
Application-aware processing may not be essential on typical file servers without databases; however, when applied to database-driven servers, it becomes imperative.
When enabled, Veeam automatically installs all required services behind the scenes to facilitate seamless recovery.
Veeam and the Power of Virtualisation
Have you experienced the anxiety associated with downtime during hardware upgrades? Imagine having to visit a store, wait until someone opens your server, add storage or memory, and cause hours of inconvenience before virtualisation came along – that was the reality before virtualisation existed.
Veeam and virtualisation have transformed infrastructure management significantly. You can now install multiple operating systems and applications without experiencing downtime on a single server, making infrastructure management seamless. It has truly revolutionised infrastructure administration.
VMware, Microsoft Hyper-V, and Citrix are leading virtualisation vendors. VMware provides solutions such as vSphere (comprising ESX and vCenter). Microsoft supplies Hyper-V while Citrix has its XenServer; today, however, we will focus on VMware and Microsoft Hyper-V as industry leaders.
Let’s examine VMware’s hypervisor in more depth. When installing VMware ESX software onto a new server, it becomes a hypervisor like MS Office is developed as an operating system tailored to virtualisation.
Once installed, hypervisors enable virtualisation. With Veeam, virtual machine management becomes effortless: deploy multiple virtual machines on one server simultaneously and scale resources instantly if additional storage for any VM is required. Change its settings to enable instantaneous updates without requiring physical intervention.
Hyper-V is similar in concept, being integrated with Microsoft servers and can be enabled using their server manager. Once activated, Hyper-V acts as a hypervisor, allowing the creation and management of multiple virtual machines, much like VMware’s ESX hypervisor.
One of the primary advantages of virtualisation with Veeam is cost efficiency. Organisations previously needed to invest in multiple physical servers, additional space for cooling systems, and extensive infrastructure for virtualised applications. Now, only one high-performance server is required to host many virtual machines, thereby drastically reducing expenses.
Types of Backup in Veeam
Understanding the various types of backups is crucial for adequate data protection. Veeam provides options such as whole, differential and incremental backups.
Full backups ensure that all data is stored, while differential and incremental backups only store modifications since the previous backup, enabling efficient storage management and providing peace of mind for business leaders.
Veeam Backup Strategies
Data security requires an effective backup strategy, and Veeam simplifies this process with its array of backup methods, aiming to restore data quickly in the event of a disaster.
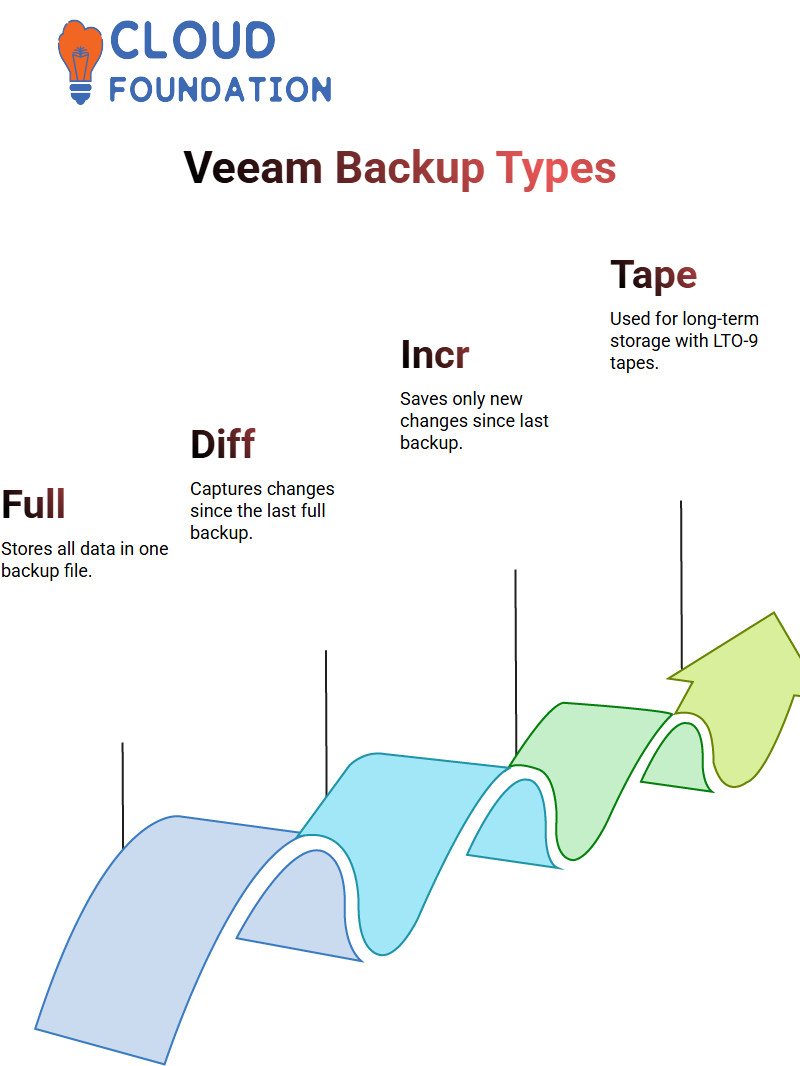
Companies often rely on tape backups as long-term storage solutions; LTO 9 tapes offer up to 9 Terabytes of capacity, making them a reliable choice. But storage options also exist on disk or NASPOS systems for alternative recovery solutions.
Veeam and Differential Backup
Differential Veeam Backup can help minimise storage requirements by recording only changes since the last full backup, thus cutting redundancies and speeding up recovery times. Veeam offers this type of differential backup service.
Example: Taking a full backup on Monday, followed by incremental and differential backups every Tuesday through Friday of that week, ensures that all changes made are captured in a single backup, making recovery more efficient.
Veeam and Incremental Backup
Incremental backups take efficiency a step further. While differentials save all changes since the last full backup, incrementals only store those made since any previous full or incremental backup was performed.
Although incremental backups occupy less space than full backups, each incremental backup must work seamlessly with the others to ensure complete data restoration.
If any step in the chain fails to restore everything as planned, if any backup fails in its sequence, it necessitates reliable tracking and management of backups, such as Veeam provides.
Why Companies Trust Veeam
Veeam provides significant protection against ransomware and virus threats; however, disk backups may become vulnerable due to cyber risks, whereas tapes remain protected.
Veeam integrates virtualised tape libraries for flexible backup options that work for organisations of any size – whether working remotely or managing large data centres, Veeam ensures reliable protection of sensitive data.
Veeam Snapshots
Experience with Veeam environments can be invaluable. By performing experiments on snapshot creation, deletion, and consolidation within your setup directly within Veeam itself, testing different scenarios will provide insight into how it handles snapshots during high-load conditions.
Veeam snapshot behaviours will be explored during an exclusive session explicitly designed to illuminate them. We’ll delve into every stage, ensuring you fully understand how Veeam efficiently manages snapshots.
Veeam Snapshot Issues
Snapshots play a vital role in virtual machine management, but they can also present unexpected issues.
In Veeam, snapshots have frequently failed to delete properly in VMware environments due to high load on ESX hosts, which prevents the smooth removal of snapshots from the backup repository.
One of the key areas to look out for in Veeam environments is any known bugs relating to snapshot deletion.

Before troubleshooting begins, always ensure Veeam has documented any related issues about snapshot removal; otherwise, it must delve deeper into environmental variables.
Exploring Snapshot Creation and Deletion in Veeam
Veeam snapshots progress through various steps during their creation and deletion. When working with Veeam snapshots, multiple actions are available, including “Delete,” “Delete All,” and “Consolidate.”
Each action enacts different behaviours that impact virtual machine performance differently.
Veeam can take some time to delete snapshots for larger virtual machines that exceed 1TB in storage size; environmental conditions, storage configuration, and load levels all play into its deletion process.
I have noticed that when deletion delays occur, they often result in orphaned snapshots, which further clog up systems.

Vinitha Indhukuri
Author



