SAP PMGM Certification Training
SAP PMGM: Getting Started with Calibration
As soon as the Home tab of SAP PMGM was accessed, the Calibration option was prominently displayed.
Once clicked, a list appeared immediately, showing any recently active accounts and began calibrating ratings accordingly. With the easy-to-use and user-friendly process in SAP PMGM’s calibration feature, felt more at ease using it.
Completed the calibration cycle successfully without issue or difficulty; the process seemed intuitive, and it was great seeing how well SAP PMGM supports this vital HR function.
As my colleague and explored SAP PMGM calibration further, having already covered most of its theory using an Excel sheet, we decided it was time to delve deeper.
So, fired up my laptop, opened our spreadsheet file for reflection purposes, shared my screen to review the key elements and steps we had covered earlier, and went over them together.
At our workshop on Facilitator and Participant Roles and Permissions (RP), we explored facilitator and participant roles, permissions and how RBP operates within SAP PMGM.
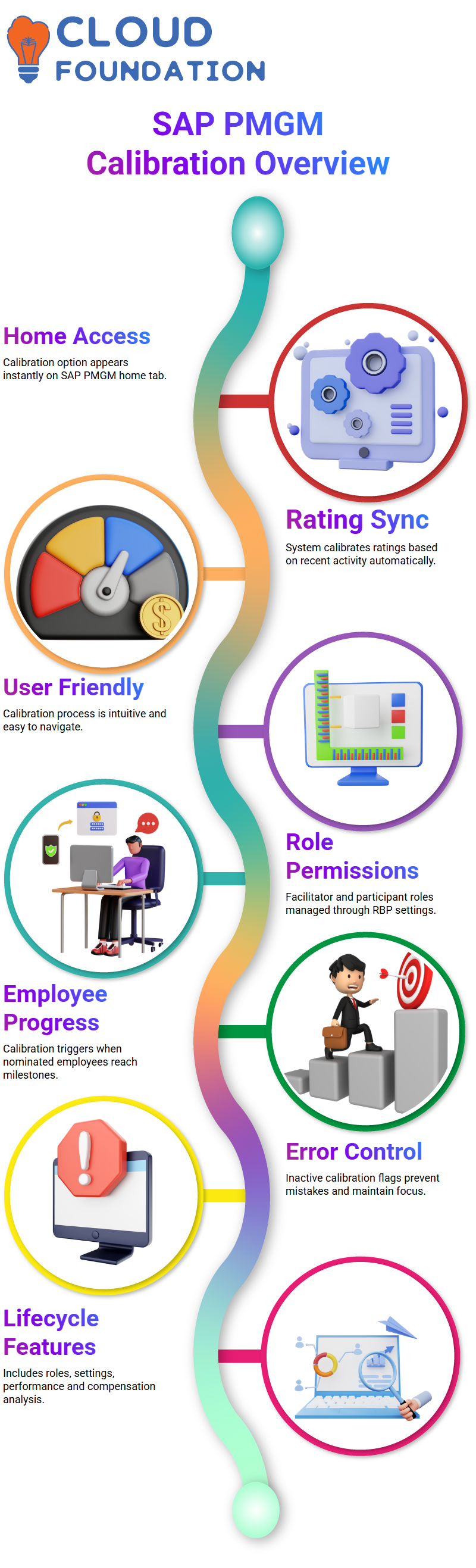
While RBP allows some permissions to be managed efficiently, calibration modules require specific settings that only become active once this module has been activated. See ‘Provisioning Permissions with RBP or Calibration-Specific Settings’ to learn more.
Calibration in SAP PMGM
Once templates have been connected to employees, SAP PMGM activates calibration steps once nominated employees reach that stage.
HR admins can easily see who has progressed as soon as relevant calibrations become active within the system.
SAP PMGM automatically flags calibration as inactive when employees fail to reach a key milestone, helping prevent errors while maintaining focus on actionable records.
The SAP PMGM calibration lifecycle encompasses permissions, enabling settings, user roles, and detailed view configurations.
We then explored its calibration areas performance analysis, people profiles, talent flags, and compensation — each uniquely supported within SAP PMGM’s architecture.
SAP PMGM: The Calibration Template
Once permissions were resolved, template creation began. SAP PMGM bases all calibration activity around three components: settings, templates and setting permissions for calibration activities to occur.
After provisioning is enabled via Provisioning, permissions should be granted before initiating the actual production of calibration templates.Consultants typically lead these efforts.
Here, the focus was to use an existing template from SAP PMGM’s Manage Calibration Template interface as a starting point, then develop new items from scratch using RBP permissions that had been appropriately set to accomplish our task.
Understanding SAP PMGM Calibration Templates
SAP PMGM calibration templates are key components. When starting work on SAP PMGM, one of its key elements is an annual calibration section, where templates can be found and reviewed every year.
Each SAP PMGM calibration template features several tabs which define its name, review period and purpose of calibration – crucial factors when planning the timeframe and purpose-specific calibration projects.
Once in the Data Section, SAP PMGM begins to shine. Here, users can specify precisely which sources to calibrate, including performance management, compensation management, talent profiles, or any other relevant areas.
For example, to calibrate performance, select “Performance Option / Template – Performance Template.” These templates often correspond with routes leading directly to calibration processes.
Once chosen, SAP PMGM checks whether its template links with performance and pay.
As soon as this stage reaches the calibration stage, its template function will work correctly, also connecting directly with an HR form, which plays a significant role during calibration processes.
Configuring People in SAP PMGM Calibration
Setting people in SAP PMGM is simple once you understand its basic function. Subjects and participants represent those being calibrated, while participants provide input from managers.
Once an employee is located within SAP PMGM, search for and click the action, then select whether they should become a subject or a participant.
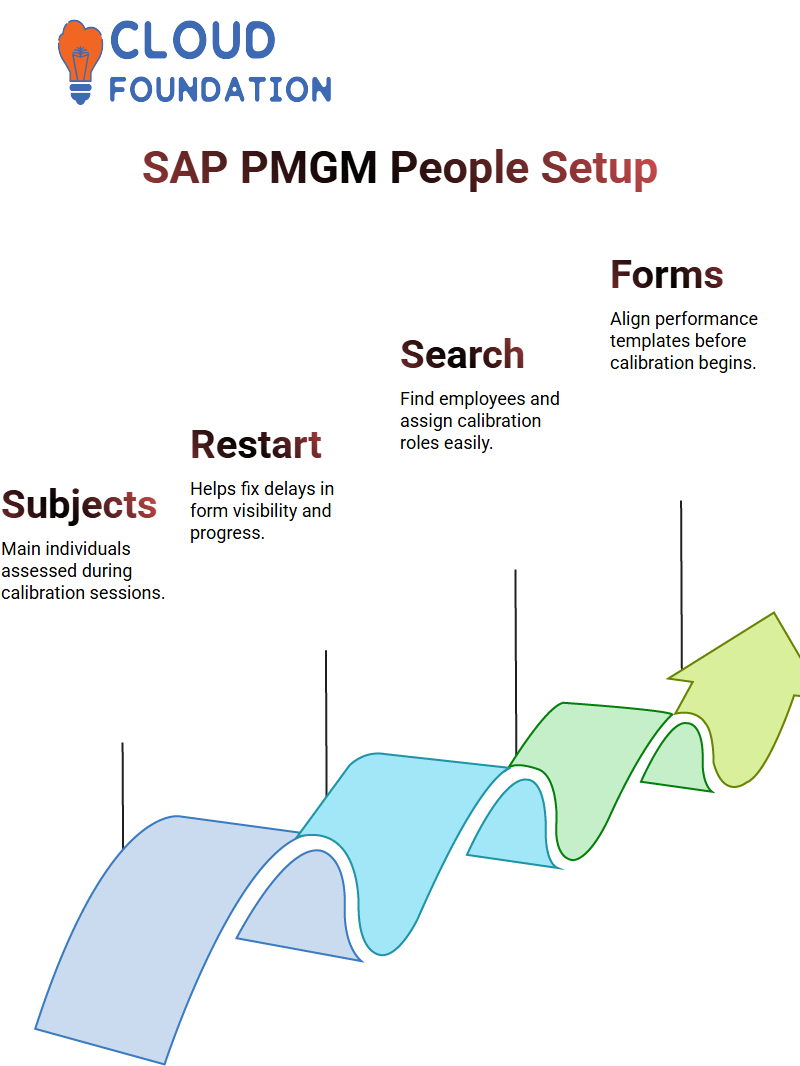
Calibration in SAP PMGM occurs with subjects, while participants support this process. We often utilise both roles when conducting testing of user behaviour.
Launching Performance Forms in SAP PMGM
Once launched, launch the form. In this step, align SAP PMGM templates and employee forms, as any inconsistencies between templates could lead to costly mismatches later.
Once launched, SAP PMGM displays a status popup showing job progress; check its Performance Tab to make sure the form reflects correctly.
SAP PMGM forms can take time to show up, particularly if previous processes weren’t closed properly. A quick restart may do the trick; otherwise, be patient.
Once they appear in SAP PMGM’s Performance tab, they take into account all employee self-assessments as well as manager steps before proceeding with the evaluation processes.
Managing Ratings and Form Progression in SAP PMGM
Ratings within SAP PMGM ratings are essential in finalising calibration. Scroll down the form, enter values according to the discussion outcomes, and then submit.
Once complete, SAP PMGM automatically sends it along for further review—possibly by another supervisory manager or even higher up the organisational hierarchy.
Before moving forward with one-to-one forms, verify their status using SAP PMGM to ensure they are in the correct stage of development.
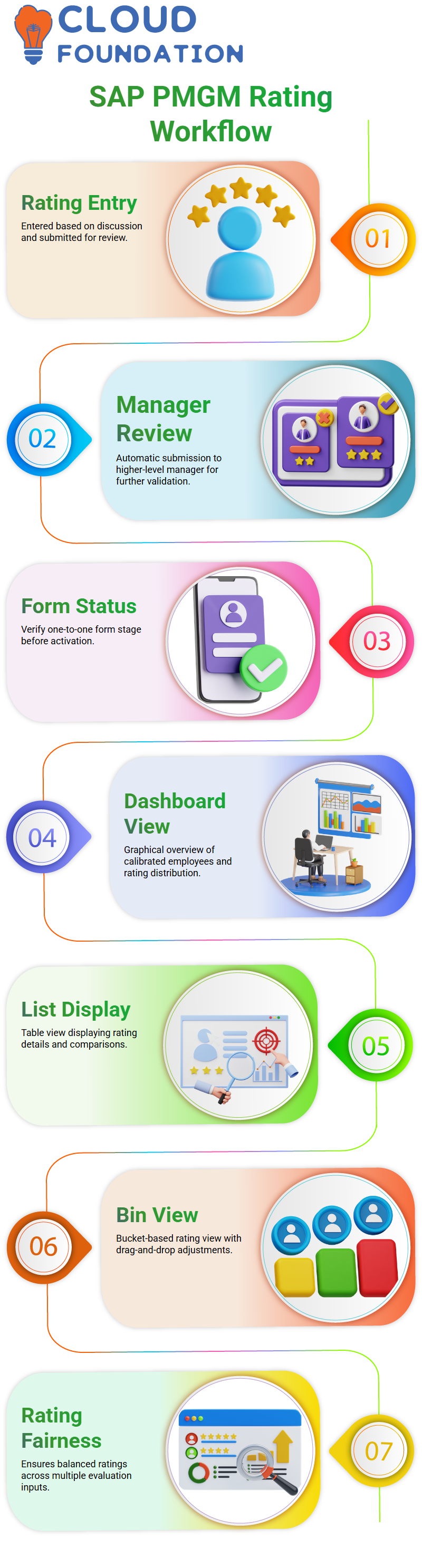
It must first enter this stage before activation can take place; until that moment arrives, SAP PMGM prevents facilitators from accessing controls.
Exploring Data Views in SAP PMGM
SAP PMGM provides various views to assist users when interacting with calibration data. One such view is the dashboard view.
This provides users with a graphical, aggregate view of employees who have been calibrated, along with charts showing either the number of subjects or distribution percentages.
Find this view invaluable when visualising overall ratings and subject data.
List View offers a straightforward method for quickly assessing calibration status, displaying ratings and data elements in a horizontal table format.
Allow this view to display elements such as overall rating or panel comparison, making it easy to assess calibration status quickly.
SAP PMGM’s Bin View provides another powerful feature. It allows for visualising ratings in buckets; for instance, subjects rated ‘Need Development’ would appear within that bucket.
This feature is beneficial when you need to adjust ratings based on multiple inputs simultaneously or ensure the fairness of results.
SAP PMGM Views and Matrix Grid
As part of SAP PMGM’s rating change enforcement feature, adding comments during rating moves provides valuable context to performance adjustments.
When moving a rating from one view to another, SAP prompts the user to justify this move with a comment, thereby facilitating transparency throughout calibration workflows.
SAP PMGM also provides us with the flexibility to customise language settings, allowing them to apply across diverse geographies. Once these have been set, end users can see firsthand how SAP PMGM views look and behave under real-world scenarios.
After setting up our pin view, we explore SAP PMGM’s Matrix Grid tool, commonly referred to as a 9-box grid, which assists companies implementing succession management by aligning different rating scales and visualising talent placement.
SAP PMGM dashboard, appears as an elegant nine-box view. Although shown as a placeholder here, in actual environments, this grid provides precise placement information regarding individuals based on their performance and potential.
SAP PMGM takes it one step further by offering the Executive View to senior HR and business leaders, providing an aggregated overview of employee activity and behaviour.
This approach helps tailor experiences around executive needs without becoming overwhelming for employees and supervisors alike.
SAP PMGM: Calibration Views That Matter
SAP PMGM is often underestimated, so decided to explore two forms of view setup: list view and dashboard view, which were tested separately.
The dashboard provided a succinct summary, while the list view offered detailed personal and organisational data, such as manager name, country, location, department, pay grade, employee class, and information.
Views were developed to show reviewers how employees interacted with employee data during the calibration process. With SAP PMGM, it becomes easy and intuitive to set up views that correspond with your decision-making hierarchy in your organisation.
Hands-On With SAP PMGM Calibration Creation
After studying how SAP PMGM calibrations are established, we set about creating one ourselves.
Reading documentation about calibration setup was beneficial; however, putting what was learned into action brought the learning to life! So that is precisely what we did.
At SAP PMGM’s interface, we performed a calibration launch.
 The experience reinforced the importance of preparation when using this program, including clearly outlining roles, aligning expectations accordingly, and customising it according to the performance objectives of any particular team or organisation.
The experience reinforced the importance of preparation when using this program, including clearly outlining roles, aligning expectations accordingly, and customising it according to the performance objectives of any particular team or organisation.
Creating SAP PMGM Calibration
After creating the template, proceeded with creating a calibration in SAP PMGM. This step defined who would participate and provided an environment in which managers and HR partners could review ratings and revise them as necessary.
At its conception, roles were assigned. A facilitator led the process, assisted by two backup facilitators.
An owner oversaw it all, with participants (usually managers) providing input. Employees being calibrated were subjected to these processes, while executives maintained access to all activities for oversight purposes.
SAP PMGMs go through multiple statuses. When first set up, it enters “Setup” mode; upon activation, it transitions into “In Progress” mode, providing valuable tracking that effectively aids in calibration lifecycle management.
SAP PMGM: Navigating Through the Calibration Interface
SAP PMGM’s calibration interface consists of five tabs: Basic Info, Data Views, Subject Views, and Executions. Care should be taken when going through each of them.
Under Basic Info, define the name and review period. The Data Source enables the selection of system inputs, including performance data, compensation metrics, or details from People Profiles.
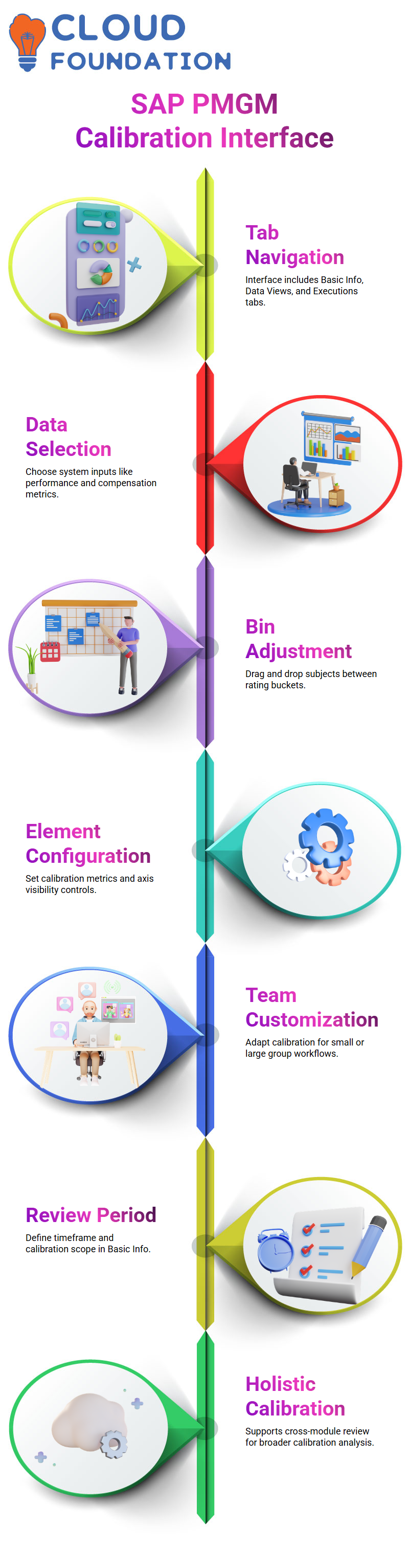
One advantage of SAP PMGM is being able to calibrate across modules for a holistic view.
Customising SAP PMGM Calibration
HR admins have the freedom to customize SAP PMGM calibration s in ways explicitly tailored to them, for instance adjusting bin views to reflect more accurate ratings or moving subjects between buckets if their ratings don’t seem justified – all using drag-and-drop functionality built right into settings so real time adjustments are seamless and real results become visible quickly.
SAP PMGM allows users to configure calibration elements. When dealing with performance, users typically choose Overall Form Rating as their calibration element, plotted on the Y-axis and with visibility controls available so that only authorised personnel can view sensitive data.
SAP PMGM also gives me control over how interactive my calibration experience will be; whether working with small teams or larger ones, SAP PMGM offers all the tools needed for effective and fair calibration management.
SAP PMGM Calibration Buckets
SAP PMGM provided an in-depth walk-through on calibration buckets (also referred to as Bini). Calibration buckets serve a vital purpose: organising performance ratings into bins (also known as buckets).
When ratings are imported into SAP, they are automatically assigned to a specific organisational bucket; users can then drag and drop these ratings between bins to create accurate performance assessments.
As part of SAP PMGM, we explored how to enable and rename buckets within it for customised calibration processes tailored to your organisation’s unique requirements.
A matrix grid, often used by management professionals for visualising performance and potential, displays nine boxes in which parameters help illustrate performance.
However, if your organisation doesn’t use such management services, then such visualisation might not be required.
Calibrating with Co-Facilitators in SAP PMGM
In SAP PMGM, learned more about the functions of facilitators and co-facilitators. When creating my initial task in the system, SAP listed itself automatically as the leading facilitator.
Then, Michael Pitt was added as a co-facilitator to divide up the responsibility; this practice is common when HR wants to decentralise control.
Even when we attempted to change the facilitator roles in SAP PMGM, SAP retained the original record since it was initially created.
That is just part of its ownership management model, so keep this in mind during configuration.
Calibration Process in SAP PMGM
As part of my SAP PMGM calibration setup, the first thing to keep in mind was saving before pushing any forms through SAP PMGM.
When this was complete, my form’s status switched to ‘Set Up’- this signalled that action needed to be taken immediately in SAP PMGM.
Clicked the activate button, and immediately the status changed from ‘In Progress’. Progressing through each SAP PMGM stage smoothly was essential at this point, as everything had been set up correctly and activities were properly aligned.
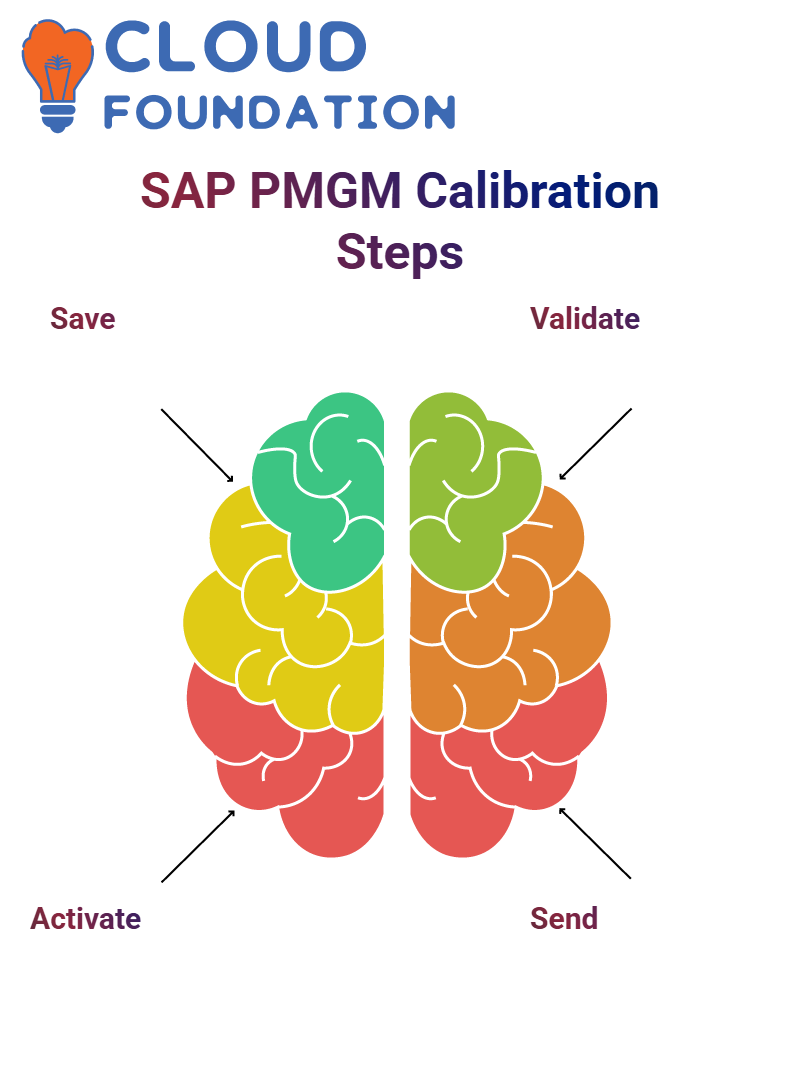
It can be easy to lose track of multiple tasks in SAP PMGM, so staying organised pays dividends.
Validating and Emailing in SAP PMGM
Once the form was validated in SAP PMGM and saved, accessing the email notification became possible—draft messages were directly accessible on that screen.
Send notifications as required, then re-activate after sending to ensure everything is correctly displayed in real-time.
As an extra safety measure, looked out for the “Deactivate” button; if this appeared, it indicated that SAP PMGM was live, and found these visual cues helpful when working within its complex workflow system.
Enhancing SAP PMGM Calibration
SAP PMGM enables you to optimise the calibration view by incorporating calculated ratings and comment features, providing more transparent feedback during calibration processes.
These options allow more comprehensive input during this calibration step and contribute to increased transparency of feedback at this stage.
Also explored advanced settings, including photo-less views and gender indicators to maintain privacy and focus during calibrations.

Furthermore, enabled the executive view for HR leaders and business leaders who need high-level access for monitoring calibrations.
Final Activation in SAP PMGM Calibration
After saving, return to SAP PMGM to activate it and unlock both the template and manager review steps. Without activation, SAP PMGM prevents managers from conducting evaluations.
Once SAP PMGM goes live, the workflow quickly picks up. All involved parties — both subjects and facilitators — clearly understand their roles.
SAP PMGM ensures that each form follows its designated path until calibration is completed, showcasing its strength as an end-to-end performance management solution.
SAP PMGM and the Importance of Configuration Practice
One frequently asked question about SAP PMGM is whether evaluation sheets and mock questions will be included; however, these are typically not the focus. Instead, mastery of configuration within SAP PMGM is what counts.
Interview questions often test your ability to handle configuration scenarios, so gaining practice in this area will prove essential to successfully passing interviews.
Immerse yourselves in real SAP PMGM screens as often as possible to become comfortable with SAP PMGM. Repetition can make the system second nature; that is the essence of mastering SAP PMGM.
SAP PMGM’s Role in Real-World Scenarios
SAP PMGM can be an invaluable asset when it comes to preparing you for unpredictable real-world scenarios.
Interviewers might throw you curveballs to see whether or not you truly understand a configuration; with a strong foundation in SAP PMGM behind you, however, any challenge can be addressed head-on with confidence and clarity.
SAP PMGM enables the quick identification of what a question truly requires and maps it back to a configuration solution that works, thereby bridging theory with practice. It offers exceptional value.
SAP PMGM Calibration Workflow
SAP PMGM calibration may seem complex at first, but once the flow is understood, it becomes simpler. SAP PMGM employs a three-step calibration process: Basic Info, People, and Validation. In SAP PMGM, once templates have been created, they are linked directly to calibrations.
Start right by giving the SAP PMGM template an appropriate name — it will save time later on. When setting it up, assigning a facilitator and choosing who the ‘on’ role holder should be is key.
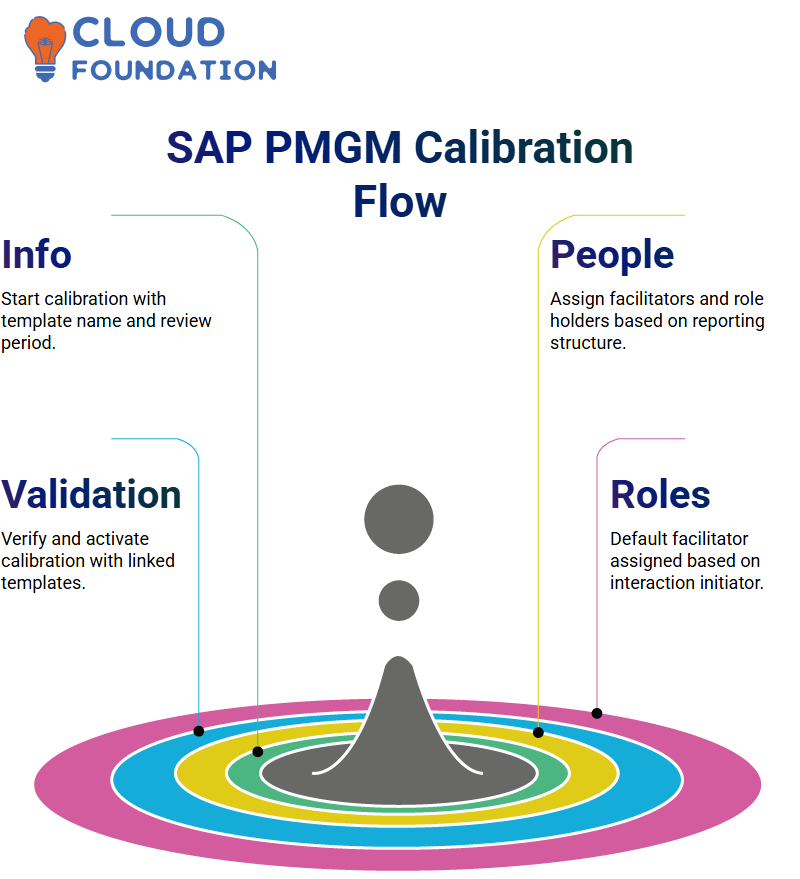
Usually, this would be one of your managers, as this system relies heavily on reporting structures, with direct reports appearing based on this decision when the auto subject and participant assignment checkbox is activated.
Understanding Roles in SAP PMGM
SAP PMGM assigned the facilitator role as part of its default settings during setup. Once created, it appeared as the facilitator.
Later, Michael Pitt was added as a co-facilitator based on who initiated it. SAP PMGM automatically assigns these roles dynamically depending on who initiates an interaction.
What matters here is how SAP PMGM tracks ownership. Even when assigning roles differently, SAP often maintains its original initiator until manual updates can be made to specific fields.
Understanding SAP’s default behaviours when managing multiple s. is paramount for effective facilitation.
SAP PMGM: Understanding Role-Based Permissions
SAP PMGM utilises Role-Based Permissions, or RBP for short, to determine who has access to what.
RBP plays a crucial role in setting access rights for calibration templates and settings, ensuring that anyone assigned those roles has access to tools such as “Manage Calibration Template” or “Manage Calibration Settings.”
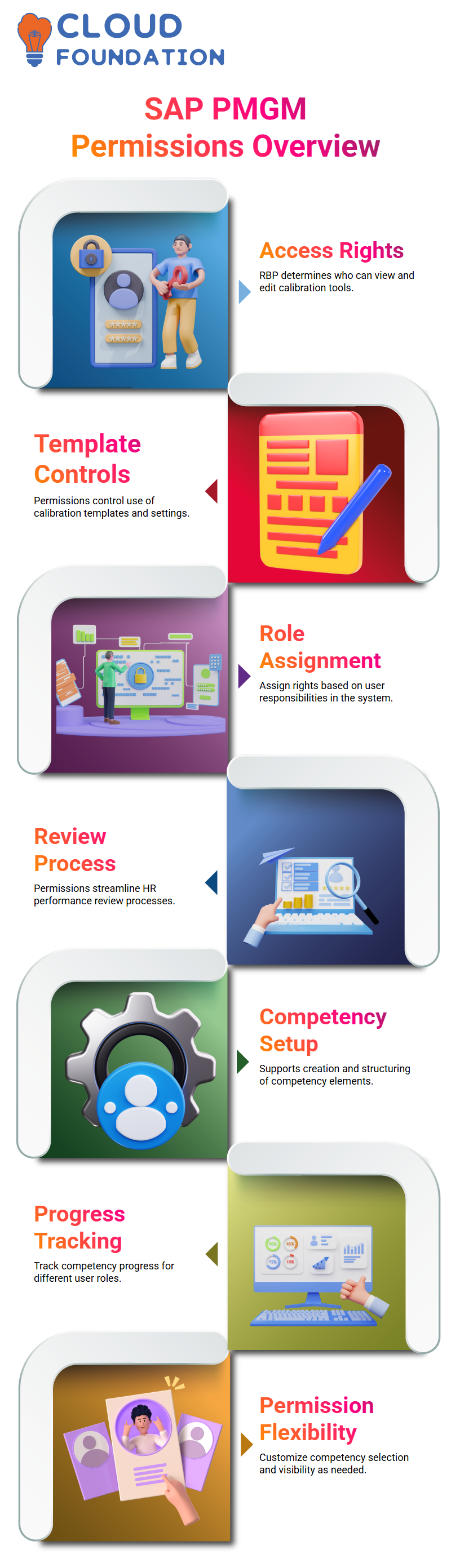
At SAP PMGM, these permissions play a crucial role in enabling HR users to conduct seamless performance review processes and workflows.
Competencies within SAP PMGM
After calibration, my focus shifted towards exploring how SAP PMGM handles competencies.
After following through each of the steps for creating competencies and being impressed at how logical everything was structured, each action added another step toward making SAP PMGM’s interface less daunting for newcomers.
SAP PMGM offers flexibility in selecting and measuring competency requirements across roles, as well as in monitoring progress against them.

Vinitha Indhukuri
Author



