SAP PLM Training | Learn SAP PLM Course
What is SAP PLM?
SAP PLM, or Product Lifecycle Management, is a software solution created by SAP, a primary corporate software provider. SAP PLM is intended to assist businesses in managing their products’ complete lifecycle, from conception and design to manufacture, sales, and support.
SAP PLM acts as a collaboration platform, enabling teams across different departments and locations to collaborate on product development projects. It creates one source of truth for product data so that every user has the latest information.
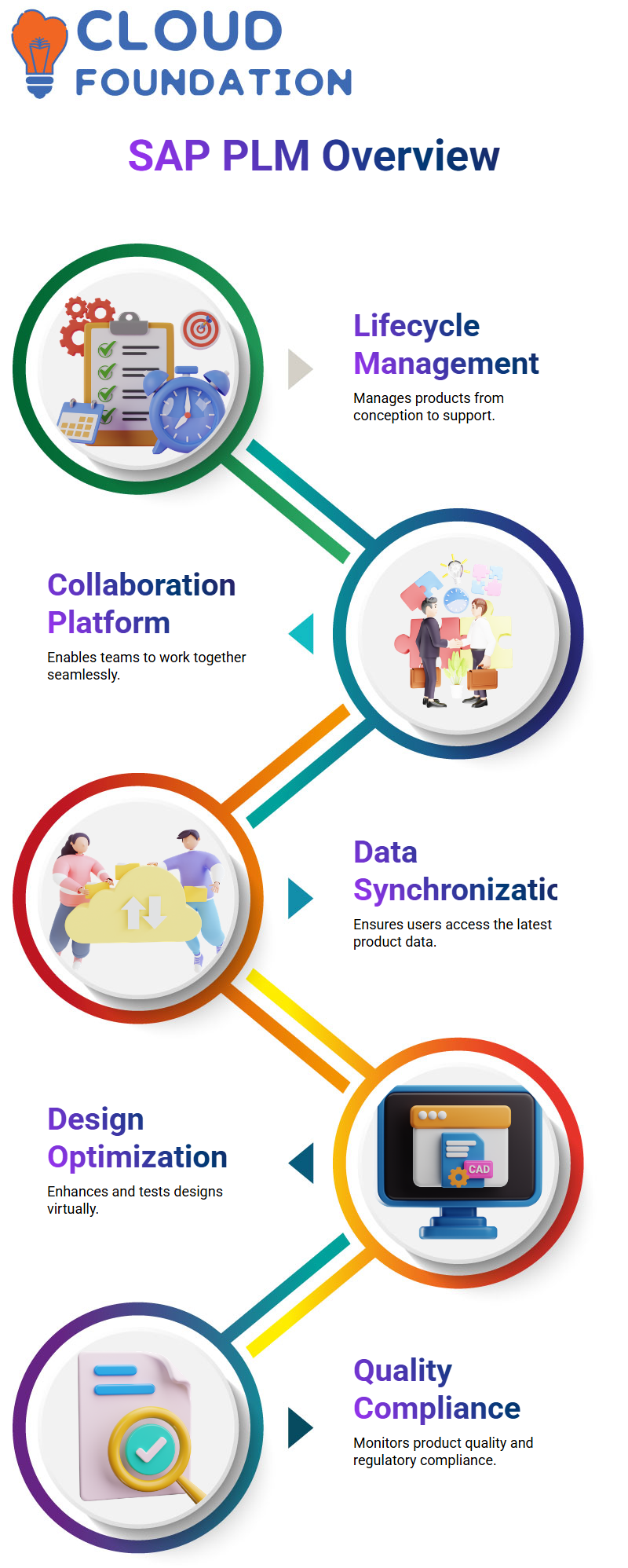
SAP PLM offers different tools and capabilities for various product lifecycle stages. For example, teams can use it to capture and evaluate new product ideas and create initial prototypes during product ideation and concept development. Similarly, engineering and simulation features enable them to enhance designs and test their performance virtually.
When the manufacturing phase approaches, SAP PLM helps manage production processes so that materials are correctly ordered on time and scheduled, and production runs smoothly. It also monitors product quality by ensuring that items meet quality standards and comply with regulations.
It has these core functions, and SAP PLM has multiple expansions and connections for specific industries.
Benefits of Using SAP PLM
The SAP Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) application provides a comprehensive solution to manage the complete product lifecycle, from the first idea through manufacturing and retirement. The following are some key benefits of using SAP PLM.
Enhanced Product Quality: With SAP PLM, companies can store their product-related data and processes in one place so all stakeholders can access the most current information. This reduces errors and inconsistencies in design and manufacturing, resulting in higher-quality products.
Increased productivity: By automating and optimising product development processes, SAP PLM enables enterprises to shorten cycle times, cut costs, and boost productivity. This allows businesses to introduce new items to the market faster and more efficiently, providing a competitive advantage.
Better Collaboration: With SAP PLM, cross-functional teams may interact more efficiently, breaking down silos and boosting communication. This helps to guarantee that all stakeholders are aligned and working toward the same goals, which leads to better outcomes and higher levels of creativity.
Enhanced Compliance: SAP PLM delivers tools that assist firms in complying with industry norms and standards. This comprises tools for managing product compliance, quality, and safety and features for monitoring and reporting compliance-related operations.

Better Visibility: SAP PLM allows businesses to view real-time data concerning product development processes, thus enabling them to improve their decision-making abilities and respond quickly to changes in the market. This lowers risk, enhances agility and increases overall business performance.
Flexibility: SAP PLM’s scalability feature can help any organisation grow as its needs change over time. It is, therefore, suitable for companies that are expanding rapidly or have complex product development requirements.
Integration: SAP PLM effectively interfaces with other SAP products, third-party tools, and systems. This allows firms to construct a uniform system for controlling product development processes, increasing productivity and decreasing errors.
SAP PLM is a powerful tool that may assist enterprises in improving product quality, increasing productivity, enhancing collaboration, ensuring compliance, improving visibility, scaling operations, and integrating other systems. Organisations can obtain a competitive advantage and achieve long-term success by capitalising on its benefits.

SAP PLM Training

Prerequisites for SAP PLM
SAP Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) is a comprehensive solution that allows enterprises to manage their products’ complete lifecycle, from conception to retirement. However, enterprises must consider many conditions before deploying SAP PLM to ensure a successful rollout.
Specific Trade Objectives: Before implementing SAP PLM, it’s imperative to set specific trade objectives. This encompasses identifying particular challenges the enterprise seeks to solve with the PLM system, such as reducing time to market, enhancing product quality, or cutting down on development costs. Well-defined trade objectives will drive the deployment of PLM and ensure it aligns with the general organization strategy.
Information Management: Accurate and current product information is essential for SAP PLM to function efficiently. Therefore, companies need to develop a good data management strategy. This involves identifying data sources, determining who owns what data, and implementing policies on data governance. It is also essential to clean and standardize data before importing it into the PLM system.
Integration: SAP PLM must be connected with other systems inside the firm, including ERP, CRM, and supply chain management systems. This necessitates careful planning and collaboration with the appropriate stakeholders. The integration should be seamless, with data flowing seamlessly between systems.
Process Mapping: Before implementing SAP PLM, organizations need to map their product development processes, which include identifying stages in the product development lifecycle, team handovers, and associated tasks and responsibilities. This is to set up the PLM solution to support the organization’s product development processes correctly.
Training: SAP PLM needs appropriate training to be used effectively. Therefore, companies should carry out change management projects and provide training. The users must be comfortable with this system, knowing what it can do and how to use it best.
Infrastructure: For SAP PLM to function correctly, there has to be a good IT infrastructure. IT structures include servers, storage devices, and network facilities. An organization must have sufficient infrastructure to support the PLM solution and accommodate future expansion.
Support: Businesses require a support system to ensure the PLM solution is always maintained and improved. This encompasses having a dedicated team for administering the PLM technology and possessing an SAP support contract or one from a certified partner.
Installing SAP PLM requires careful planning and consideration of many prerequisites. Meeting these requirements will guarantee success during SAP PLM implementation, enabling companies to manage their product lifecycle more efficiently and effectively.
SAP PLM Tutorial
SAP PLM (Product Life Cycle Management) is crucial in product development and manufacturing. It’s the process of bringing a better product to market, letting customers use it, and then making it even better according to their feedback from start to finish.
After that, this information goes back downstream, where manufacturing takes on board these comments about what was done right or wrong so that they can meet people’s needs with new product development or changes/updates of current ones.
Product Development:
Product development consists of many stages like: research & and development, manufacturing and launching. WVS (Work Breakdown Structure) captures product costs and financial happenings.
When a need has been confirmed as a requirement, it is sent for testing, prototyping and finalisation where appropriate. Formulation can only begin after verifying that one version of the need works appropriately.
Once the formulation has been completed, checks are carried out to ensure the product meets all applicable government regulations. Each stage of this process involves a particular set of users or authorised persons.
After completing the compliance checks, the item is handed over to production, where the production engineer takes it from the R&D and commences manufacturing before eventually introducing it into the market.
New Product Development:
New product development triggers happen during the development process and can be used for innovation, launching a new product, renovating current products, or making a new formulation.
This formulation has several critical points or pain points. These points deal with what should be achieved, who it should target, and what measures need to be taken to avoid failure in meeting the customer’s needs better.
Product Life Cycle Management (PLM) offers another view of this process and its best practices. For the processing industry to apply Statistical Process Control, a standard pre-configured procedure must be purchased with a pre-configured license.
SAP has introduced Innovation Management:
The company termed innovation management a cloud component created by SAP that allows people from within and outside the company to suggest ideas about product improvement. SAP presents this as a solution linked with project and portfolio management and R&D resub development models.
Innovation management is an open platform for exchanging concepts for better products. Through innovation management, a software-as-a-service system, clients may request enhancements or new flavours for their current items and input suggestions.
After an idea becomes a requirement, it is certified and authorised by the product stakeholders. Owners file these ideas against products within organisations before working with suppliers on their incorporation and installation.
Project and portfolio management are connected to the module for managing innovation, as is the development of applications for refunds through the R&D department. When a person buys innovation management, they get controlled feedback from clients or other consumers, including recipe designing.
The customer’s needs are on the left side; when the R&D unit has made changes, the new component is delivered directly to the company concerned. The product being asked for in recipe design should be developed around its constituent elements.
The innovation management system can be linked to recipe creation so that the marketing team can record input and send it to a simulator or formula designed for such recipes.
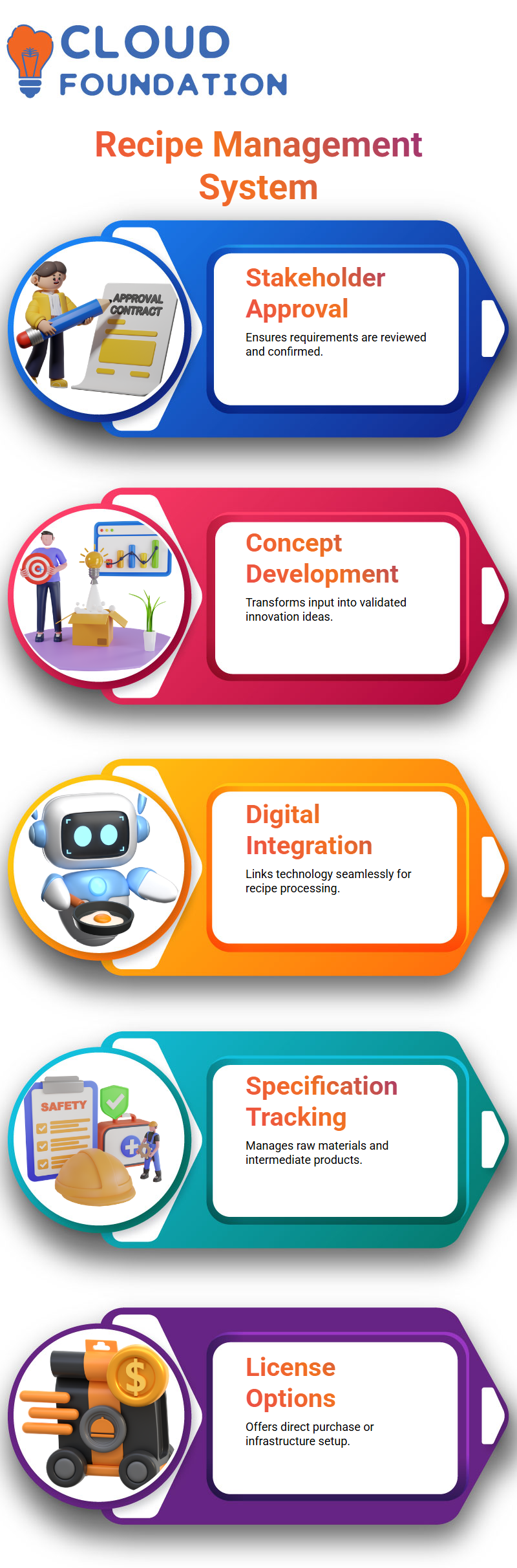
Before creating recipes, stakeholders of these products must approve and confirm their desire as a requirement.A release plan is configured for approval, and the status of a requirement is specified.
The innovation management process includes gathering input, coming up with a concept in innovation management, having it reviewed by different stakeholders and releasing the idea as a requirement. An ID for the requirement is created once it has been approved and is linked to the recipe.

The recipe creator then creates a new product version by substituting one specific part for another or changing one component with another. Different teams will discuss the concept and generate access forms if the need arises later.
Digital Technology Integration:
Digital technology integration will become more common in the processing business. The first stage of SAP PLM is a specification, which entails building a recipe from another. Recipe developers utilize SAP PLM specification management to keep track of raw materials, semi-finished items, and intermediate product information. In the standard business process, recipe developers save all data somewhere, either in an ERP or a third-party application.
In SAP PLM, recipe development entails generating specifications for semi-finished, raw, and intermediate items. This specification is preserved in SAP terms, and a recipe is created to load these raw materials into the system. Once all values are satisfactory, the recipe can be filed and approved for manufacturing.
When customers purchase a product from SAP PLM, they have two choices: buy the license directly from SAP or purchase the license for infrastructure setup from SAP.
SAP will pre-configure the system by assigning a license number. As a functional or business process consultant, you must handle several requirements that address all raw materials, self-finish, finished, and intermediates.
SAP provides customers several alternatives for implementing their products, including specification management, recipe creation, document management, and change management.
Customers who select the pre-configured system option can save money on license fees while still using the SAP PLM system without purchasing the whole package.
Four stages of SAP PLM
Product life cycle management (SAP PLM) has four primary stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Before a product is released to the market, it goes through the introduction stage, which includes research, conception, and design. Manufacturing, marketing, and product release are all part of the growth phase, including client segmentation and distribution.
The second stage comprises increased competitiveness and client demands, which result in higher distribution and demand.
The third stage is maturity, during which the product becomes widely available and has no significant impact on advertising. At this point, advertising has little effect on demand.
The fourth stage is decline, in which the product becomes obsolete due to rising client demand and is rendered irrelevant. This is illustrated in the graph of product life cycle management.
During the introduction phase, the product increases in response to client demand and competition, but as it matures, its scale reduces or becomes irrelevant. The decline phase is when a product becomes irrelevant and obsolete.
If we map out the stages in a generic product life cycle, these are applied designs, supply chain management, production and delivery, consumption and service, and end-of-life. The introduction phase and the decline stage output are used as inputs for each other.

Finally, products must be designed to meet quality and environmental characteristics. Attributes that can be built into products at the design stage include durability, reparability, and upgradability. This is why there need not be such a trade-off between economic requirements regarding the environment.
Quality refers to a product or service’s total features and characteristics that affect its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs.
The description includes operational performance, durability, reparability, appearance, spare availability, ease of maintenance, and serviceability.
If we look at it correctly, this would imply higher costs in the short run due to higher initial investments. Still, they pay off through lower expenses over time because they reduce material depletion rates.

SAP PLM Online Training

Modes Of Learning SAP PLM
SAP PLM, also known as Product Lifecycle Management, is an advanced technology that enables companies to oversee the entire life cycle of their products, from creating an idea to design, manufacturing, servicing, and disposal. To fully harness this tool, one must learn how it should be used optimally. Below are ways through which one can study SAP PLM
Classroom Training: SAP provides various training courses for individuals to learn about PLM. These courses are taught by instructors with a thorough knowledge of the subject matter. They usually occur in a physical classroom, allowing for direct communication between the teacher and students through lectures, demonstrations, and practical activities. Such training is recommended for people who prefer structured learning environments and immediate feedback on their queries.
Online Training: SAP further offers various online training courses, which enable learners to get information and do tasks when they have time. The training is found online, meaning even those far away can benefit. On its platform for online training, SAP has set up interactive simulations, quizzes, and exams that help evaluate how much a student knows their skills.
Self-paced E-Learning: SAP provides numerous e-learning courses based on high-quality content guidelines. These courses allow students to optimize them at will. They feature interactive simulations, videos, and other multimedia. This option is perfect for individuals who want to control their learning process and have access to training resources whenever they need them.
Virtual Classroom Training: SAP provides virtual classroom training, which combines classroom and online training benefits. Virtual classroom training occurs in real-time, with an instructor directing the class through lectures, demonstrations, and exercises. Learners can ask questions and receive real-time feedback, like in a typical classroom setting. Virtual classroom training is a good choice for those who prefer the structure of a classroom setting but require the flexibility of online training.
Coaching and Mentoring: SAP offers coaching and mentoring services, allowing learners to work one-on-one with a skilled SAP PLM specialist. Coaching and mentoring are good options for those needing individualized assistance and support when using SAP PLM. Coaches and mentors can provide feedback, answer questions, and assist learners in overcoming any problems.
SAP PLM Certification
SAP, the company behind popular business software systems such as logistics and accounting, offers a certification called SAP Product Lifecycle Management (PLM). The program is intended for people who want to demonstrate their ability to manage the entire process of developing a product, from idea generation through disposal, using SAP PLM systems.
This certification examines various aspects, including but not limited to product data management, engineering change control, collaboration, etc., which are all covered within SAP’s scope.

Get the SAP PLM certification by passing a difficult exam with multiple-choice questions and practical scenarios. This test is multilingual and available at SAP certification centers worldwide.
Having the SAP PLM certification offers several advantages for people and organizations. With it, individuals can develop their skills in PLM, learn more about different job opportunities, and earn more money simultaneously.
On the other hand, this certificate will enable companies to ensure their staff is well-equipped with the skills needed for proper product lifecycle management. This will reduce mistakes and rework, thereby enhancing quality across all products.

SAP PLM Course Price


Deepthi
Author