SAP MDG Tutorial for Beginners
Definition of SAP MDG
SAP MDG allows organisations to build, exchange, and manage master data across applications and processes – centralising master data by pooling it from various applications – thus saving time while improving master data accuracy while streamlining procedures.
It supports data validation, version control workflow multilingual support. Furthermore, it covers suppliers’ customers commodities plants cost centres etc as key master dataelements.
SAP MDG Overview
Organizations may use SAP MDG to securely store, administer and update master data entities like customers, products, vendors and suppliers in one central repository.
Data analysis tools help ensure data correctness, quality, integrity, and regulatory needs. SAP MDG also facilitates simplified maintenance tasks by automating data processing tasks; reports on legal issues; facilitates replication across systems; and makes maintenance tasks simpler overall.
SAP MDG also facilitates organisational master data through application-specific modules, keeping up-to-date industry-specific material lists and project mandates while managing organisational master data like cost centres and organisational structures.
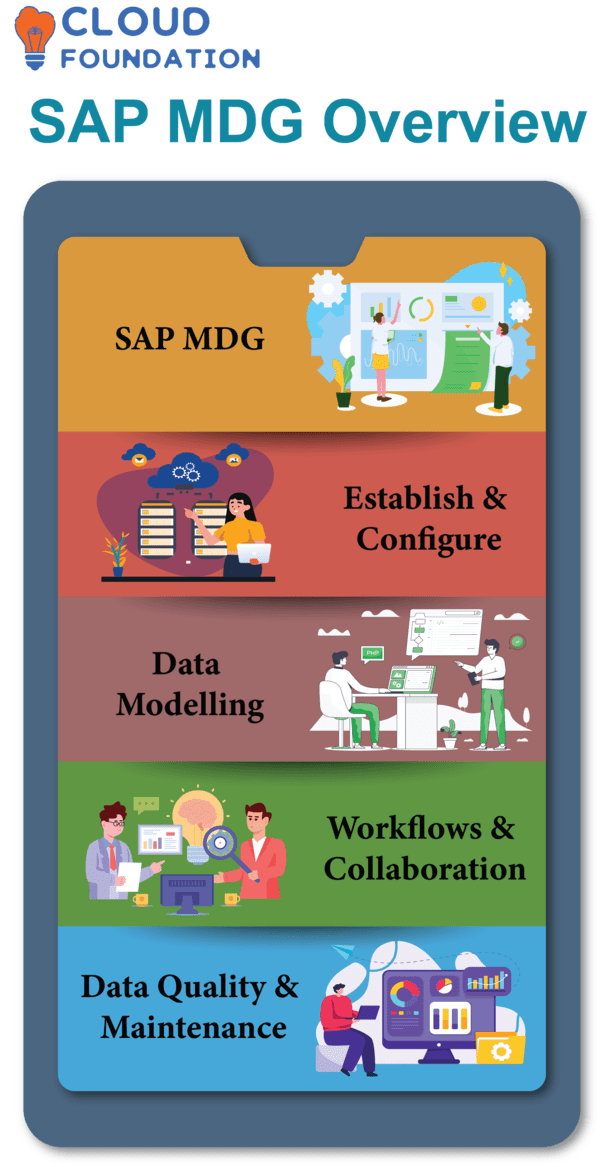
SAP MDG: SAP MDG is designed to enhance data quality and control across an enterprise by means of modelling, consolidation, collaborative workflow and validation services integrated within its comprehensive master data management (MDM) platform.
Establish and Configure: Setting up SAP MDG requires system configuration and source data loading; create user profiles and data validation rules before beginning this step.
Data Modelling: After setting up the environment, create a data model which establishes data structure and relationships for every MDG project.
Workflows and Collaboration: SAP MDG offers unique capabilities for improving business-IT collaboration, such as designing workflows to ensure data entry accuracy as well as giving business users a standardized cloud-based platform from which they can access Master Data.
Data Quality and Maintenance: SAP MDG offers solutions for master data cleansing and management. Validating user input and cleansing the data help maintain data integrity, as does managing hierarchies and maintaining object relationships.
SAP MDG Tutorials or MDG SAP Tutorial
SAP Master Data Governance Tutorial (MDG SAP tutorial), ensures data quality and consistency across a company’s sales, operations, marketing, finance and more – across sales force automation (SFMC), CRM/ELN systems as well as standardised master data management systems and across business areas by standardising master data governance across systems and business areas.
It can speed up data entry while decreasing errors and tracking changes more efficiently and tracking changes more closely than traditional forms.
With process automation and validation tests in place, this expedites entry speeds and errors reduction while streamlining and tracking any future modifications to data changes.
This can serve as the focal point of an integrated master data source that is shared throughout a corporation.
Data integrity, consistency and completeness provide key advantages in standardizing structures across diverse systems.An SAP MDG tutorial can demonstrate how this platform can assist a company.
Topics often covered during an SAP MDG tutorial include mastering data design, creating SAP-certified MDG scenarios, automating processes, validating tests, correcting discrepancies in data, data provisioning/maintenance as well as SAP application interaction.
SAP MDG Tutorial usually covers these topics:
SAP MDG Data Model
SAP MDG Tools
SMT Mapping in SAP MDG
UI Modelling in SAP MDG
SAP MDG Consolidation
SAP MDG Finance
Key Mapping in SAP MDG
SAP MDG Workflow
MDG Security
SAP MDG Architecture

SAP MDG Training

SAP MDG full form or MDG full form in SAP
SAP Master Data Governance (MDG) is the MDG full form SAP or MDG in SAP full form.
SAP MDG Data Model or Data Model in SAP MDG
The SAP MDG data model features unique data domains with automatic governance rules, strong validation rules and configurable fields – everything needed for efficient master data management as well as completeness.
Businesses rely on this solution for master data integrity management.
SMT Mapping in SAP MDG
SAP Master Data Governance (MDG)/SMT Mapping assists SAP MDG users to connect custom master data fields from SAP ERP or other external systems directly into its Standard Master Template database for creation and maintenance purposes, simplifying system-wide master data creation.
This mapping capability saves both time and resources during maintenance efforts.SMT mapping involves mapping SAP ERP or external master data fields into SAP MDG fields.
It will establish how source values will be converted to target values for each field mapped; setting business rules helps set conditions that determine this mapping condition.
Entering master data into SAP MDG follows mappings and business rules; SMT mapping and master data values will automatically populate. This ensures consistent master data modifications across platforms.
SAP MDG Tools
SAP MDG’s Tools unify master data assets across systems, applications and divisions to ensure data accuracy for increased system resiliency, reduce discrepancies which lead to errors and inefficiency while automating approvals/notifications/integrations with business rules as well as real time display of assets via its web-based interface for ease of master data management as well as real time asset displays.
SAP MDG Module
SAP MDG Module allows enterprises to rapidly produce, modify and deprecate master data such as customers, materials, vendors, financials and organizational/employee records.
Real-time audit trail information ensures data consistency across systems and democratises master data maintenance, change, and retirement processes.
SAP MDG solutions also support integration between SAP and non-SAP databases as well as secure workflow task management for improved productivity.
By creating one centralized master data source that remains up-to-date and consistent across business processes, ERP provides one consistent master data source that supports them all.
SAP MDG gives organisations an effective solution for increasing master data accuracy, reducing duplications and managing versioning with effective validations against business rules.
In addition, industry-specific features allow it to control and manage master data more effectively for certain enterprises while its user interface modelling feature gives it added depth of functionality.
UI Modelling in SAP MDG
Data Model-Driven User Interface Modelling makes it simple and quick for users to design and implement user interface models for Master Data objects.
User interface modelling enables users to easily build models of how objects should be represented and utilized within business operations.
A typical User Interface Model comprises forms, tables and lists which interact with an object being modelled; forms for user input as well as rules governing data input/output are often part of such models.
Data Stewards can easily customize master data object behavior and display, improving user experience while making Master Data maintenance much simpler.
SAP MDG’s data validation features allow data stewards to quickly implement business standards into valid data submission into SAP MDG’s system, while its user interface modeling capabilities make designing master data forms and presentations quick and user friendly – streamlining data entry/manipulation operations for end users.

SAP MDG Online Training

SAP MDG Course
SAP MDG Course provides students with an in-depth introduction to master data management concepts and methods, with topics including master data governance, quality, metadata management and integration being covered by this comprehensive SAP course.
Students will explore all facets of building the product suite architecture development, implementation and maintenance while configuring components and mastering master data governance principles.
Business analysts, system architects and developers can all gain something from taking this SAP MDG course. Students will develop an understanding of master data governance as they prepare to adopt SAP MDG solutions within their organisation following completion.
SAP MDG Consolidation
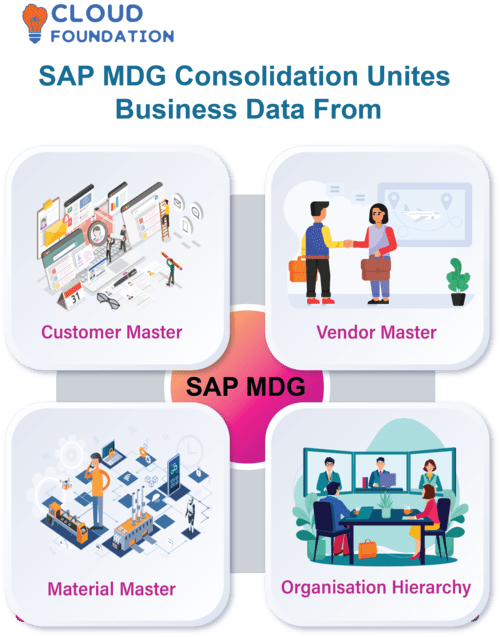
SAP MDG Consolidation unites business data from Customer Master, Vendor Master, Material Master and Organisation Hierarchy intoone central source.
MDG Consolidation filters out redundant variables, duplication and homonyms while standardising master data to achieve alignment and standardisation of master records.
Recognizing records which require consolidation because they were created from diverse sources with inconsistent data is the first step.
A consolidation rule must then be devised in order to integrate records and calculate value accordingly.
Validated records are distributed to other systems and departments, including legacy ones, to maintain one source of truth across all information quality enhancement initiatives.
SAP MDG Finance
SAP MDG Finance serves a number of uses, such as global consolidation, profit center hierarchy alignment, customer credit replication and interest rate table maintenance.
Automated validation and maintenance of customer financial master data with seamless integration to core SAP applications like FI-GL, S/4 HANA and Revenue Recognition.
Centralised financial master data management that empowers stakeholders to collaborate quickly while meeting evolving business requirements.
Client financial master data and credit management; role-based access for sensitive financial data; and Fiori technology to instantly access this data from anywhere enables finance teams to make faster decisions faster.
Key Mapping in SAP MDG
SAP MDG’s extensible object-oriented key mapping architecture gives users a range of tools for custom data keys creation and management.
Users can utilize multilevel parent/child hierarchies, object correlation functions and value assignment functions allowing flexible key mapping solutions that serve a range of uses effectively.
Uniqueness, sequence numbering and dates can all be included into a key mapping structure, while user-specific mapping functions may also be created and maintained.

Finally, the key mapping framework offers an API that enables customisable automated key mapping functions – an essential feature to enable easy implementation and maintenance of SAP MDG key mapping system.
SAP MDG Workflow
SAP MDG Workflow SAP MDG workflow enables an organisation to control, monitor and update master data throughout its lifetime – from creation through destruction.
It enforces data standards to guarantee organization-wide data quality while automating modifications as well as tracking updates to make sure they have proper clearances.
MDG SAP Meaning or SAP MDG Meaning
MDG SAP Meaning or SAP MDG Meaning SAP Master Data Governance automates master data management across business processes and enterprises, saving manual work while increasing data correctness and consistency – helping companies comply with data privacy and security requirements.
MDG Security
Data Backup Solutions Master Data Governance (MDG) Security safeguards Master Data Governance (MDG) data and applications against external threats like viruses.
MDG security includes encryption, role-based access control mechanisms, secure authentication mechanisms, backup solutions and network protection measures that monitor system activity while restricting sensitive information to authorized individuals/resources.
SAP MDG Architecture
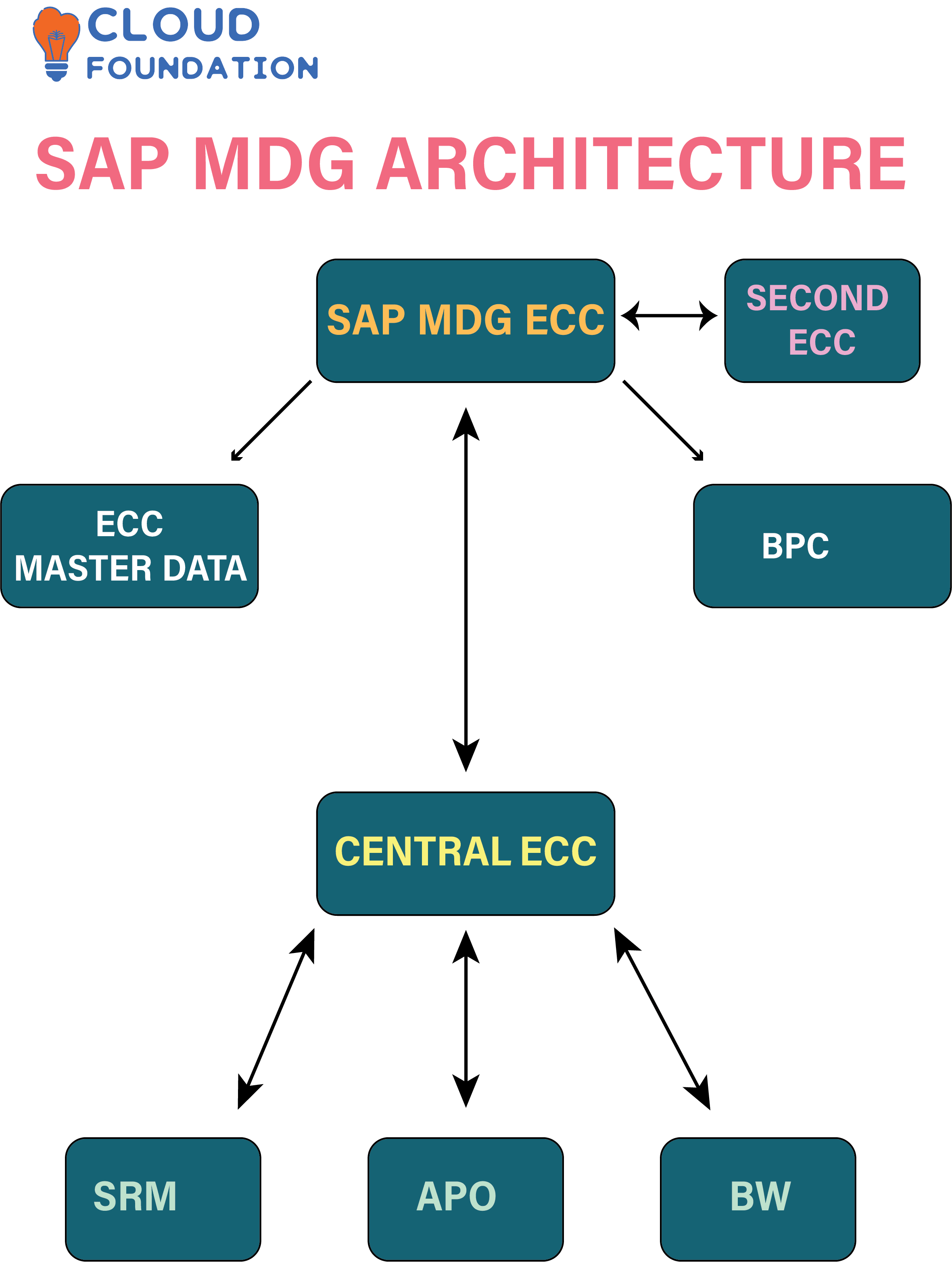
SAP MDG features a 3-tier architecture: data, application and presentation layers. SAP ECC and BW databases serve as its data layer; while its application layer contains an ABAP-written MDG program written using Java Script for data entry/viewing/entry and presentation respectively.
Furthermore, its ERP/MDM integration makes its architecture highly adaptable; many data replication/synchronisation methods exist between SAP MDG and non-SAP systems through these options.
SAP MDG EAM
SAP MDG-EAM (Enterprise Asset Management) helps companies effectively develop, integrate, and manage asset data. Enterprise Asset Master and Configuration Management allow organisations to centralise asset data.
SAP MDG-EAM ensures accuracy, completeness, and relevance – accessing it is made effortless via its user-friendly user interface (UI).
SAP MDG Configuration Guide
This configuration guide walks users through installing and using SAP Master Data Governance (MDG).
Installation, customization, data migration and business procedures are covered within its pages; providing users with all of the knowledge required to efficiently set up and use this product efficiently – configuring SAP MDG suite functions such as master data management, workflow scoring analytics as well as API services are addressed here as part of an easy tutorial experience.

SAP MDG Course Price


Kiranmai
Author
“Bringing you the latest in tech news and insights to ignite your creativity & spark positive change – Welcome to my world of words”