SAP EDI Training | Learn SAP EDI Course
In this blog post, we’ll examine its advantages, implementation methods, and best practices so that your organisation can successfully use SAP EDI with its business partners.
This blog serves as your SAP EDI resource, whether you are new to or experienced in electronic data interchange (EDI).
What is SAP EDI?
SAP EDI facilitates the immediate exchange of business transactions such as purchase orders, delivery orders and advanced shipment notices between two organisations without human involvement or intervention.
Schedule Advance Warning In advance scheduling, Supply Network Operations (SNO) manages jobs sourced before delivery, accounts for GST charges and alerts the user if delivery doesn’t satisfy requirements; this feature enables back-to-back scheduling agreements and external scheduling agreements.
SAP EDI is an invaluable asset to any business; its use automates and simplifies complex processes, relieving users of manual tasks while freeing them to focus on more strategic aspects of their work.
It covers everything for you; no more point-to-point systems require complex coding.
Sending and receiving messages within SAP standards and various implementation levels directly supporting SAP are supported.
SAP EDI training provides an adaptable EDI solution designed to meet the demands of large enterprises and mid-tier organisations.
SAP Inbound & Outbound Scenario enhances direct relationships among EDI partners for large enterprises while offering inbound/outbound processes to mid-sized organisations requiring flexibility.
All Inbound and outbound Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) situations incorporate Runtime Workbench processing phases and static Communication Channel setup.
While EDI helps automate business processes, Point-to-Point Systems often require custom programming.
Further, Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) uses an industry standard for sending and receiving messages.
SAP-EDI directly supports several implementation levels; large enterprises often access EDI Partners directly, while Mid-Range Organizations utilise mid-range, which may either come from or go outward.
SAP Inbound, Outbound Scenario for Renewing an EDI Business Process, runtime Workbench Processes of both Incoming and Outgoing Situations with Communication Channel Set Up Static Communication Channel Setup Framework Partnership Profile, etc
EDI transmits data between applications via electronic systems. Transactions use this format within companies, while documents form organised exchange networks.
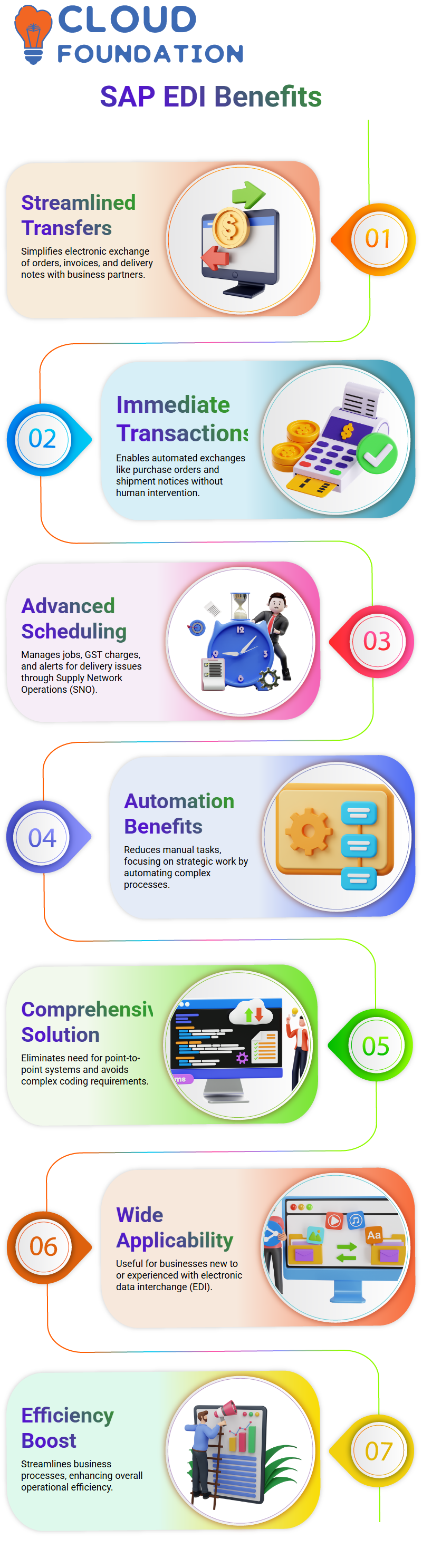
Benefits of SAP EDI
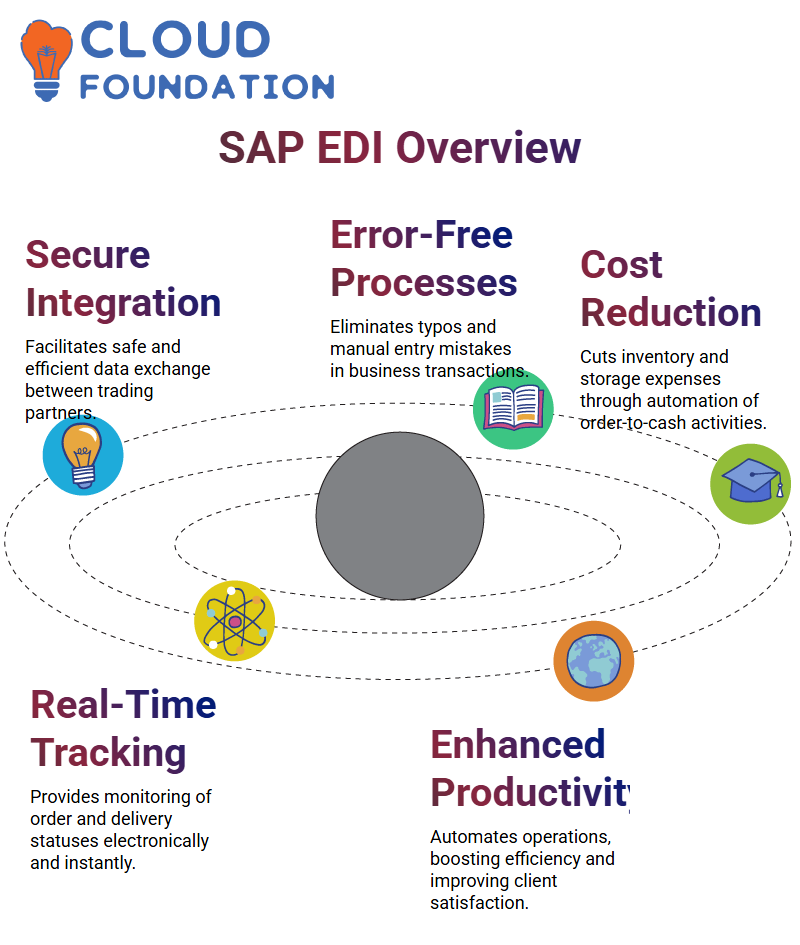
Trading partners can easily integrate communication using SAP EDI transactions to exchange data safely, quickly, and clearly.
Furthermore, SAP EDI eliminates manual entry mistakes, and its computerised approach eliminates typos while supporting correct manual submissions to linked systems.
Automated order-to-cash activities reduce inventory and fulfilment expenses; manual order-to-cash activities become automated, thus reducing inventory storage expenses by half and warehouse storage expenses by half, respectively.
It unifies corporate operations while unifying trading partner business transactions and control, and finally, EDI boosts operating efficiency!
Order, fulfilment, data delivery and payment processing automation reduce overhead costs while increasing productivity.
It helps manage financial flows more effectively while streamlining administration; for instance, EDI automatically generates invoices and delivery notes.
Integrating SAP EDI helps organisations manage orders and deliveries swiftly, accurately, and without errors or delays, improving client happiness, service, and business operations.
SAP EDI’s real-time tracking functionality and tracking capability for transaction orders and deliveries electronically as they occur electronically for tracking purposes is excellent for monitoring order fulfilment status in real-time prerequisites of SAP EDI, including the SAP platforms.
SAP offers SAP-to-SAP and SAP-to-other transmissions using its electronic Data interchange protocol, SAP EDI.
Prerequisites of SAP EDI
Learners should understand basic programming concepts.
I need a firm grasp of SAP ABAP systems and associated technologies, solid communication abilities for effective partner communications, and active listening capabilities to comprehend stakeholder demands entirely.
Time management and solid skills are required to meet service level agreements (SLA) commitment deadlines and troubleshooting skills for handling electronic data interchange issues by SLAs and customer standards.
Spread awareness of cybersecurity practices designed to safeguard IT infrastructure against external and internal threats.

SAP EDI Training

SAP EDI Tutorial
What should you consider when implementing SAP EDI?
Mapping and Translation
When implementing EDI within SAP systems, mapping and translation play an integral part; for optimal results, this requires knowledge of your data structure within both systems and any additional formats that might exist for translation between SAP systems and their target formats requiring translation.
Communication Protocols
SAP EDI supports AS2, FTP, and VAN (Value-Added Network) communication protocols based on data volume, security needs, and cost considerations; the protocol used will depend on data size requirements and cost.
Data Validation
It must include data validation processes that ensure accuracy and integrity, such as creating checks and filters to identify message problems or discrepancies in data sets.
Partner Configuration and Administration

SAP EDI requires trade partner profile setup and administration to function, including communication protocols, mapping standards, and data validation procedures tailored specifically for each trade partner.
Exception Management
Any communication problems and exceptions related to EDI transactions must be managed appropriately to ensure users’ productivity and seamless experience. This usually involves finding the source of any issue before fixing it and reprocessing transactions as soon as possible.
SAP Process Integration
SAP EDI must work seamlessly with SAP order processing, invoicing, and inventory management, and this requires careful design and testing to ensure data flows efficiently between systems.
Security
For adequate SAP EDI data to work correctly, secure communication methods, encryption techniques, and frequent security reviews must be employed.
Scalability
As businesses grow, more trading partners will join, so expanding SAP EDI solutions must handle additional volumes of information while planning and executing them effectively.
Training and Assistance
Users require training and assistance to operate SAP EDI systems effectively. Training should cover EDI, data mapping, and troubleshooting, while support staff must address possible communication difficulties.
How to read SAP EDI File?
Standardised SAP EDI files exchange business documents across computer systems, and these may include sales orders, shipment documentation, and financial transactions.
Steps for reading SAP EDI files:
Launch the SAP EDI Message Monitoring screen (transaction code: WE02).
Please enter a message type (such as ORDERERS), partner number and date range to find an EDI file that meets your specifications.
Select an EDI file from your results and press “Display”.
An additional window displays all segments and data items in an EDI file.
Scroll the file using its scrollbar or navigation buttons and access data quickly and efficiently.
Use Ctrl + F to search your file for specific details.
Click “Display as Basic Type” to examine structured EDI file data.
Expand and collapse segments to examine data pieces within a tree-like data display.
Choose “File” and then “Export” to save an EDI file in Excel or PDF formats.
Once you have finished reading an EDI file, close and return to EDI Message Monitoring.
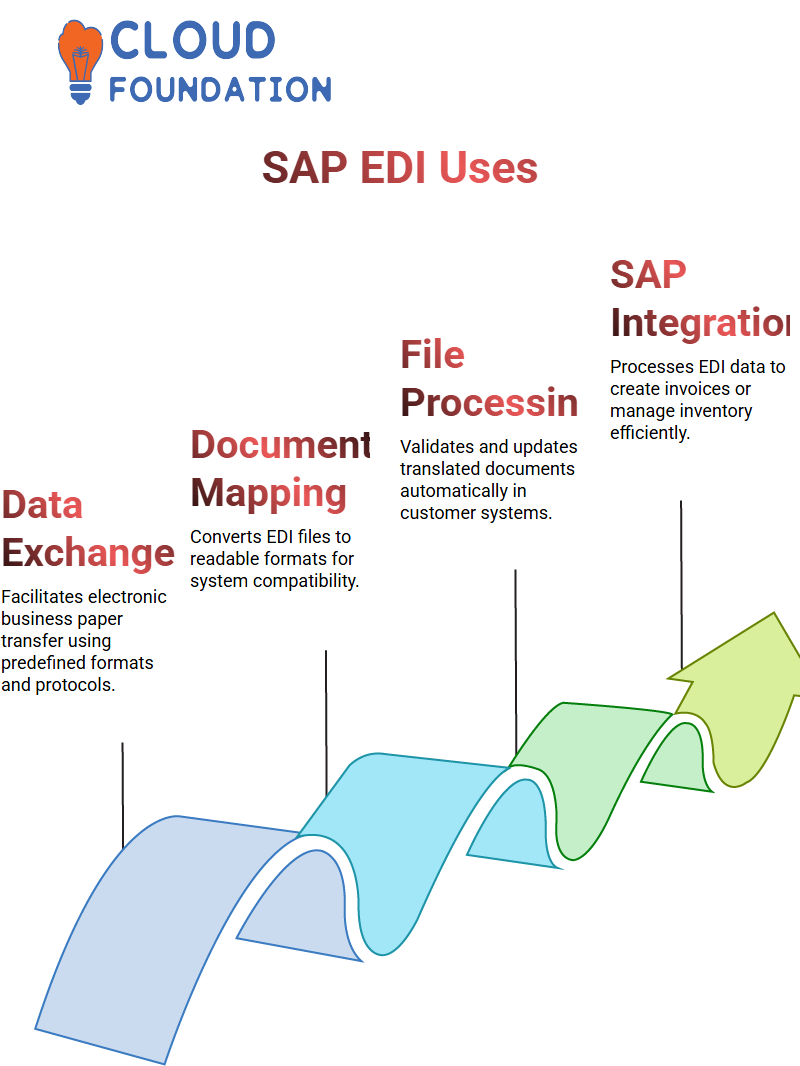
What is SAP EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) Used For?
Computer systems can exchange business papers electronically using predetermined formats and protocols among trading partners.
Configuring Data
SAP EDI setup begins by configuring and outlining which business papers, like purchase orders, invoices, and delivery notes, are to be exchanged via electronic data interchange; additionally, the system needs to be set up to define data interchange formats and protocols.
Document Creation
Once installed and the business papers generated are shared among suppliers and their clients, suppliers use SAP to create purchase orders that they convert to EDI to send to clients using secure channels such as VAN or AS2.
Translating and Mapping Documents
A customer system converts an EDI document to a human-readable form for human reading; in contrast, mapping software converts its standard form to suit customer system formats.
File Processing
Customers’ systems automatically process translated documents, validate data, detect mistakes, and update customer databases as necessary.
Appreciation and Response
After document processing is completed, the customer system acknowledges or responds to inform the supplier’s system that their document has been received and processed successfully.
SAP Integration
Integrating EDI data with SAP completes the process; as part of this step, data sent over from EDI will be received, stored, processed, and used by SAP to create invoices or update inventory levels.
SAP EDI Architecture
SAP’s Electronic Document Interchange Architecture refers to its systems, components and procedures for exchanging electronic documents between SAP systems and external partners or systems.
The architecture includes three core components: SAP system, EDI subsystem and communication infrastructure.
SAP System
At its core lie all business applications and SAP database data for applications and business practices within it, including procedures, information sharing, and document management services.
Subsystem for Electronic Data Interchange
This component enhances SAP EDI capabilities. An EDI converter transforms SAP-specific data to standard EDI format while mapping technology connects EDI documents directly with SAP documents and communicates with other systems.
Communication Infrastructure
Communication Infrastructure is the hardware and software necessary to exchange electronic documents between SAP and external systems via an electronic data interchange protocol such as AS2, FTP or SFTP.
What are Outbound and Inbound Processes Within SAP EDI?
SAP Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) data flows between SAP and external trading partners in two directions: outbound (data transmission from SAP to trading partners) and inbound (transformation into an EDI format for transmission).
Data can flow either way (from SAP), or both directions; inbound processes involve receiving and sending backwards and processes of electronic information exchange with partners from both directions simultaneously.
Data could include purchase orders, invoices or any other SAP business documents; trade partners receive them using AS2, SFTP or FTP and process them using their system.
Incoming data transfer involves data flowing inward into SAP from external trading partners.
An external partner sends data in EDI format directly to SAP, which converts and processes it before importing it into SAP for further processing. There are various modes for learning SAP EDI online training.

SAP EDI Online Training

Modes of Learning SAP EDI Course
Online Training: Online training uses webinars, videoconferencing, and live-streaming technology to offer learners flexibility in timing and location; they can access instruction from any location with internet connectivity.
Instructor-Led Training Sessions: Experienced instructors lead physical training sessions so you can experience and use SAP ODI technology.
Self-Paced Learning: Students may access pre-recorded videos, online courses, e-books, and other study resources at their own pace. This option suits independent learners well.
Classroom Training: Classroom training involves having one instructor instruct multiple participants at once in an organised and controlled learning environment with ample opportunity for structured learning and peer interactions.
On-the-Job Training: Students work on real projects and assignments as part of their learning experience, making this training invaluable to ODI experts who wish to expand their expertise further.
E-Learning: E-learning educational content is delivered online through modules, quizzes, and study material.
SAP EDI Certification
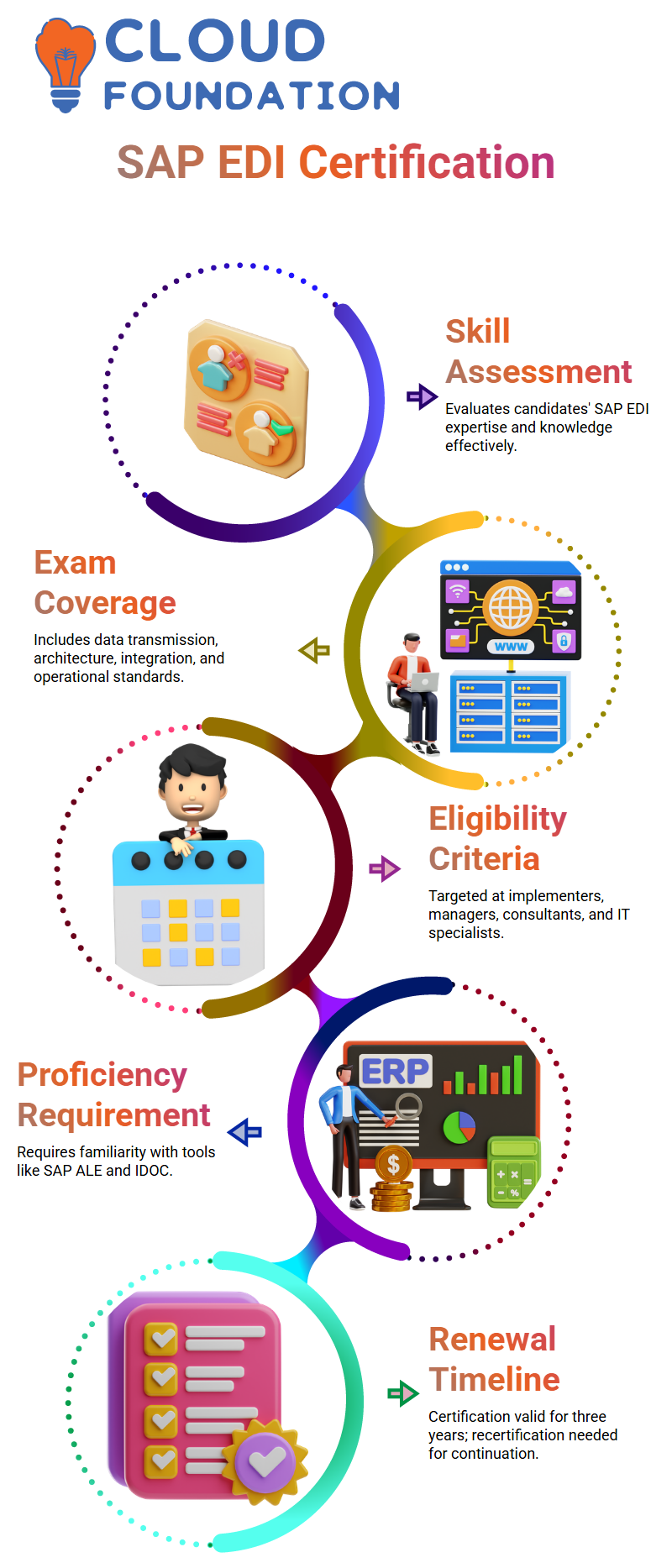
It provides SAP EDI Certification that tests candidates’ SAP EDI skills and knowledge.
Document Management Systems allow companies to exchange corporate documents among computer systems using an established format.
SAP EDI online course certification involves passing the SAP Certified Application Associate EDI exam, which covers aspects like architecture, data transmission methods, SAP integration, and standards for business operations.
Qualification for implementers, configures, managers, and consultants of electronic data interchange (EDI).
This certification process includes functional consultants for SAP functional modules and IT specialists integrating SAP with external data systems.
When applying for the certification test for the SAP EDI online classes, one must demonstrate proficiency with SAP tools and technologies such as SAP ALE and IDOC.
Certification lasts three years; therefore, recertification tests must be passed before expiration to retain it.

SAP EDI Course Price


Srujana
Author