OSPF Tutorial
What is OSPF?
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is one such link-state routing protocol. As one-link state writing protocols go, OSPF uses interconnection information from each router in a specific part of a network to determine interconnectivity among them and thus make up interconnected network that knows its next router’s position in real-time.
OSPF works by connecting various routers within an area to various networks within this zone, so they may share resources and share information across their connections.
Routers exchange this data, so all have an accurate picture of their network.
OSPF is an essential routing protocol used in corporate networks. This powerful routing protocol creates a comprehensive map of their networks for ease of navigation as well as sharing of information between routers.
OSPF works like a puzzle: different routers come together in specific areas to form networks that serve them all.
Optimal Network Address
The Optimal Network Address (ONA) is an open standard that enables routers to exchange information and build adjacency and neighbor relationships among themselves.
These routers work in concert to form the link state database and map of their network, which stores information regarding all available and interlinked networks.
Routers exchange link-state advertisements (LSAs) in order to inform each other about available networks and their interconnections, with LSAs within each router being combined together into network maps.
Once this map has been established, its location becomes apparent along with an understanding of all interconnections among routers as well as their respective bandwidth capacities.
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol provides routers with an essential means for communicating and cooperating on all aspects of their network, from communication among routers themselves through exchanging LSAs (link state advertisements) and exchanging other forms of data exchanged among them.
By understanding their network’s connections and available bandwidth for each link, routers can make more informed decisions regarding its best path forward.
Optimal Route Selection in OSPF
Optimal Route Selection algorithm provides a tool for locating the shortest path between any network and an intended destination.
An algorithm and data are utilized in making informed decisions regarding the most cost-efficient routes to a specific network. Once created, this pathfinder determines what path will lead there.
Route information from other sources that still advertise this network could have an influence on where to place the route in its IP routing table; if they seem more believable than OSPF, routers will most likely believe them instead of placing the data directly in OSPF’s routing tables.
An OSPF network gives routers the power to select different routes based on information from source devices.
The Optimal Route Selection (OPS) algorithm provides an effective means of optimising network routing and decision-making.
By understanding its terms, routers can make informed choices regarding which routes would provide optimal routes to reach certain networks thereby improving overall network performance.
Router
A router may request missing components from other routers if its attempts at building its link state database but come up short; should such components exist elsewhere and cannot be located, other routers might provide it as part of their inventory.
Routers are communication systems used for sending and receiving information between routers.
A router does not exchange packets directly but rather exchanges forms of information exchange between its members.
An attempted link state database construction by one router but lacking one piece can request assistance from other routers to see if anyone may possess that piece.
By doing this, work can continue unimpeded while checking to see who might have what it needs for completion of their puzzle.
Routers play an indispensable part in shaping neighborhoods and the exchange of information among them, acting like information between routers. While technically they do not exchange packet types themselves but instead exchange information.
Concept of a neighborship and an adjacency in OSPF
Neighborship and adjacency refer to two forms of relationships. In essence, neighbors refers to anyone sharing a router on their network who exchanges hello messages with another neighbor on it.
Neighborly hello messages use IPv4, not broadcast, to reach their neighbor at 224.0.0.5 address.
A neighborship relationship occurs between people living together who work on projects together.

When one neighbour provides helpful information or assistance that fills an informational void for another neighbour, this relationship shows its appreciation by exchanging this link state link state link state state link state link state link state
Neighborly relationships include those in which two neighbors share common interests or boundaries; neighbors typically form this kind of bond through sharing these resources or communicating regularly about common events that happen between themselves.
Distinguishing between neighborship and adjacencies to foster healthy and productive relations among neighbors.
Adjacency plays an essential part in creating link states between routers. By exchanging information to form this state, they help facilitate efficient communications.
Adjacency in OSPF
Adjacency plays an essential role in building link states. Proponents argue that having only a neighbor would not work due to scaling concerns; all routers cannot be adjacent with each other in all cases.
Adjacency plays an essential part in creating link states between routers.
Allowing for faster communications and information exchange, adjacencies help foster more robust networks with fewer failures and breakdowns.
Open System Protocol
Open System Protocol broadcast networks are designed to minimize the number of adjacencies necessary for communication among routers; with six routers alone, this would result in 45 adjacencies required for effective operation.
To address this challenge, designated routers (DRs or BDs), with backup designated routers available should they become unavailable, can be selected as designated routers to reduce adjacencies required and facilitate better communication among routers.
OSPF allows routers to share an understanding of their network in terms of shared views of an OSPF area; they do, however, not technically cover every OSPF area (some networks only having one OSPF area while others having multiple).
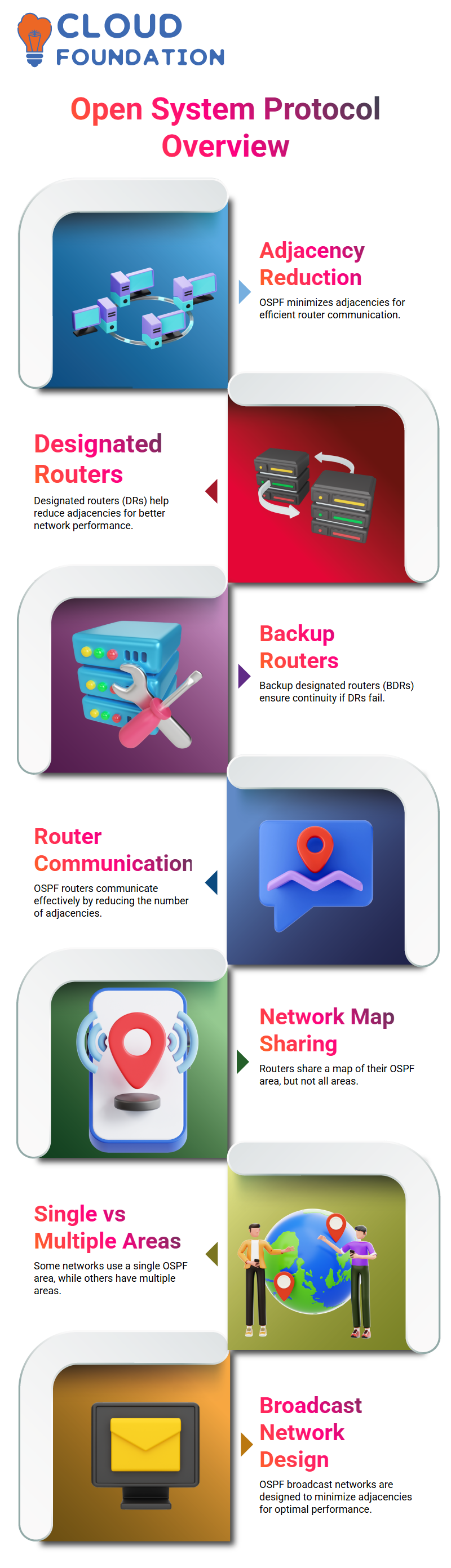
OSPF broadcast networks are designed to reduce the number of adjacencies required for communication among routers, by selecting designated and backup routers as communication partners.
By doing this, OSPF networks can significantly decrease adjacency requirements.
OSPF Organisational Specific Function
OSPF areas vary between networks; some networks only contain one OSPF area while it’s possible to subdivide it further using OSF’s algorithmic division system.
If only one network had OSPF area available to them it wouldn’t make much difference since each OSPF area can then be divided up further using its algorithm.
An ABR’s job is to ensure the network is visible in area zero and can be advertised to area one.
If your OSPF network contains more than one area, all backbone areas with numbers zero must exist or all individual OSPF areas can have zero numbers as backbone areas.
Conclusion
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is an efficient link-state routing protocol which plays a significant role in large scale network communications.
OSPF allows routers to make smart decisions about network design by exchanging information through link-state advertisements (LSAs) and utilising its Optimal Route Selection algorithm, known as OPS.
OSPF facilitates these decisions via its LSA exchange mechanism and OPS implementation. This combination enables OSPF routers to select routes with optimal efficiency across their networks.
As part of their dedication to network performance and effective communication, routers must establish reliable relationships in order to work on building link states collaboratively and maintain an accurate shared view of their networks.
Neighbourship and adjacency relationships play an essential role here; their establishment allowing routers to collaborate on creating link state while sharing an equal view.
OSPF optimizes network topology by minimising adjacencies required and using mechanisms like designated routers and backup designated routers, to achieve maximum network scalability and ensure network topological optimisation.
OSPF provides adaptable and efficient routing in modern enterprise networks through organizational-specific functions and IP prefix lists that enhance its adaptability and efficiency in different network environments. As a result, it serves an indispensable purpose – seamless dynamic routing.

Navya Chandrika
Author



