SAP GRC Tutorial for Beginners
In this blog you will learn about SAP GRC Tutorial and its basics, tool and modules.
About SAP GRC
SAP’s Governance, Risk, and Compliance suite consists of modules integrated within their Enterprise Resource Planning platform to make their GRC suite available to their users.
SAP GRC gives businesses the power to improve corporate governance and mitigate risks in all facets of business operations, automate operational procedures to protect regulations and mandates more easily and minimise operational errors.
By providing key insights that empower decision-makers with knowledge that helps them to take a proactive approach towards any potential hazards or risks to mitigate those risks, predictive analysis provides invaluable support.
SAP GRC can assist businesses in reducing audit expenses, detecting fraudsters quickly, and protecting customer privacy by helping protect customer data privacy and protecting audit costs.
Advantages of SAP GRC
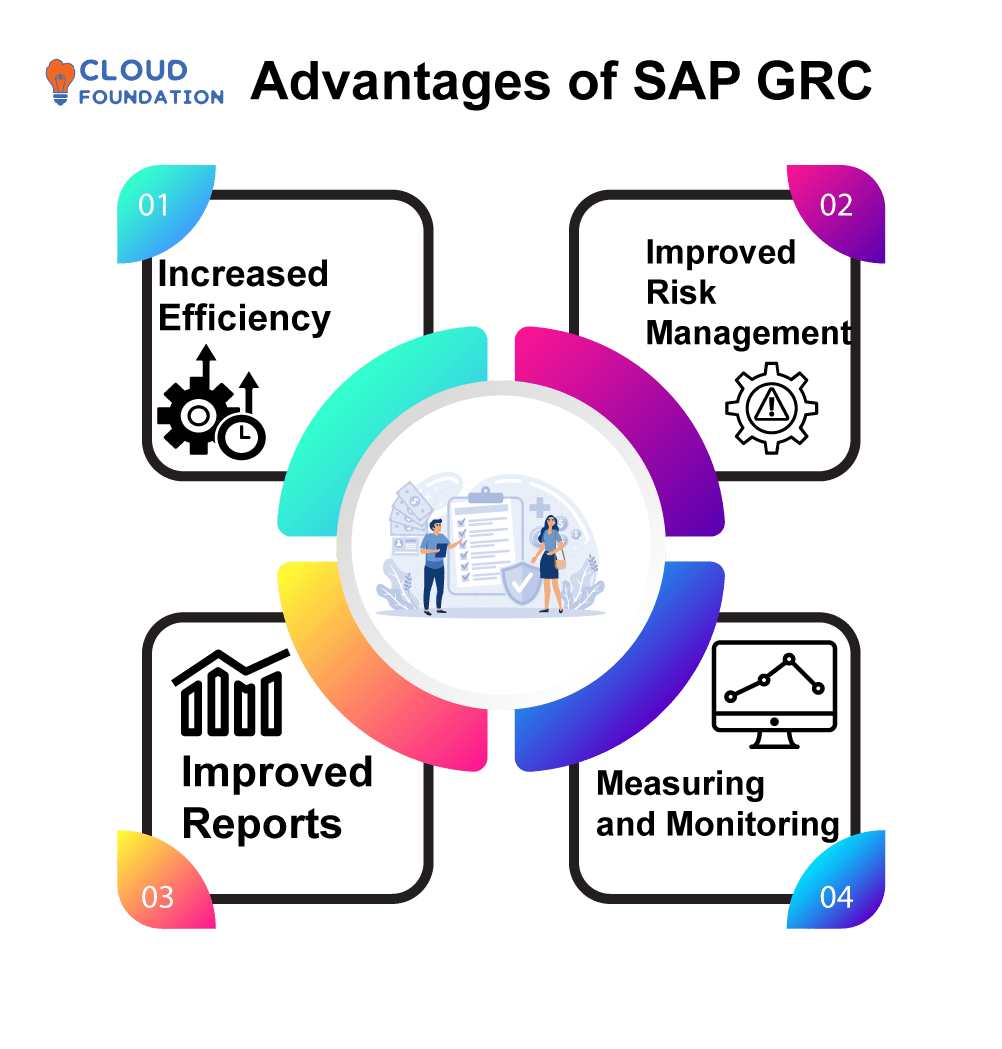
Increased Efficiency: With SAP GRC, businesses are able to transition away from manually performed processes towards automatized ones by taking advantage of GRC solutions to automate workflows and provide consistent access for approved users.
Time and money savings result, in addition to increased efficiency and productivity.
Improved Risk Management: SAP GRC offers companies tools they need to more easily comply with all rules and regulations currently in effect.
By decreasing potential harm and making data more secure while cutting expenses associated with risk management, organizations are better prepared for future situations and can protect themselves more easily against adverse incidents.
Improved Reports: SAP GRC is an invaluable platform for collecting and analysing data that allows organisations to enhance the reports generated about, risk and security activities – offering clear insight into where an organisation should place short and long-term investments.
Measuring and Monitoring: Organizations can leverage this practice to take preventive steps that lower risk, and achieve their business goals more easily.
Features of SAP GRC
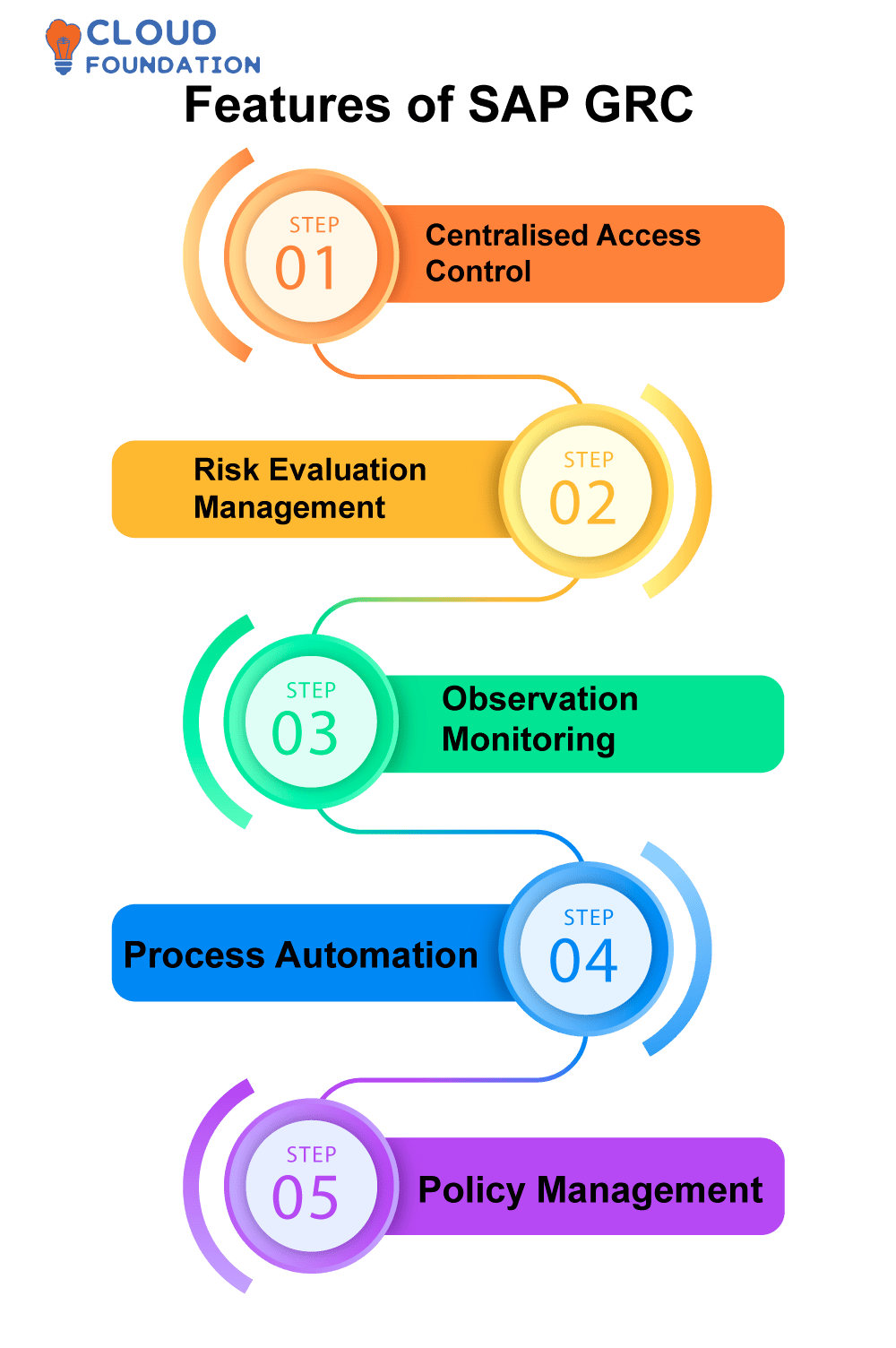 Centralised Access Control: The SAP GRC technology facilitates real-time monitoring and control of access rights, to ensure operations occur according to what has been defined as acceptable parameters.
Centralised Access Control: The SAP GRC technology facilitates real-time monitoring and control of access rights, to ensure operations occur according to what has been defined as acceptable parameters.
Risk Evaluation Management: SAP GRC provides organisations with tools they need to assess potential risks and understand how these could potentially interfere with operations.
Observation Monitoring: GRC allows businesses to effectively track whether or not their processes and policies comply with finance, accounting and legislative rules.
Process Automation: SAP GRC uses workflows to automate essential activities, helping organisations streamline operations while cutting costs while remaining compliant. This makes SAP GRC an indispensable asset.
Policy Management: Our solution equips companies with all of the tools required for overseeing policies related to internal controls and access controls in multiple domains, such as internal controls.
Benefits of SAP GRC
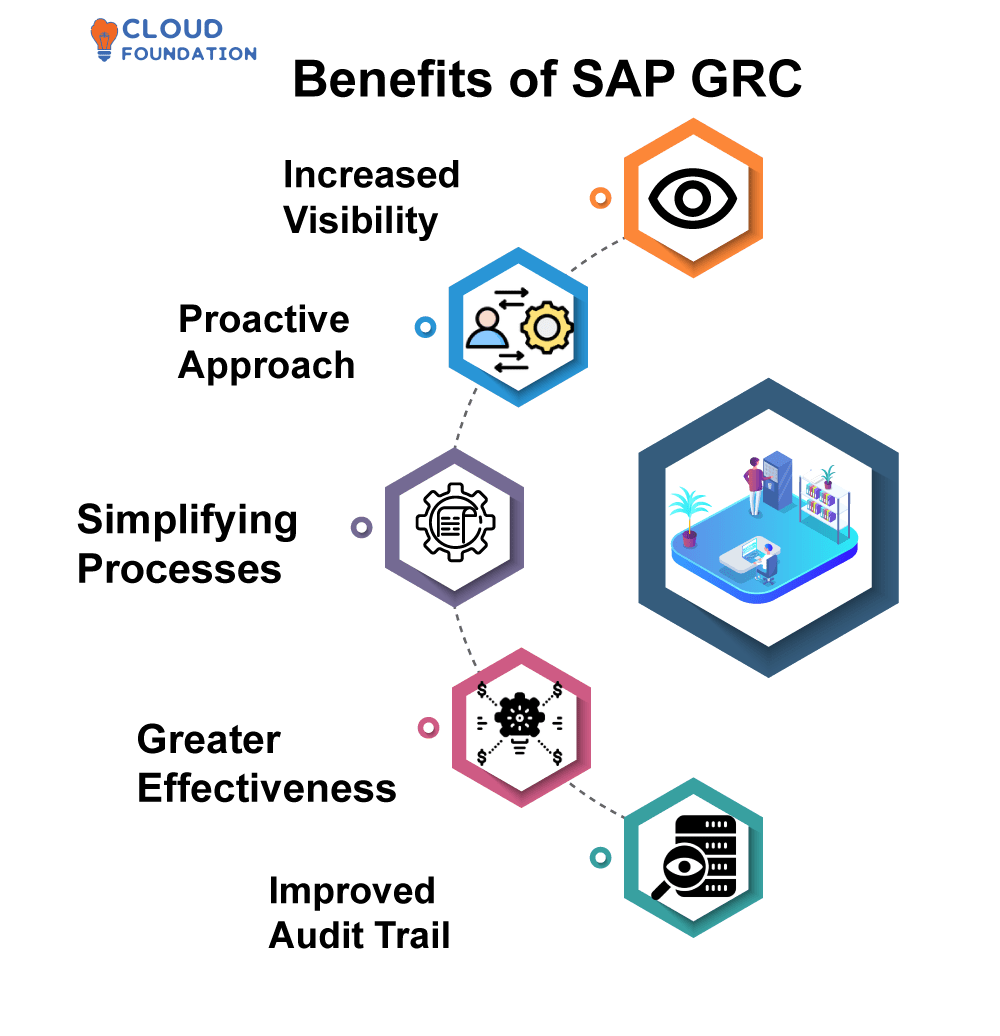
Increased Visibility of Enterprise Risk: SAP GRC ensures all risk and operations for any given business are connected in one centralised location, leading to enhanced visibility into enterprise risk, providing more insight into any faults or problems which may occur in real time.
Proactive Approach to adherence Management: SAP GRC can quickly identify any non- conformityconcerns before they escalate into more significant problems, providing organizations with a faster, more effective response to any risks or difficulties that arise.
Simplifying processes: SAP GRC has features and tools designed to assist with automating and streamlining procedures – one of its three pillars – so as to minimize physical labour requirements as well as resources. As a result, monitoring costs could potentially decrease significantly.
Greater Effectiveness: Businesses using SAP GRC can utilize it to reduce both time and resource requirements associated with -related tasks, freeing them up for other core activities within their organisation that increase efficiency and enhance efficacy.
An Improved Audit Trail: SAP GRC’s audit trail feature can offer organizations a detailed insight into any concerns from the beginning, helping quickly detect and respond to non-concerns quickly and efficiently.
SAP GRC Version
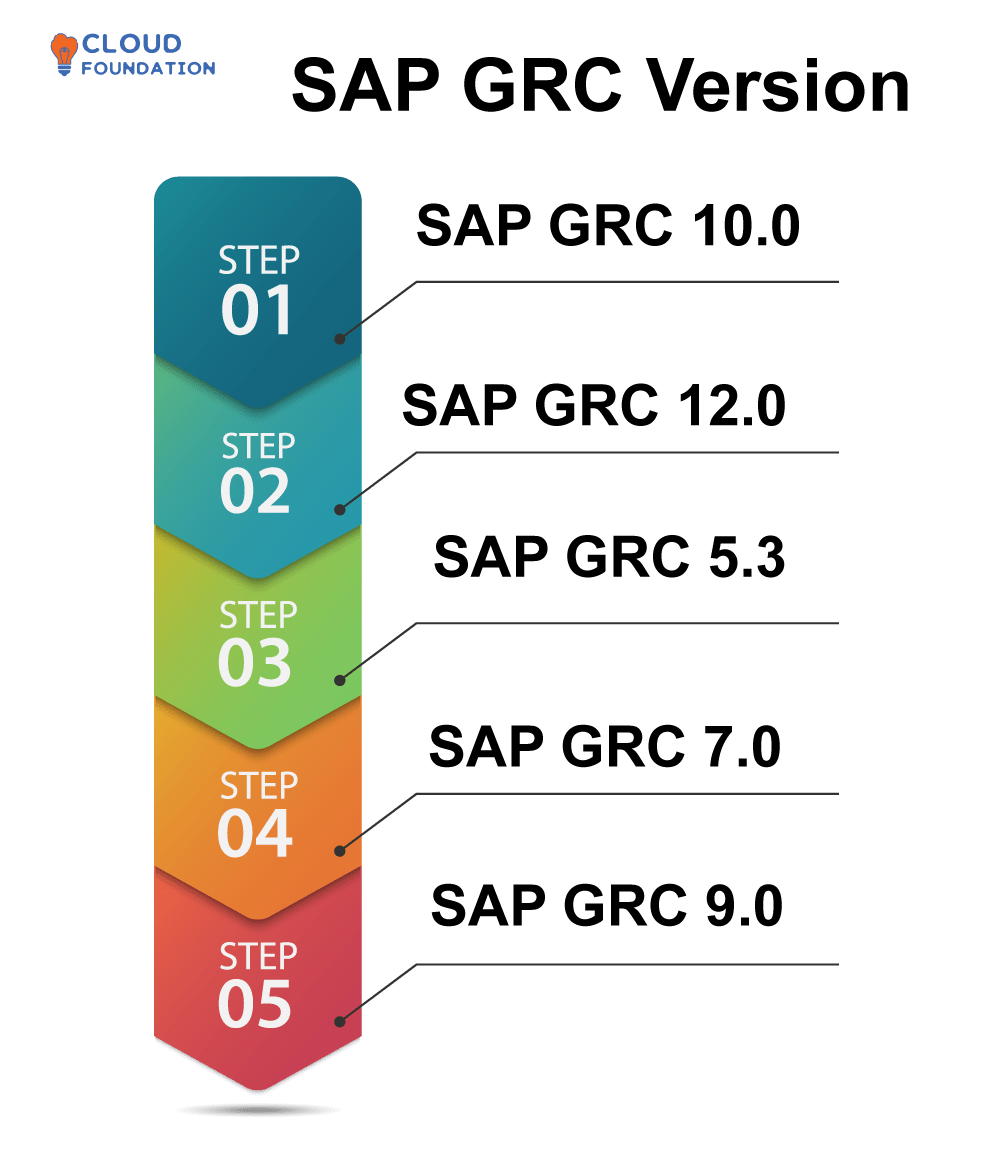
SAP GRC 10.0: SAP GRC’s most up-to-date release is GRC 10.0 and offers an integrated solution designed to oversee risk and observance throughout an organisation.
SAP GRC 12.0 offers organizations comprehensive risk management solutions designed to identify risks, conduct investigations into them, monitor them over time and take appropriate actions against them. Furthermore, integrated tools exist for optimising processes, restricting access and continuously tracking activity levels.
SAP GRC 5.3: Launched in October 2015, this version of SAP GRC allows companies to actively manage user accesses and authorizations as well as design control frameworks, assess risk actions and report findings.
SAP GRC 7.0: SAP GRC 7.0 provides advanced capabilities for tasks, such as budget control, contract administration and problem administration as well as risk measurement and analytics.
SAP GRC 9.0: SAP GRC 9.0 is the latest release of their GRC software and provides an integrated platform to control processes, manage risks, conduct process analytics and control access as well as providing tools needed for continuously observing as well as behaviours related to fraud.
SAP GRC Roles And Responsibilities
 Establishing and overseeing GRC policies and procedures: Proper internal controls must comply with all relevant laws and regulations to be considered part of sound corporate governance practices, so companies may use GRC policies and procedures as an efficient method for overseeing activities, operations and processes while meeting any necessary scrutiny or supervision levels more easily.
Establishing and overseeing GRC policies and procedures: Proper internal controls must comply with all relevant laws and regulations to be considered part of sound corporate governance practices, so companies may use GRC policies and procedures as an efficient method for overseeing activities, operations and processes while meeting any necessary scrutiny or supervision levels more easily.
Delivering Technical Assistance: SAP GRC consultants have the responsibility of offering assistance and advice with respect to designing and implementing efficient GRC systems that adhere to relevant regulatory standards, providing risk assessment and mitigation methods as needed in accordance with regulations.
Monitoring GRC Systems: SAP GRC specialists must continuously oversee and adjust GRC systems performance as part of monitoring GRC systems requirements, taking any remedial actions as necessary when required. Furthermore, they are obliged to regularly give top management feedback as well as advise.
Conduct Audits: SAP GRC consultants must periodically perform formal audits and evaluations on the greater GRC environment, in which effectiveness, safety and risk evaluation systems for GRC systems as well as existing policies and procedures are surveyed and scrutinised will all be measured against.
Training and Educating Staff: SAP GRC specialists should have the ability to effectively train personnel on how to use GRC systems efficiently so they are compliant with regulations. In addition, they must effectively communicate any changes on legislation or policies to users so they remain up-to-date.
SAP GRC Access Control Tutorial
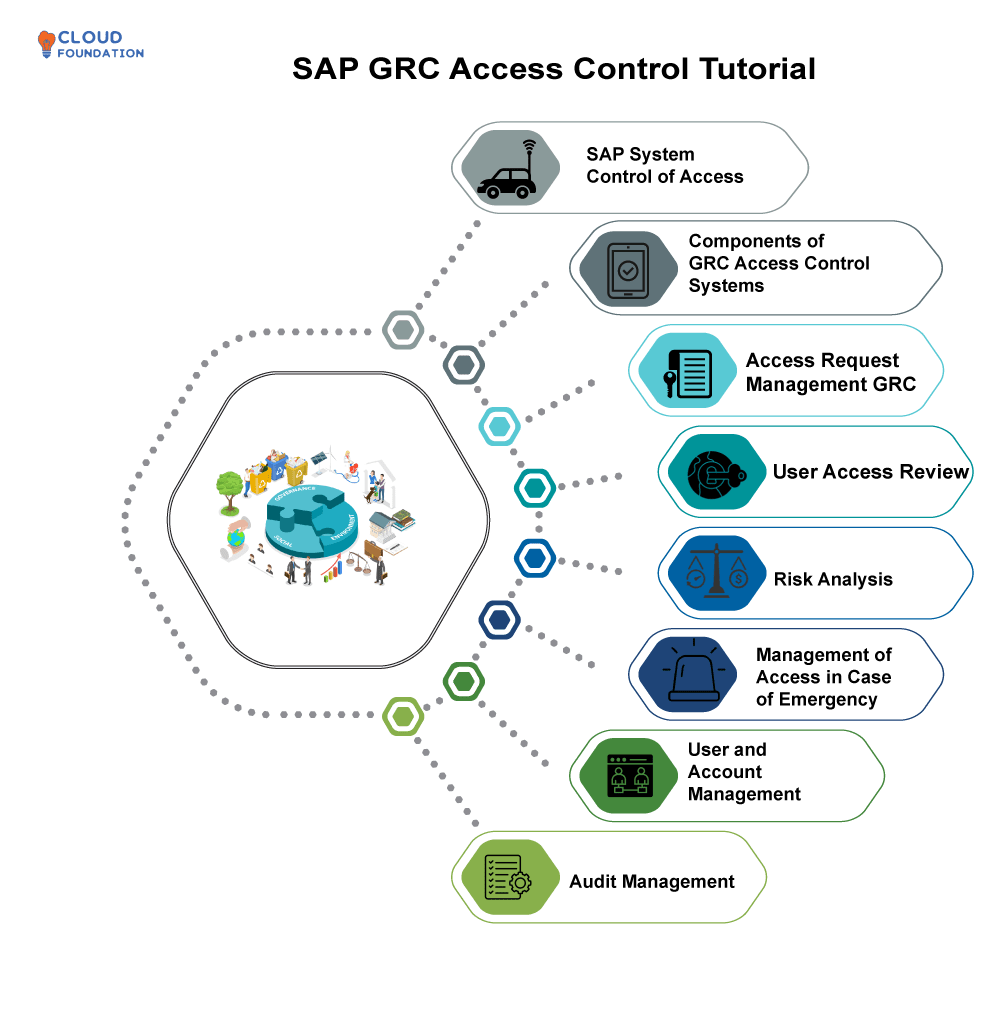 An Introduction to SAP System Control of Access
An Introduction to SAP System Control of Access
GRC Access Control is one of several modules included within the SAP Governance, Risk, and Compliance package and offers automatic user account administration as well as access control functionality in SAP systems. By making sure access granted is both compliant and secure.
Components of GRC Access Control Systems
Components included within GRC Access Control systems include Request Management, User Access Review, Risk Analysis, Emergency Access Management, User Administration and Audit Control.
Access Request Management GRC
Access Control offers businesses an Access Request Management feature to set and administer individual user privileges, help manage requests for accessing various computer applications or systems and to customise procedures for providing, authorising or refusing such access to individuals and groups of users.
User Access Review
GRC Access Control offers numerous features, one being User Access Review. With this capability in hand, organisations are given the power to assess and review user access in accordance with governing rules and procedures – helping identify threats or security problems early.
Risk Analysis
GRC Access Control offers a function called Risk Analysis that allows companies to detect any holes in their network security, and offer countermeasures in order to lower the chances of sensitive information being compromised. Companies using Risk Analysis also gain the capability of tracking unauthorised use or access of resources and can monitor unauthorised activity on them more easily than before.
Management of Access in Case of Emergency
GRC Access Control features Emergency Access Management that enables organisations to respond more rapidly in times of time-sensitive emergencies by temporarily authorising access or withdrawing it as required – helping maintain firm data security by giving and withdrawing permission temporarily or temporarily revoking access rights altogether.
User and Account Management
User Administration is an element of GRC Control which gives organisations the capability to oversee user accounts across numerous computer systems and software programs, providing organizations with assistance in determining if user accounts meet access regulations as well as whether access privileges granted are appropriate for individual users.
Audit Management
Audit Management is a component of GRC Access Control that gives companies the capability to evaluate and investigate individual user behaviours, identify security threats and devise responses accordingly, review user access records and analyse account login records.
SAP GRC Components
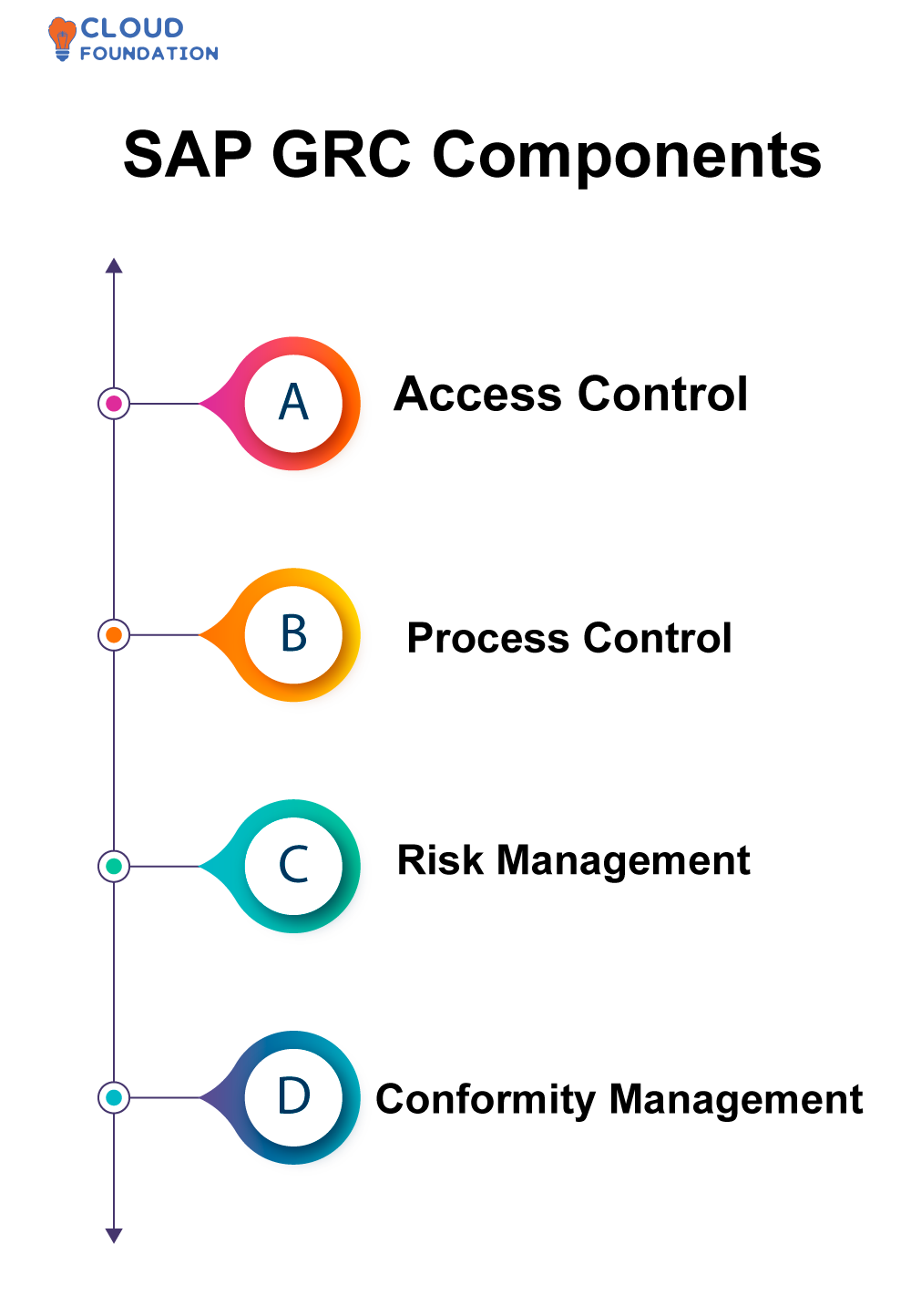
Access Control: This element’s primary aim is to establish and keep in place controls over who can gain entry to which data and systems, by setting policies, limits and controls which give companies an effective means to manage access restrictions to essential systems and information.
Process Control: Organisations can utilize process control as an aid in streamlining their business activities to ensure they run in an organised and safe manner. Specifically, process control provides visibility into how procedures operate while also guaranteeing all phases of processes run as desired.
Risk Management: This component assists organisations in identifying, evaluating and controlling any associated business risks that they encounter through their business activities. It offers them a thorough view of any hazards they could potentially face as well as measures they can implement quickly to address such threats.
ConformityManagement: This component of a system ensures an organisation abides by any externally applicable rules or standards, providing businesses the chance to proactively address potential concerns as they arise and inform authorities if suspected violations exist.
SAP GRC Basics
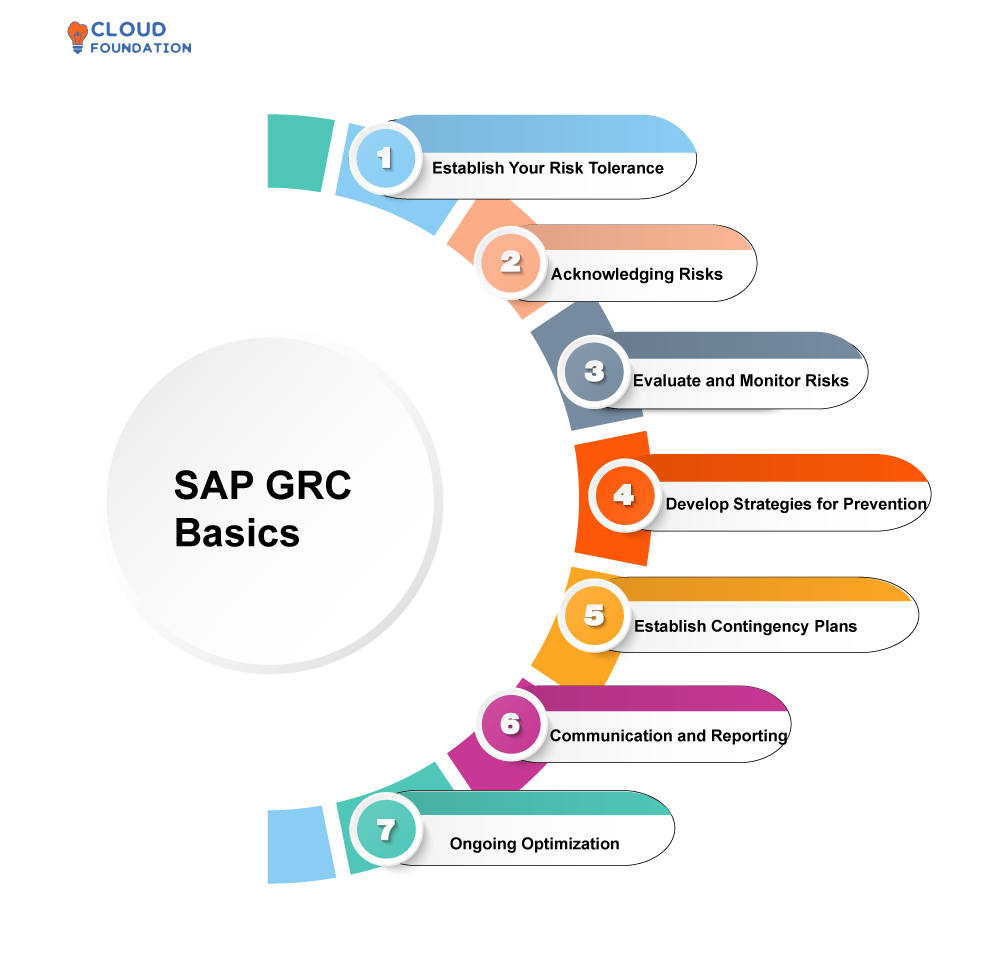
To address its risks associated with its business processes more proactively, corporations often employ GRC programmes as part of an overall risk-mitigation plan. Such plans typically consist of tools and control mechanisms designed specifically for this task.
Establish Your Risk Tolerance: Companies need to clearly establish their level of tolerance for risk in regards to operations, trade activities, business strategies and the use of resources – this is known as their “risk appetite.” This provides structure for decision making about risk management as well as policies and procedures.
Acknowledging Risks: It is crucially important for businesses to accurately and fully identify all of the risks they are exposed to so as to accurately measure them and find methods of mitigating or mitigating them. Companies have an obligation to assess both internal and external threats to their operations – which may involve money-related, operational, legal and considerations – in order to effectively operate.
Evaluate and Monitor Risks: The organization has a duty to measure and monitor risks by calculating both their potential financial effect as well as likelihood and severity if any occur.
Regular risk monitoring must take place to detect changes that have taken place in its risk profile, so as to be alert for any shifts that have taken place over time.
Develop Strategies for Prevention: It is always preferable to prevent issues rather than treat them; companies have an obligation to identify preventive actions which could reduce or eliminate risks that have been identified, including internal controls, policies, procedures and training programs.
Establish Contingency Plans: It is imperative that organizations create comprehensive contingency plans in case any potential dangers emerge; these may involve remedial steps being implemented as well as correcting procedural defects.
Communication and Reporting: It is crucial that a culture of transparency and openness be fostered so all stakeholders are made aware of risks, their management, as well as efforts taken by all to address them. Furthermore, reporting should take place regarding such efforts that exist along with risks themselves that need addressing.
Ongoing Optimization: Risk management should be constantly examined and adjusted as necessary so it stays current with evolving firm needs and requirements.

Shreshtha
Author
Life is a long lesson in humility – Life is either a daring adventure or nothing at all.



