SAP CPQ Integration Training
SAP CPQ Integration with CRM Applications
I really enjoy how SAP CPQ enables me to govern integrations simple true or false parameters within bespoke apps.
With SAP CPQ, I can explicitly specify when and how the CRM opportunity data comes into the quotation process.
I regularly inform my learners that SAP CPQ does not confine them to a specific CRM.
SAP CPQ can interact with many CRM systems, and that flexibility makes SAP CPQ strong.
Whether it’s a web-based CRM, SAP CRM, or another cloud-based CRM, I approach CRM as a general notion while configuring SAP CPQ.
When properly configured, SAP CPQ adjusts to these systems.
SAP CPQ, CPI, and Third-Party Integrations
I bring up SAP CPI whenever SAP CPQ has to communicate with third-party apps.
SAP CPQ employs CPI when we connect Salesforce, Microsoft CRM, NetSuite, or even older SAP ECC-based CRM systems.
As a result, proper field mapping in CPI is necessary for SAP CPQ interfaces.
I always tell Learning that SAP CPQ integration is a collaborative process, with SAP CPQ consultants concentrating on the quote logic and CPI developers handling iFlows and mappings.
SAP CPQ Admin Roles and Custom Field Mapping
Inside SAP CPQ, I spend time going through admin duties since they matter a lot. I may create distinct admin roles for financial, transactional, and master data SAP CPQ.
I enjoy how SAP CPQ clearly divides roles so administrators may concentrate only on what they are allocated.
Custom field mapping is another place where SAP CPQ provides me with versatility.
I can map both standard and custom data between CRM and quote objects in SAP CPQ.
I generally describe how SAP CPQ initiates data exchange based on certain events, like code development or modifications.
These event-driven connections make SAP CPQ efficient and dependable.
SAP CPQ Scripting for Opportunity-Based Quotation
Custom scripting is one of my favourite SAP CPQ topics. SAP CPQ enables me to develop scripts that regulate how data flows between the cart, user settings, and CRM possibilities.
The CRM item is usually the opportunity in SAP CPQ, and I constantly emphasise that best practice.
Instead of leads, SAP CPQ often incorporates opportunities into the quote process.
I can easily map the firm name, account ID, or customer ID into quotes SAP CPQ programming.
With little modification, SAP CPQ scripting enables me to precisely match the system with business goals.
Roles Mapping in SAP CPQ
When I deal with SAP CPQ integrations, I usually start with role mapping since this is where everything starts.
In SAP CPQ, clients frequently have various responsibilities, such as the sold-to party, the ship-to party, the bill-to party, and the payer.
In order for SAP CPQ to comprehend who is participating at each step of the quotation process, I meticulously outline these responsibilities.
In SAP CPQ, I individually manage fields like account, opportunity account, and contact data.
I determine if partner-based data, contact details, or even first names should be captured by SAP CPQ.
I utilise the flexibility that SAP CPQ offers to manage this mapping in order to make the CRM and SAP CPQ speak the same language.
I, too, depend significantly on event-based mapping in SAP CPQ. I pick whether SAP CPQ should activate mappings on quote creation, quote changes, or both.
This control helps me maintain SAP CPQ aligned with actual business activity and assures data consistency across platforms.

SAP CPQ Training

Managing Opportunity Data with SAP CPQ
At the opportunity level, SAP CPQ plays a critical role in how I manage customer interactions.
I usually associate the first contact with ship-to or sold-to parties because SAP CPQ expects clear ownership of the opportunity.
This makes SAP CPQ extremely effective during negotiations. SAP CPQ allows me to manage opportunity statuses in a very structured way.
I work with statuses like approved, awaiting internal approval, customer accepted, expired, lost, and open.
SAP CPQ also supports order confirmation pending and order failure statuses, which help me track the entire lifecycle.
What I really like about SAP CPQ is that I can customise these statuses based on business needs.
Even though SAP CPQ already provides enough standard statuses, I still fine-tune them so SAP CPQ mirrors how sales teams actually work.
Price Book and Market Mapping in SAP CPQ
Price book setup is another area where SAP CPQ provides me with complete flexibility.
I map various price books to different marketplaces so SAP CPQ can automatically apply the right pricing.
This is extremely beneficial when I deal with several areas or consumer segments.
SAP CPQ already comes with conventional markets. When I feel something is lacking, I develop bespoke markets straight in SAP CPQ.
Then I connect those markets to the necessary price books so SAP CPQ always uses the proper pricing model.
I ensure that quotations stay accurate, consistent, and in line with market expectations by keeping these mappings up to date inside SAP CPQ.
SAP CPQ becomes a dependable pricing engine rather than merely a quotation tool.
User and Role Alignment within SAP CPQ
User mapping within SAP CPQ is generally uncomplicated for me since most sales users operate in both CRM and SAP CPQ.
I tie CRM users to CPQ users in SAP CPQ so that the same individual may easily manage opportunity qualifying and quotation.
There are rare circumstances when distinct users manage CRM and SAP CPQ operations.
When that occurs, I explicitly describe custom roles in SAP CPQ. This minimises misunderstanding and assures SAP CPQ understands who owns which duty.
Maintaining the same user across CRM and SAP CPQ decreases communication gaps. SAP CPQ works best when one person oversees negotiation, price, and quote without losing context.
Custom Actions and Automation in SAP CPQ
Custom actions are where SAP CPQ actually seems strong to me. I utilise custom actions to automate operations throughout the SAP CPQ quote process.
In order to maintain SAP CPQ’s efficiency and cleanliness, these activities only take place after important procedures are finished.
I normally write custom actions in IronPython since SAP CPQ was created around it.
For instance, I immediately update the CRM opportunity with the quote ID and description when I save a quotation in SAP CPQ. SAP CPQ handles this easily custom actions.
All custom actions in SAP CPQ exist under the developer menu.
I specify how SAP CPQ transmits data back to systems such as S4HANA, where the action appears, and how it functions on the quote page.
This strong connectivity enables SAP CPQ to be a primary point for quotation and order creation.
Working with SAP CPQ Custom Actions in Real Projects
When I deal with SAP CPQ, one of the first things I concentrate on is custom actions. In SAP CPQ, custom actions enable me to manage what occurs before or after a given occurrence.
I normally explain this to my learners by explaining that SAP CPQ provides developers a dedicated location where they can create scripting code and automate genuine business situations.
I build and maintain scripts in SAP CPQ the developer workbench.
This is where I feel most comfortable playing with logic, testing integrations, and learning how SAP CPQ responds to events like storing a quote or producing a quotation.
I commonly use Python in SAP CPQ programming since it is easy, legible, and strong enough to handle most integration use cases.

SAP CPQ Online Training

SAP CPQ Developer Workbench for Scripting
I don’t have to start from scratch since SAP CPQ’s developer workbench offers a number of built-in ways.
SAP CPQ currently has established packs and methods, and I always recommend that developers examine them before implementing new logic.
This saves time and assures higher performance.
I use the workbench’s help menu often while writing scripts in SAP CPQ.
SAP CPQ makes it easier to verify syntax, comprehend accessible functionalities, and validate code before storing it.
I generally present a simple script where SAP CPQ updates the opportunity as soon as a quotation is made and saved.
SAP CPQ Workflow, Pre-Actions, and Post-Actions
Workflow plays a crucial role in SAP CPQ. Every time I describe a process, I take Learning through the standard SAP CPQ workflow screen.
On the left-hand side, SAP CPQ shows numerous states such as Preparation, Open, Customer Accepted, Approved, Rejected, Expired, and Lost.
Different actions are supported by each state in SAP CPQ.
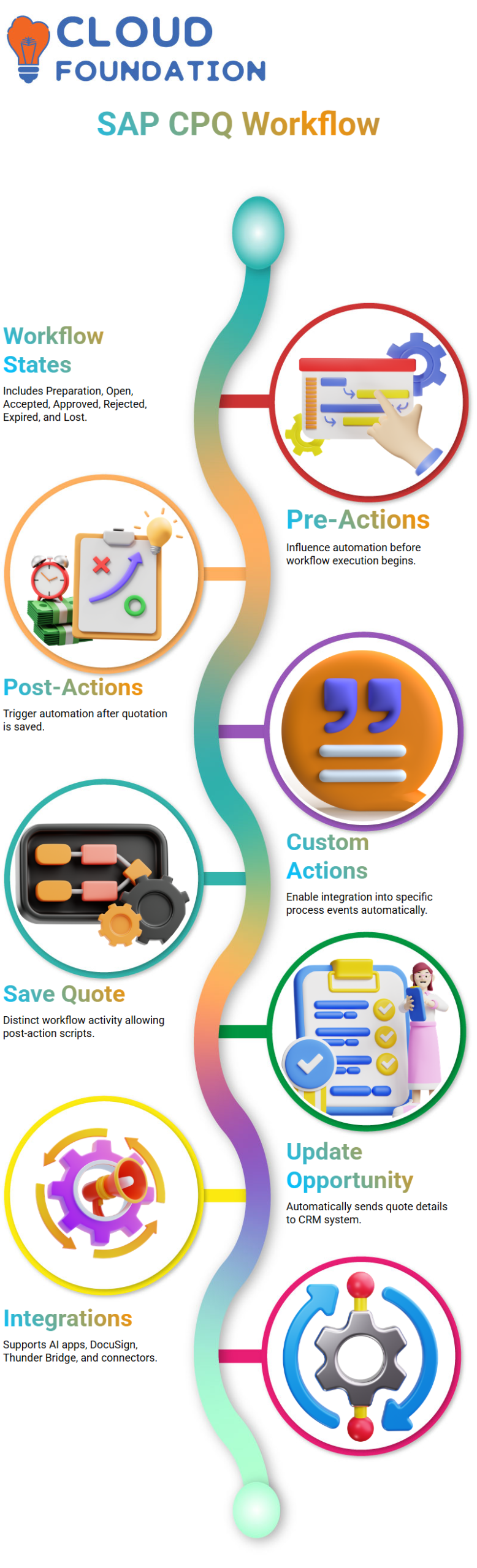
Because pre-actions and post-actions have a direct influence on automation, I often concentrate on them. In SAP CPQ, my custom action executes as a post-action after the quotation is saved.
This implies that as soon as the quote is formed, SAP CPQ initiates my script.
I often emphasise how SAP CPQ enables me to integrate custom actions into certain process events.
Once I map the activity appropriately, SAP CPQ automatically sends the quotation information back to the opportunity without any user involvement.
Saving Quotes and Updating Opportunities in SAP CPQ
One practical example I regularly present in SAP CPQ is the Save Quote function.
SAP CPQ has a distinct Save Quote workflow activity, and here is where I attach my own post-action script.
After establishing the custom action in SAP CPQ, it shows in the list of possible custom actions.
I just chose my “Update Opportunity” script and applied it to the Save Quote post-action. SAP CPQ takes care of everything automatically after that.
The process starts as soon as the quotation is saved in SAP CPQ, and SAP CPQ replies to the CRM system with the opportunity ID, quote information, and description.
Businesses that use SAP CPQ place a great emphasis on this smooth flow.
Exploring SAP CPQ Integrations and Extensions
SAP CPQ offers a variety of integration possibilities in addition to scripting and workflows.
I describe in my seminars how SAP CPQ may be integrated with AI-based apps, enablement platforms, and DocuSign.
Nevertheless, these connections are often not included in the basic SAP CPQ package and must be purchased separately.
SAP CPQ also enables connectors like Thunder Bridge and Artificial Intelligence modules.
I make it clear that, like Salesforce connectors, SAP CPQ views them as feature additions.
Organisations determine what they need depending on their business objectives.
Every time I teach SAP CPQ, I remind learners that quote procedures vary from one firm to another.
Although SAP CPQ has sufficient flexibility to accommodate various corporate architectures, the effectiveness of our integration and workflow design inside SAP CPQ will determine its success.

SAP CPQ Course Price


Vanitha
Author